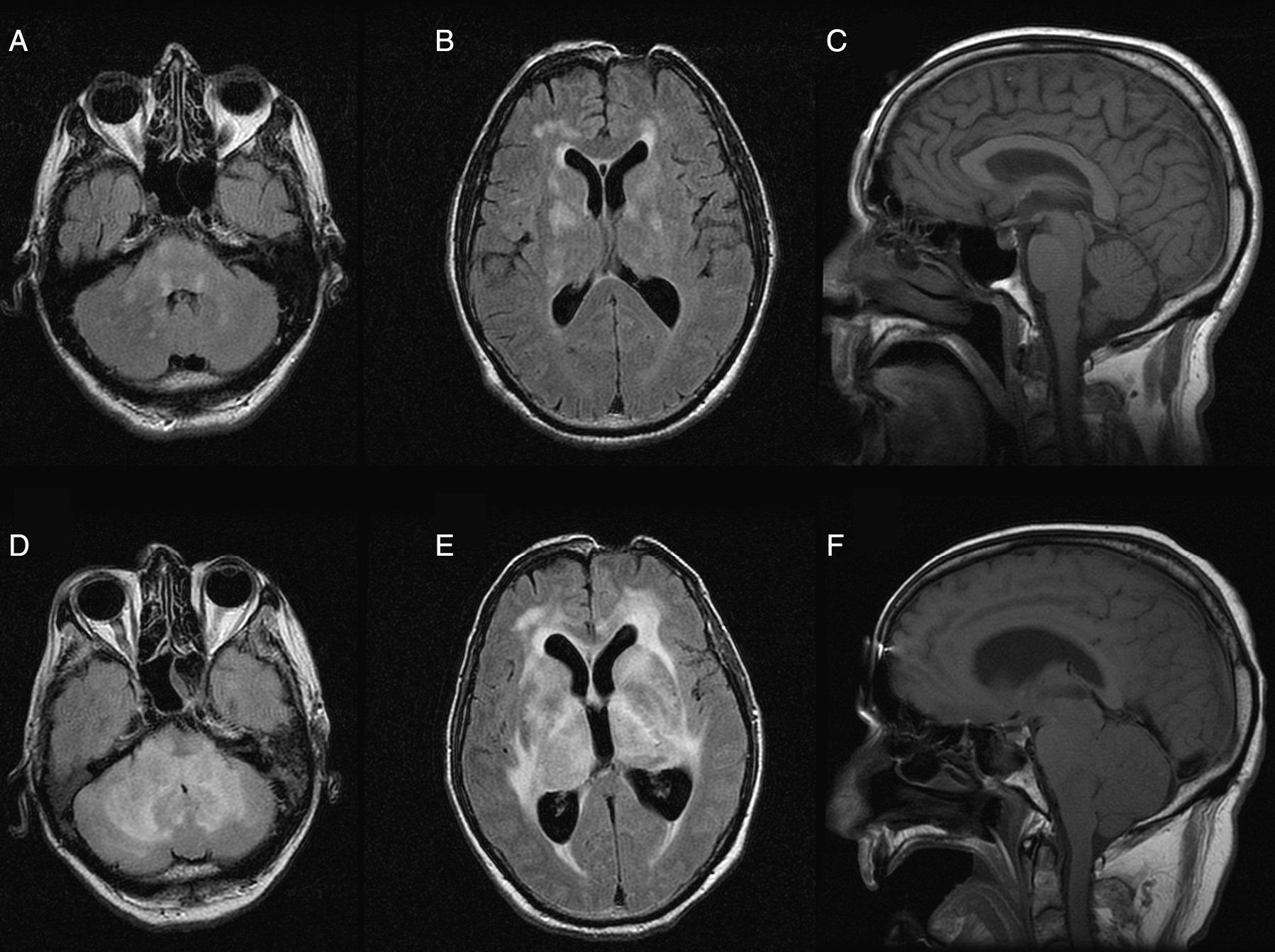
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2387020616002126" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.03.021" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2015-11-20" "aid" => "3256" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U.. All rights reserved" "copyrightAnyo" => "2015" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2015;145:e23-4" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 1 "HTML" => 1 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S0025775315001141" "issn" => "00257753" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.02.011" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2015-11-20" "aid" => "3256" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2015;145:e23-4" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 14 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 5 "PDF" => 9 ] ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Carta al Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Hiperventilación central neurogénica en un paciente con encefalomielitis aguda diseminada posvacunal" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "e23" "paginaFinal" => "e24" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation in a patient with post-vaccination acute disseminated encephalomyelitis" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figura 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1344 "Ancho" => 1800 "Tamanyo" => 310929 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Resonancia magnética nuclear inicial (A, B, C): lesiones focales bilaterales en la sustancia blanca (A, B), sin hidrocefalia (C). Resonancia magnética nuclear un mes después (D, E, F): extensa infiltración y edema de la sustancia blanca en los hemisferios cerebrales y el cerebelo (D, E), e hidrocefalia obstructiva no comunicante (F).</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Jesús Monterrubio-Villar, José Pedro Mora-Encinas, Juan Diego Jiménez-Delgado, Rocío Almaraz-Velarde" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Jesús" "apellidos" => "Monterrubio-Villar" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "José Pedro" "apellidos" => "Mora-Encinas" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Juan Diego" "apellidos" => "Jiménez-Delgado" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Rocío" "apellidos" => "Almaraz-Velarde" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2387020616002126" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.03.021" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616002126?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315001141?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/00257753/0000014500000010/v1_201510290045/S0025775315001141/v1_201510290045/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020616002023" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2016.03.014" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2015-11-20" "aid" => "3253" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2015;145:e25-7" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism vs progressive osseous heteroplasia in absence of family history" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "e25" "paginaFinal" => "e27" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Seudoseudohipoparatiroidismo frente a heteroplasia ósea progresiva en ausencia de historia familiar" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 2396 "Ancho" => 2998 "Tamanyo" => 710358 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">(A) Left hand X-ray of patient 1, at four years of age, where no alteration is observed and (B) at eight years of age, showing shortening of the III, IV and V metacarpal and phalanx I. (C) Feet X-ray of patient 1, showing shortening of the IV and V metatarsals, particularly. (D) Hands X-ray of patient 2, at three years of age, where hypoplasia of the middle phalanges of II and V fingers in both hands and discordance in carpal/metacarpal bone maturation is observed.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Arrate Pereda, Eva González Oliva, Isolina Riaño-Galán, Guiomar Pérez de Nanclares" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Arrate" "apellidos" => "Pereda" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Eva" "apellidos" => "González Oliva" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Isolina" "apellidos" => "Riaño-Galán" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Guiomar" "apellidos" => "Pérez de Nanclares" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775315001116" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.02.009" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315001116?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616002023?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000014500000010/v1_201604230100/S2387020616002023/v1_201604230100/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020616002114" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2015.01.002" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2015-11-20" "aid" => "3242" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2015;145:462-3" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 1 "HTML" => 1 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Neuralgic amyotrophy associated to hepatitis E virus infection" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "462" "paginaFinal" => "463" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Neuralgia amiotrófica en relación con infección por el virus de la hepatitis E" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Laura Martínez Rodríguez, Paula Carvajal, Germán Morís" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Laura" "apellidos" => "Martínez Rodríguez" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Paula" "apellidos" => "Carvajal" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Germán" "apellidos" => "Morís" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775315000846" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2015.01.021" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775315000846?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616002114?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000014500000010/v1_201604230100/S2387020616002114/v1_201604230100/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:15 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation in a patient with post-vaccination acute disseminated encephalomyelitis" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "saludo" => "Dear Editor," "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "e23" "paginaFinal" => "e24" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Jesús Monterrubio-Villar, José Pedro Mora-Encinas, Juan Diego Jiménez-Delgado, Rocío Almaraz-Velarde" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Jesús" "apellidos" => "Monterrubio-Villar" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "suso1@orangecorreo.es" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "José Pedro" "apellidos" => "Mora-Encinas" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Juan Diego" "apellidos" => "Jiménez-Delgado" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Rocío" "apellidos" => "Almaraz-Velarde" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Don Benito-Villanueva, Don Benito, Badajoz, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Radiología, Hospital Don Benito-Villanueva, Don Benito, Badajoz, Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Hiperventilación central neurogénica en un paciente con encefalomielitis aguda diseminada posvacunal" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1343 "Ancho" => 1798 "Tamanyo" => 317382 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Initial magnetic resonance imaging (A–C): bilateral focal lesions in the white matter (A, B) without hydrocephalus (C). Magnetic resonance imaging a month later (D–F): extensive infiltration and oedema of the white matter in the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum (D, E), and non-communicating obstructive hydrocephalus (F).</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Central neurogenic hyperventilation (CNH) is a rare disorder, described in patients in a coma or without a deteriorated level of consciousness caused by the progressive tumoral infiltration of the brain stem, mainly secondary to lymphoma or glioma. After conducting a literature search in PubMed without time restrictions, with the MeSH terms “hyperventilation”, “encephalomyelitis, acute disseminated” and “central nervous system diseases”, we describe the first case of CNH secondary to acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after trivalent flu vaccination.</p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A male, 63 years old with no personal medical history who was admitted to our hospital with dysarthria, dysphagia, peripheral facial weakness and gait disturbance without fever, headache or prodromal signs of infection. The symptoms had gradually appeared and had started approximately two weeks after being vaccinated with a trivalent adjuvant flu vaccine a month before. On admission, the examination showed neither impairment of consciousness nor visual field or ocular motility disorder. The patient had severe dysarthria with palatal and tongue movement restrictions, intention tremor, abnormal heel–knee test and proximal weakness of the left arm. The tendon reflexes were hyperactive, without clonus, while both proprioception and vibratory sensation were preserved.</p><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Lab tests, chest X-ray, ECG and Chest-Abdomen CT scan were normal. CSF analysis showed: 11<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>cells/mm<span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span>, 28<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>red blood cells/mm<span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span>, proteins 61<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/dl and glucose 69<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/dl. There were no neoplastic cells or oligoclonal bands or intrathecal IgG synthesis. The PCR in CSF for herpes simplex, varicella zoster, cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, JC and tuberculosis were negative as well as serology for measles, parvovirus B19, <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">Brucella, Toxoplasma, Borrelia, Rickettsia</span> and VDRL. Levels of angiotensin converting enzyme in serum and CSF were normal, and tumour markers and antinuclear antibodies were negative. Cranial MRI showed bilateral focal lesions in the white matter which were hyperintense on T2, with minimal enhancement after contrast (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>A–C). During his hospital stay he developed constipation and urinary retention. Taking into account his medical history, lab tests and MRI results, he was diagnosed with post-vaccination acute disseminated encephalomyelitis and treatment was started with a high dose methylprednisolone.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Due to the emergence of a significant tachypnea he was admitted to intensive care. The arterial blood gas analysis showed the following results: 7.486 pH, PaO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span> 126<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mm Hg, PaCO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span> 12<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mm Hg, HCO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">3</span> 14.6<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mmol/l. The blood lactate was 4.7<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mmol/l (VN<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span><<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>2<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mmol/l). Since the patient had hyperpnoea and difficulty to protect the airway due to involvement of the lower cranial nerves, he was intubated and sedated with remifentanil and midazolam, which decreased the respiratory alkalosis. Repeated attempts to disconnect the respirator failed due to severe hyperventilation, ruling out concomitant infection, lung disease or heart disease, therefore intravenous treatment was started with immunoglobulins for 5 days and 5 plasmapheresis sessions were performed. Despite treatment the patient progressively deteriorated and went into a coma. In a second MRI, performed one month after the first, involvement of deep grey substance was observed with extensive oedema of the white matter of both cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum, with brainstem compression and secondary triventricular hydrocephalus (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>D–F). With his family's consent, it was decided to limit the life-sustaining treatments and he died shortly after in our unit.</p><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The CNH was first described in 1959 by Plum and Swanson.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0055"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> It is characterized by a sustained hyperventilation that persists during sleep, a marked decrease in PaCO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span>, an elevated PaO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span> and a high blood pH, together with the absence of cardiac or respiratory diseases or metabolic-drug causes. Neoplasms, mainly the primary CNS lymphoma, are the most common cause of CNH, particularly in tumours infiltrating the protuberance.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0060"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a> It has also been described in association with other locations, such as the high cervical cord or the bilateral medial thalamus,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0065"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3,4</span></a> and with non-neoplastic diseases. The underlying pathophysiological mechanism of CNH is not well known, both biochemical and structural factors have been proposed for its genesis.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0075"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5,6</span></a> There is no effective therapy for this entity, but the intensive treatment of the primary tumour or disease can induce a CNH remission.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0085"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">7,8</span></a> In a patient with multiple sclerosis CNH was successfully controlled by plasmapheresis.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0080"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">6</span></a> Symptomatic treatment involves the repeated or continuous intravenous administration of midazolam, propofol and opioids such as morphine or fentanyl.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0075"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5,8</span></a> Also, the oral administration of opioids may be useful.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0095"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">9</span></a> Some patients with severe CNH may require mechanical ventilation to prevent respiratory distress, and even the use of neuromuscular blocking agents.</p><p id="par0030" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The CNH forecast is ominous, with a survival of only a few months in most of the reported cases. In our patient, the CNH was refractory to treatment of the primary disease, consistent with increased severity and extent of brain and brain stem lesions. Although this adverse reaction to the flu vaccine was not communicated to the pharmacovigilance service, its causation was considered at least possible using the Karch and Lasagna algorithm.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0100"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">10</span></a></p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Monterrubio-Villar J, Mora-Encinas JP, Jiménez-Delgado JD, Almaraz-Velarde R. Hiperventilación central neurogénica en un paciente con encefalomielitis aguda diseminada posvacunal. Med Clin (Barc). 2015;145:e23–e24.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1343 "Ancho" => 1798 "Tamanyo" => 317382 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Initial magnetic resonance imaging (A–C): bilateral focal lesions in the white matter (A, B) without hydrocephalus (C). Magnetic resonance imaging a month later (D–F): extensive infiltration and oedema of the white matter in the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum (D, E), and non-communicating obstructive hydrocephalus (F).</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0005" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:10 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0055" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation in man" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "F. Plum" 1 => "A.G. Swanson" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arch Neurol Psychiatry" "fecha" => "1959" "volumen" => "81" "paginaInicial" => "535" "paginaFinal" => "549" ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0060" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation. A case report and discussion of pathophysiology" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "A.W. Tarulli" 1 => "C. Lim" 2 => "J.D. Bui" 3 => "C.B. Saper" 4 => "M.P. Alexander" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1001/archneur.62.10.1632" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arch Neurol" "fecha" => "2005" "volumen" => "62" "paginaInicial" => "1632" "paginaFinal" => "1634" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16216951" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0065" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation in invasive laryngeal carcinoma" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "B.A. Dubaybo" 1 => "I. Afridi" 2 => "M. Hussain" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Chest" "fecha" => "1991" "volumen" => "99" "paginaInicial" => "767" "paginaFinal" => "769" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1995243" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0070" "etiqueta" => "4" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Chronic dysnea and hyperventilation in an awake patient with small subcortical infarcts" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "S.C. Johnston" 1 => "V. Singh" 2 => "H.J. Ralston" 3 => "W.M. Gold" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Neurology" "fecha" => "2001" "volumen" => "57" "paginaInicial" => "2131" "paginaFinal" => "2133" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11739843" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0075" "etiqueta" => "5" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Brain stem encephalitis with central neurogenic hyperventilation" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "D. Nystad" 1 => "R. Salvesen" 2 => "E.W. Nielsen" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1136/jnnp.2006.094375" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry" "fecha" => "2007" "volumen" => "78" "paginaInicial" => "107" "paginaFinal" => "108" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17172579" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 5 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0080" "etiqueta" => "6" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Reversible central neurogenic hyperventilation in an awake patient with multiple sclerosis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "M. Takahashi" 1 => "T. Tsunami" 2 => "T. Miyayosi" 3 => "H. Mizusawa" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1007/s00415-007-0662-0" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Neurol" "fecha" => "2007" "volumen" => "254" "paginaInicial" => "1763" "paginaFinal" => "1764" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18004639" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 6 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0085" "etiqueta" => "7" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation in an anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "A. Vural" 1 => "E.M. Arsava" 2 => "N. Dericioglu" 3 => "M.A. Topcuoglu" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Intern Med" "fecha" => "2012" "volumen" => "51" "paginaInicial" => "2789" "paginaFinal" => "2792" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23037476" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 7 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0090" "etiqueta" => "8" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Persistent severe hypocapnia and alkalemia in a 40-year-old woman" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "C.H. Chang" 1 => "P.H. Kuo" 2 => "C.H. Hsu" 3 => "P.C. Yang" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Chest" "fecha" => "2000" "volumen" => "118" "paginaInicial" => "242" "paginaFinal" => "245" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10893387" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 8 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0095" "etiqueta" => "9" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Central neurogenic hyperventilation: pharmacologic intervention with morphine sulphate and correlative analysis of respiratory, sleep, and ocular motor dysfunction" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "K.A. Jaeckle" 1 => "K.B. Digre" 2 => "C.R. Jones" 3 => "P.L. Bailey" 4 => "P.C. McMahill" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Neurology" "fecha" => "1990" "volumen" => "40" "paginaInicial" => "1715" "paginaFinal" => "1720" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2234427" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 9 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0100" "etiqueta" => "10" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Toward the operational identification of adverse drug reactions" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "F.E. Karch" 1 => "L. Lasagna" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Clin Pharmacol Ther" "fecha" => "1977" "volumen" => "21" "paginaInicial" => "247" "paginaFinal" => "254" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/837643" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/23870206/0000014500000010/v1_201604230100/S2387020616002126/v1_201604230100/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "43309" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Letters to the Editor" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23870206/0000014500000010/v1_201604230100/S2387020616002126/v1_201604230100/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020616002126?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Journal Information
Vol. 145. Issue 10.
Pages e23-e24 (November 2015)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 145. Issue 10.
Pages e23-e24 (November 2015)
Letter to the Editor
Central neurogenic hyperventilation in a patient with post-vaccination acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Hiperventilación central neurogénica en un paciente con encefalomielitis aguda diseminada posvacunal
Visits
1
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail