El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar el grado de adecuación de tromboprofilaxis en pacientes médicos hospitalizados aplicando 2 guías de práctica clínica y analizar el grado de acuerdo entre ambas.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio de corte transversal en servicios médicos de un hospital de tercer nivel. Calculamos el riesgo tromboembólico y la adecuación de tromboprofilaxis aplicando las recomendaciones de la viii conferencia de la American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) y la Guía de Profilaxis de Patología Tromboembólica en Patología Médica (PRETEMED), así como su concordancia.
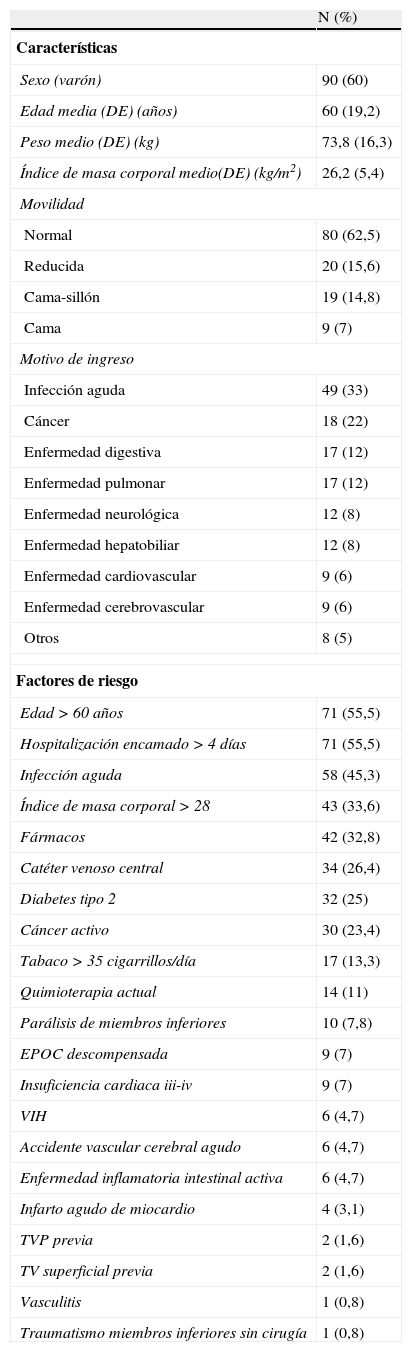
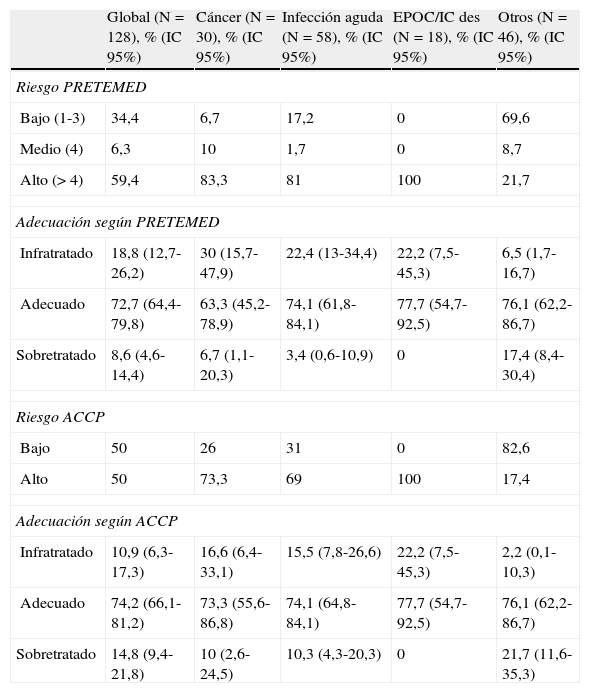
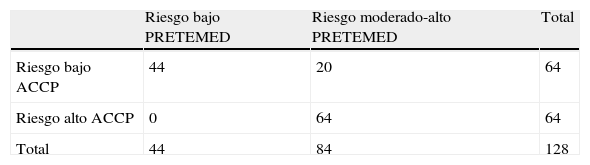
ResultadosSe analizaron 128 pacientes. Según la guía PRETEMED, el 34,4% de los pacientes tenían riesgo bajo, un 6,3% moderado y un 59,4% alto; la tromboprofilaxis fue adecuada en el 72,7% (intervalo de confianza del 95% [IC 95%] 64,4-79,9), fueron infratratados el 18,8% (IC 95% 12,7-26,2) y sobretratados el 8,6% (IC 95% 4,6-14,4). Según las recomendaciones de la ACCP, un 50% tenían bajo riesgo y un 50% alto; la tromboprofilaxis fue adecuada en el 74,2% (IC 95% 66,1-81,2), fueron infratratados el 10,9% (IC 95% 6,4-17,3) y sobretratados el 14,8% (IC 95% 9,4-21,8). Agrupando el riesgo PRETEMED en bajo o moderado-alto frente a riesgo ACCP bajo o alto, el índice de concordancia entre guías fue de 0,68 (IC 95% 0,56-0,81). Agrupando el riesgo PRETEMED en bajo-moderado o alto frente a riesgo ACCP bajo o alto el índice de concordancia fue de 0,81 (IC 95% 0,71-0,91).
ConclusionesAlrededor de un cuarto de los pacientes médicos hospitalizados no recibieron tromboprofilaxis adecuada, demostrándose un importante margen de mejora. La guía PRETEMED y los criterios de la ACCP presentan diferencias en la valoración del riesgo debido principalmente a que PRETEMED sobrestima el riesgo de enfermedad tromboembólica venosa al contemplar más factores de riesgo.
The aim of this study is to evaluate the use of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in hospitalized medical patients using 2 clinical practice guidelines and to analyze the agreement between them.
Patients and methodsCross-sectional study of medical services in a third level hospital. We calculated the thromboembolic risk and the thromboprophylaxis adequacy by implementing the recommendations of viii conference of the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) and PRETEMED guide as well as their agreement.
ResultsOne hundred and twenty eight patients were included in the study. According to the PRETEMED guide, 34.4% of patients were low risk, 6.3% moderate and 59.4% high, with appropriate prophylaxis in 72.7% of patients (CI95%: 64.4-79.9), 18.8% (CI95%: 12.7-26.2) were undertreated and 8.6% (CI95%: 4.6-14.4) overtreated. According to ACCP recommendations, 50% of patients were low risk and 50% high, with appropriate prophylaxis in 74.2% of patients (CI95%: 66.1-81.2), 10.9% (CI95%: 6.4-17.3) were undertreated and 14.8% (CI95%: 9.4-21.8) overtreated. When PRETEMED risk was classified into low or moderate-high group versus ACCP risk low or high, the grade of concordance between both guides was 0.68 (CI95%: 0.56-0.81). When PRETEMED risk was classified into low-moderate or high group versus ACCP risk low or high, the grade of concordance between both guides was 0.81 (CI95%: 0.71-0.91).
ConclusionsAbout a quarter of hospitalized medical patients did not receive adequate prophylaxis, showing an important room for improvement. PRETEMED guide and ACCP recommendations differ in risk assessment mainly because PRETEMED guide overestimates the risk of venous thromboembolism since it includes more risk factors.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora