To evaluate the treatment modalities and their effects in primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD).
MethodsIn this chart review study, patients diagnosed with pSS-related ILD (pSS-ILD) between January 2004 and August 2022 were screened. Glucocorticoid use and administered disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) were determined. The difference between forced vital capacity (FVC) and diffusion capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) before and after treatment was evaluated.
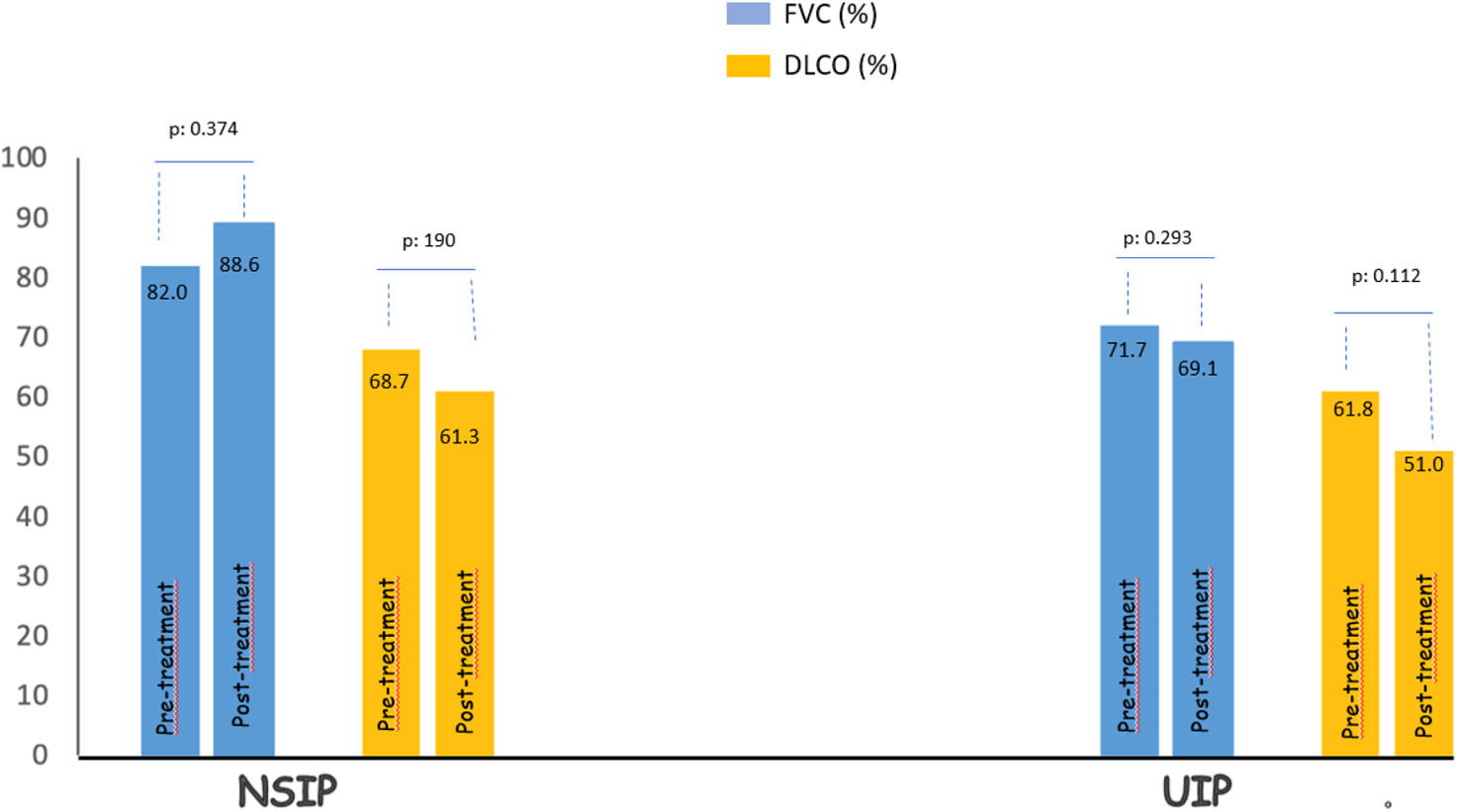
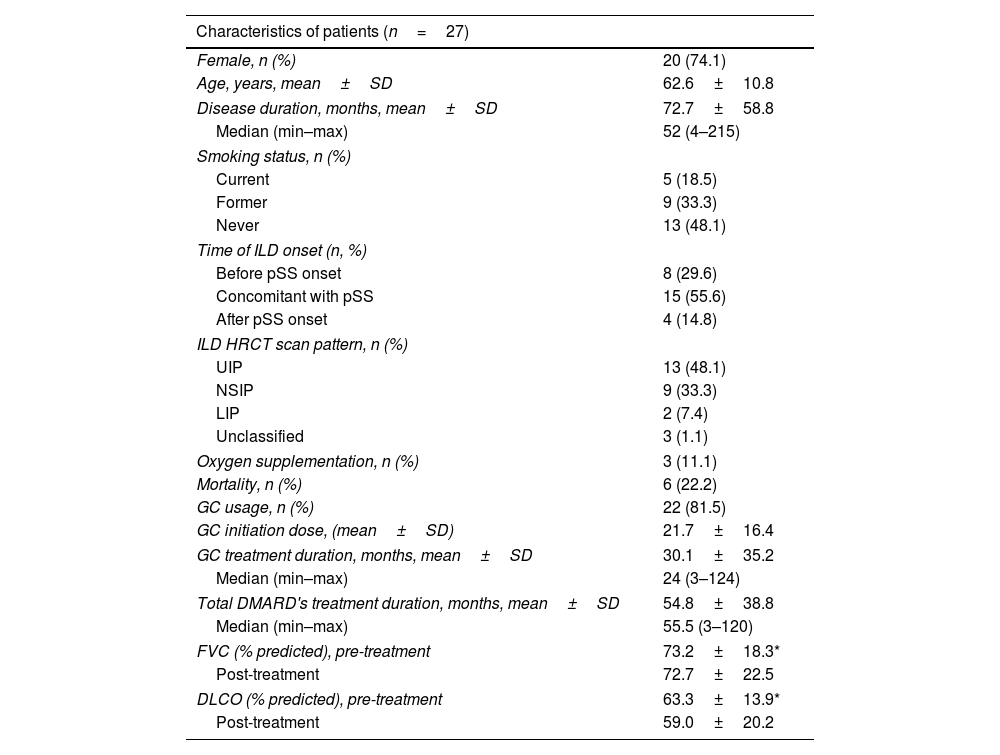
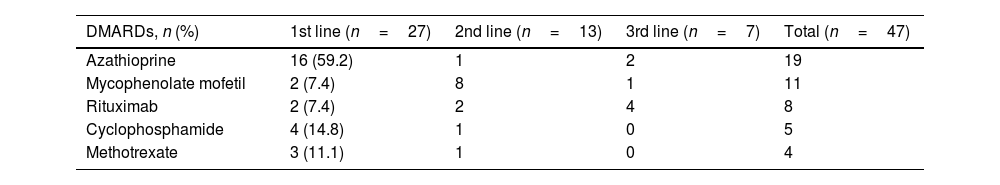
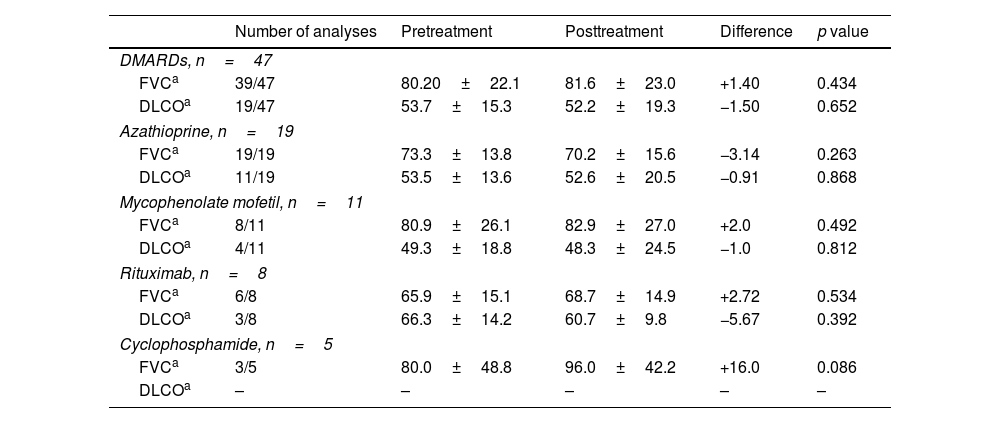
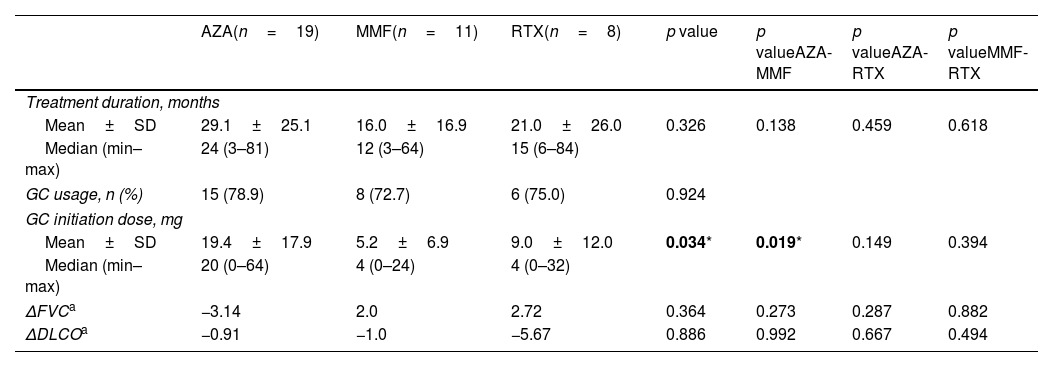
ResultsILD was present in 44 of 609 patients (7.2%) diagnosed with pSS. In 27 patients included in the study, steroid usage was 81.5%. There was a statistically insignificant increase in FVC% (from 80.20±22.1 to 81.6±23.0) and a decrease in DLCO% (53.7±15.3–52.2±19.3) with DMARD treatment (p=0.434 and p=0.652, respectively). There was no significant difference between the treatment groups (azathioprine [AZA], mycophenolate mofetil [MMF], and rituximab [RTX]) in terms of the change in FVC% and DLCO% compared with baseline levels. The effect of treatment on FVC and DLCO was similar in UIP and NSIP patterns.
ConclusionsAZA, MMF, and RTX have similar effects on pulmonary functions in pSS-ILD and provide disease stabilization.
Evaluar las modalidades de tratamiento y sus efectos en pacientes con síndrome de Sjögren primario (SSp) y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial (EPI).
MétodosEn este estudio de revisión de historias clínicas se examinó a los pacientes diagnosticados con EPI relacionada con SSp (SSp-EPI) entre enero de 2004 y agosto de 2022. Se determinó el uso de glucocorticoides y fármacos antirreumáticos modificadores de la enfermedad (FAME) administrados. Se evaluó la diferencia entre la capacidad vital forzada (CVF) y la capacidad de difusión de los pulmones para el monóxido de carbono (DLCO) antes y después del tratamiento.
ResultadosLa EPI estuvo presente en 44 de 609 pacientes (7,2%) diagnosticados con SSp. En 27 pacientes incluidos en el estudio, el uso de esteroides fue del 81,5%. Hubo un aumento estadísticamente insignificante en el porcentaje de CVF (de 80,20±22,1 a 81,6±23,0) y una disminución en el porcentaje de DLCO (53,7±15,3 a 52,2±19,3) con el tratamiento con FAME (p=0,434 y p=0,652, respectivamente). No hubo diferencias significativas entre los grupos de tratamiento (azatioprina [AZA], micofenolato de mofetilo [MMF] y rituximab [RTX]) en términos del cambio en el porcentaje de CVF y en el porcentaje de DLCO en comparación con los niveles iniciales. El efecto del tratamiento sobre la CVF y la DLCO fue similar en los patrones de neumonía intersticial común y de neumonía intersticial no específica.
ConclusionesAZA, MMF y RTX tienen efectos similares sobre las funciones pulmonares en SSp-EPI y proporcionan estabilización de la enfermedad.