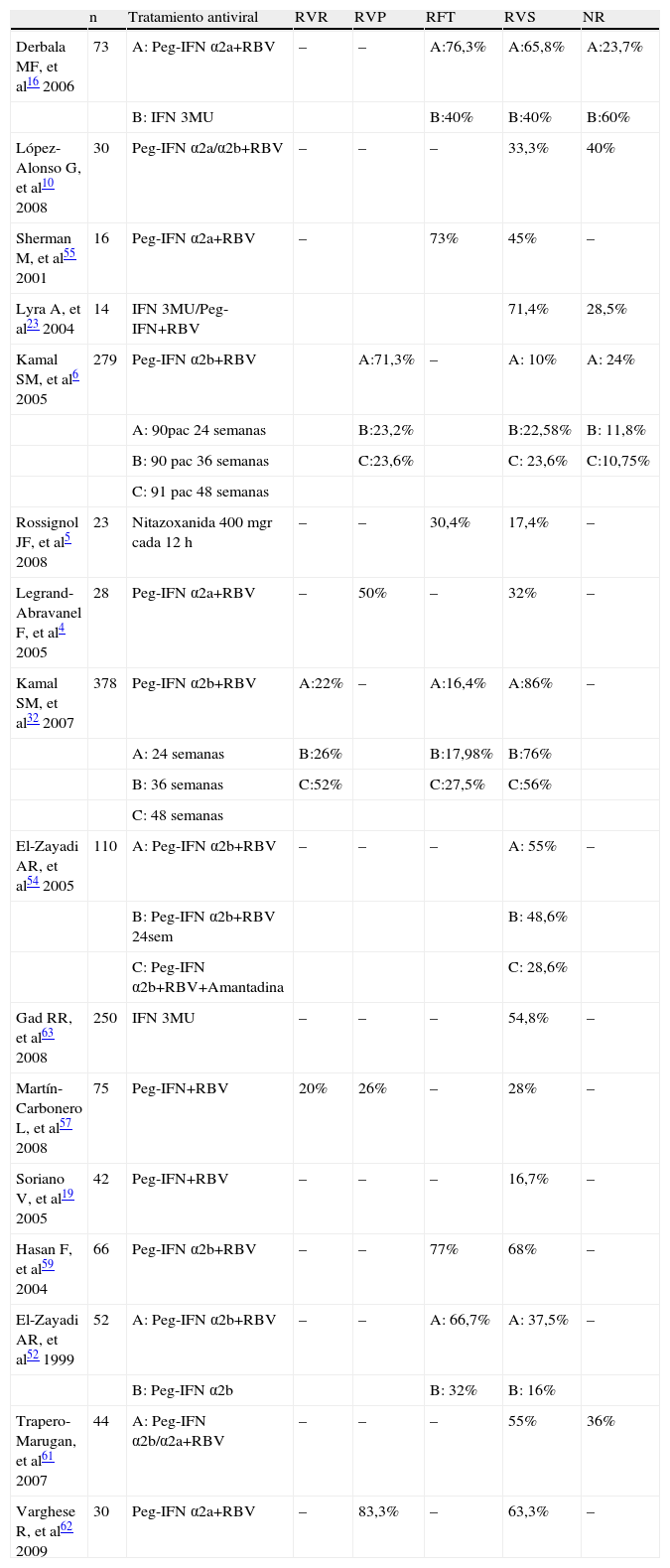
El virus de la hepatitis C (VHC) es uno de los agentes causales más importantes de enfermedad hepática. El genotipo 4 es responsable del 20% de las hepatitis crónica y en varios países de la cuenca mediterránea se ha comunicado que la prevalencia está aumentando. La infección por el VHC evoluciona a la cronicidad en más del 90%, un 20% puede presentar cirrosis y entre un 5–10% desarrollar un hepatocarcinoma. Se ha especulado sobre una posible asociación del genotipo 4 con el desarrollo de hepatocarcinoma, pero parece relacionado con otras causas concomitantes de hepatopatía. El tratamiento se basa en el uso de interferón pegilado α-2a (a dosis de 180μg/sem) o interferón pegilado α-2b (1,5μg/kg/sem) más ribavirina (1.000–1.200mg/día) durante un año. Con este régimen terapéutico se han observado tasas de respuesta virológica sostenida (RVS) en torno al 65%. Se han apreciado diferencias en las tasas de RVS según el grado de fibrosis, las infecciones concomitantes asociadas y la presencia de determinados marcadores serológicos. Se ha utilizado la nitazoxanida en combinación con el tratamiento combinado clásico, alcanzándose una mejoría en los resultados.
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is one of the most important causal agents of liver disease. Genotype 4 is responsible for 20% of chronic hepatitis and in several countries of the Mediterranean area it has been reported that the prevalence is increasing. The HCV infection develops to chronicity in more than 90%, 20% may have cirrhosis and 5–10% develop hepatocellular carcinoma. There has been speculation about a possible association of genotype 4 with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma, but it seems related to other concomitant causes of liver disease. Treatment is based on the use of pegylated interferon α-2a (180mg/week) or pegylated-interferon α-2b (1.5mg/kg/wk) plus ribavirin (1000–1200mg/day) for one year. With this regimen, there have been reported sustained virological response (SVR) rates around 65%. There are differences in the SVR rates according to the degree of fibrosis, associated concurrent infections and the presence of specific serologic markers. Nitazoxanide has been used in combination with the classic combination therapy, achieving an improvement in the results.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora