La nefropatía diabética (ND) es la principal causa de enfermedad renal crónica terminal. Hay componentes metabólicos y hemodinámicos que se encuentran directamente involucrados. Sin embargo, hay datos convincentes de que la inflamación participa en las complicaciones de la diabetes. El objetivo de este estudio fue investigar si la inhibición de la inflamación y de las citocinas proinflamatorias con pentoxifilina (PXF) atenúa la progresión de la ND.
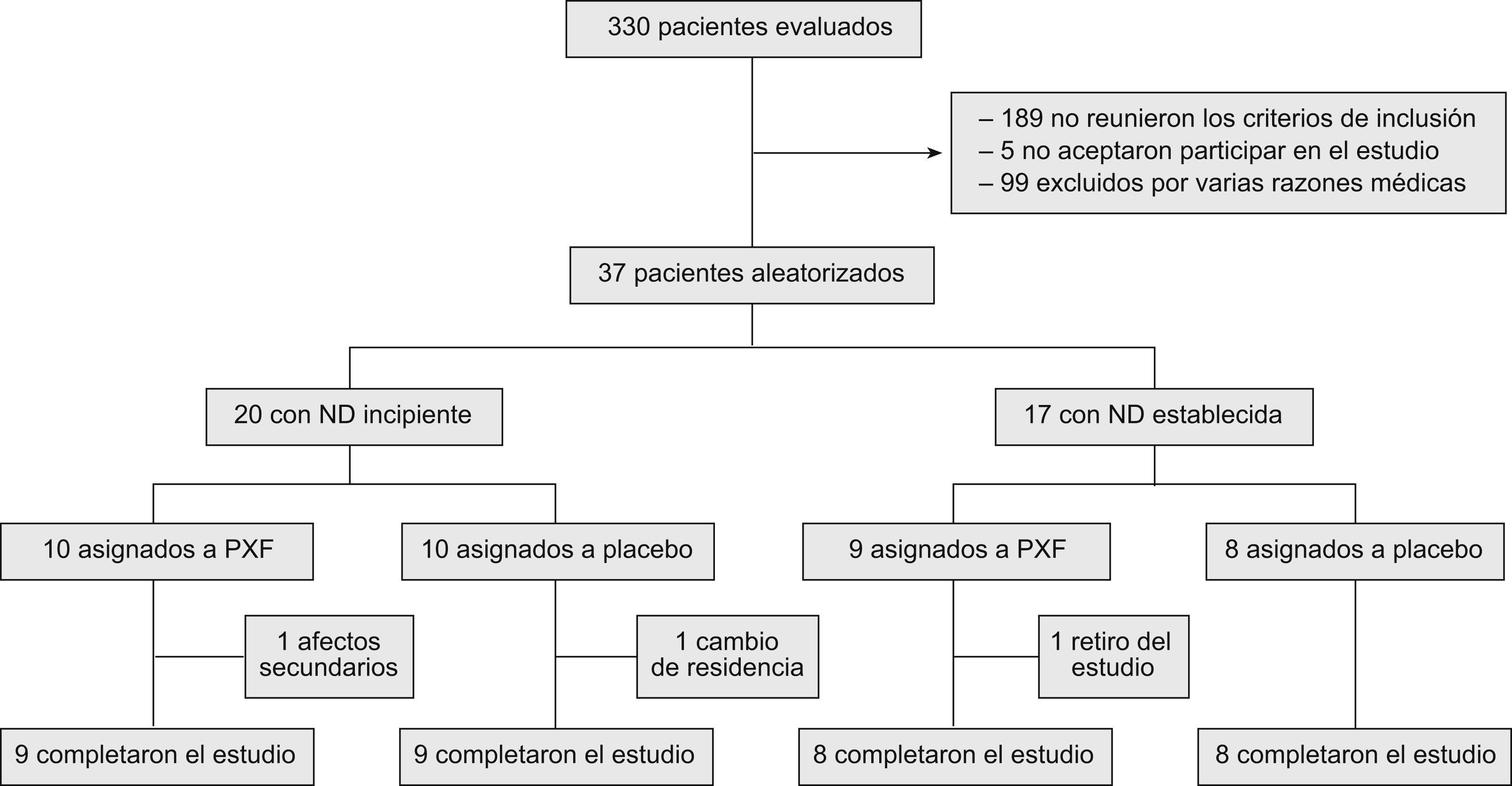
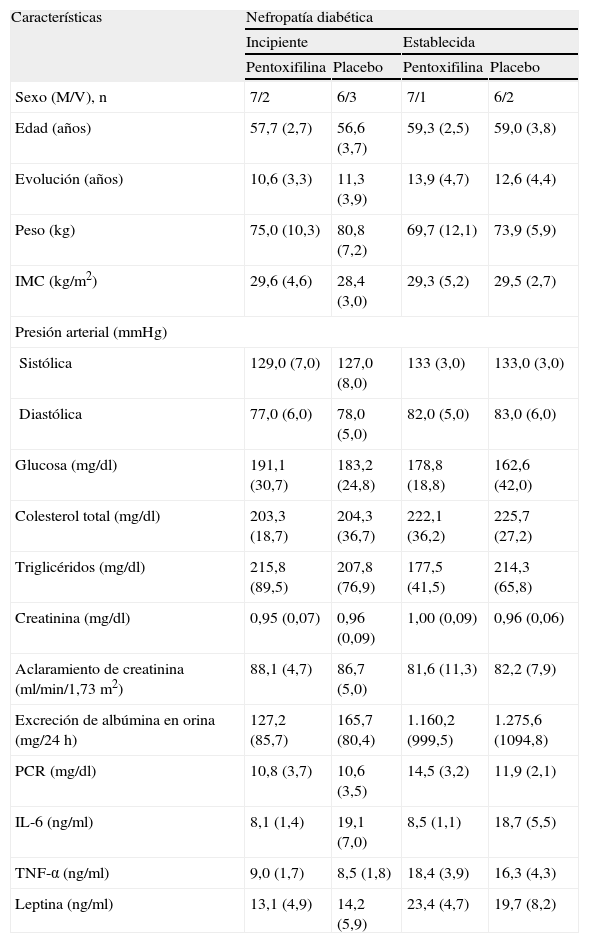
Sujetos y métodoEn un estudio prospectivo, aleatorizado, doble ciego y controlado con placebo se evaluó el efecto nefroprotector de la PXF (1.200mg diarios) usada durante 12 meses en 34 pacientes con ND incipiente o ND establecida. Los parámetros analizados fueron la inflamación, las citocinas proinflamatorias y la excreción de albúmina en orina (EAO).
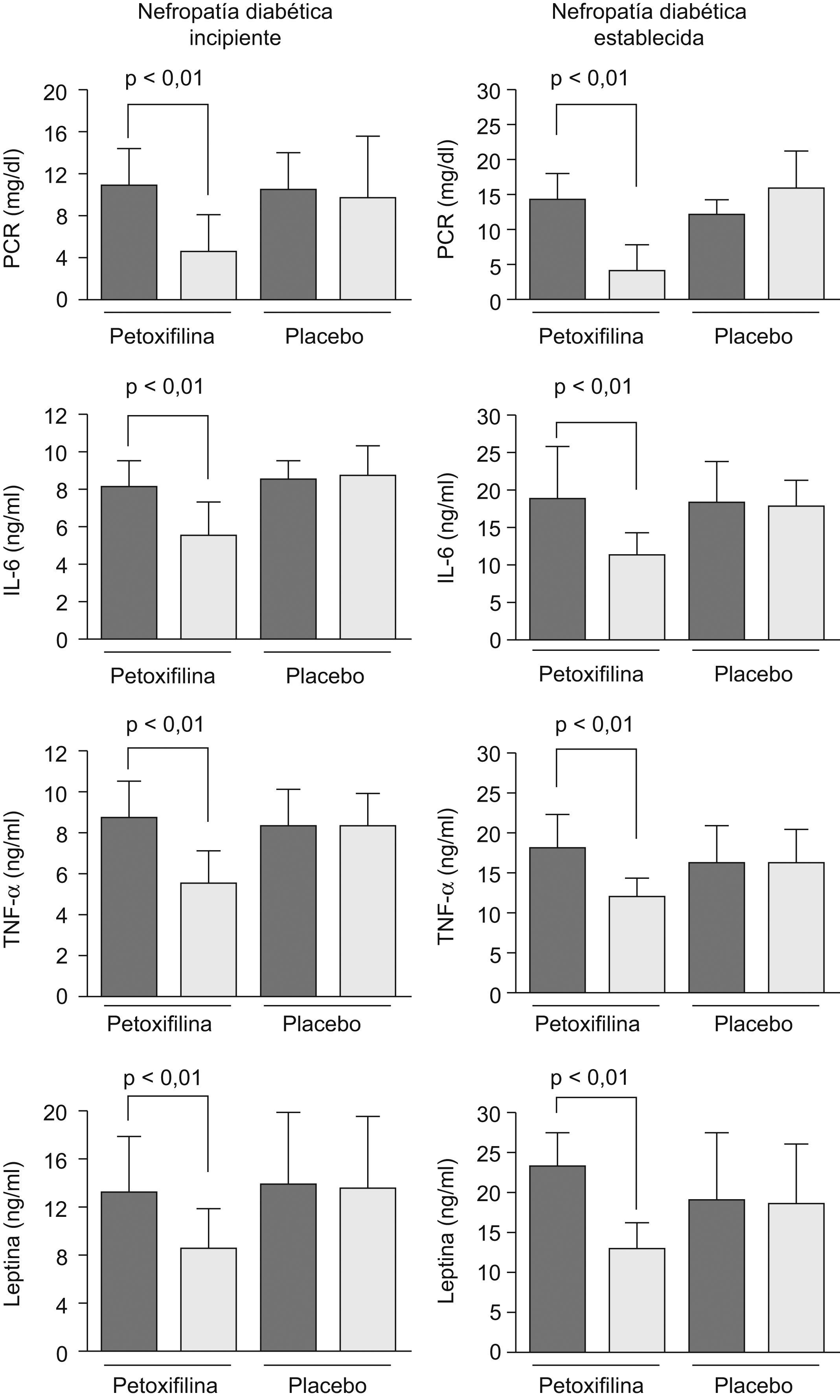
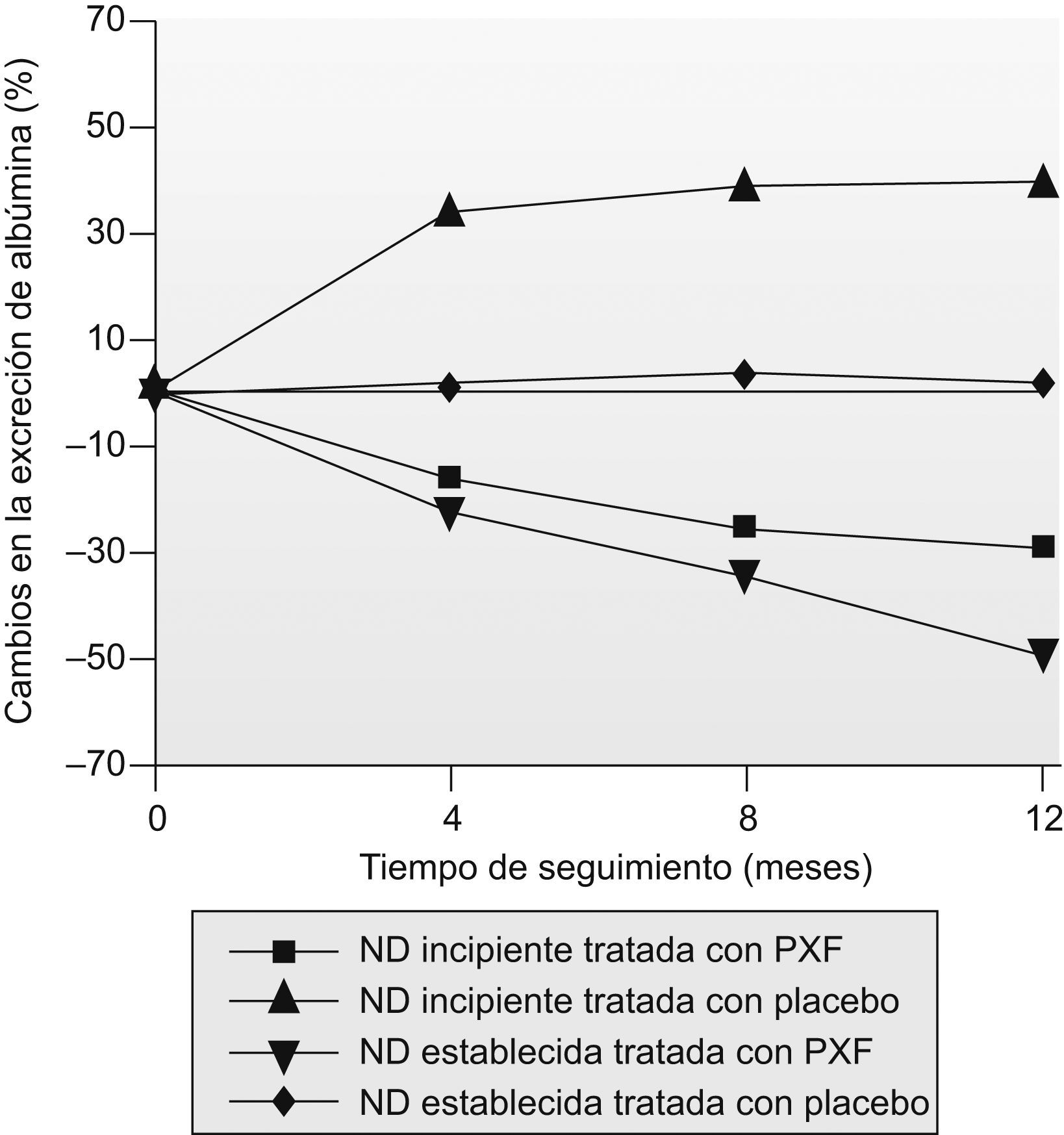
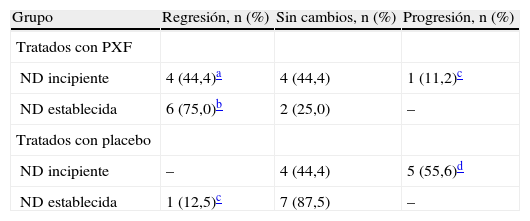
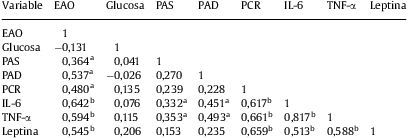
ResultadosEl tratamiento con PXF tuvo un efecto nefroprotector determinado por una reducción significativa en la EAO en los pacientes con ND incipiente y ND establecida (p<0,01). Este efecto se atribuyó a una disminución en los valores séricos de la proteína C reactiva, de la interleucina-6, del factor de necrosis tumoral-α y de la leptina (p<0,01).
ConclusionesEl tratamiento con PXF produjo una regresión y previno la progresión de la lesión renal en el paciente diabético. Por su efecto nefroprotector, la PXF debería emplearse en el tratamiento preventivo de la ND. Los resultados indican que la inflamación y que las citocinas proinflamatorias participan en la progresión de la ND.
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the principal cause of end-chronic kidney disease. Metabolic and hemodynamic components are directly involved. However, convincing data have shown that inflammation participates in the diabetic complications. The aim of this study was to investigate whether the inhibition of the inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokines with pentoxifylline (PXF) attenuate the progression of the DN.
Subjects and methodIn a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled study, we evaluated the effect of PXF (1200mg daily) during 12 months, in 34 patients with incipient or established DN. Evaluated parameters were inflammation, pro-inflammatory cytokines and urinary albumin excretion (UAE).
ResultsPXF treatment had a reno-protective effect determined by a significant reduction in the UAE in both incipient and established (p<0,01) DN patient. This effect was attributed to a reduction in the C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α and leptin serum levels (p<0,01).
ConclusionsPXF treatment caused regression and prevented the progression of renal damage. Thus, PXF should be used in the preventive treatment of DN. These results showed that inflammation and pro-inflammatory cytokines are related to the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora