La valoración del paciente con hemorragia digestiva (HD) aguda requiere de una evaluación clínica y analítica precoz. El objetivo de este estudio es valorar la concordancia de la determinación de hemoglobina (Hb) y hematocrito (HTC) precozmente mediante gasometría venosa (GSV) y de forma convencional por el Laboratorio (LAB) de Urgencias.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio observacional y prospectivo de pacientes ingresados en la Unidad de Hemorragias Digestivas por HD aguda alta y baja. Se recogieron variables demográficas, clínicas y muestras de sangre venosa simultáneas para la determinación de Hb y HTC por GSV y LAB. Se analizó la concordancia de ambos métodos mediante el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI) y el análisis de Bland-Altman.
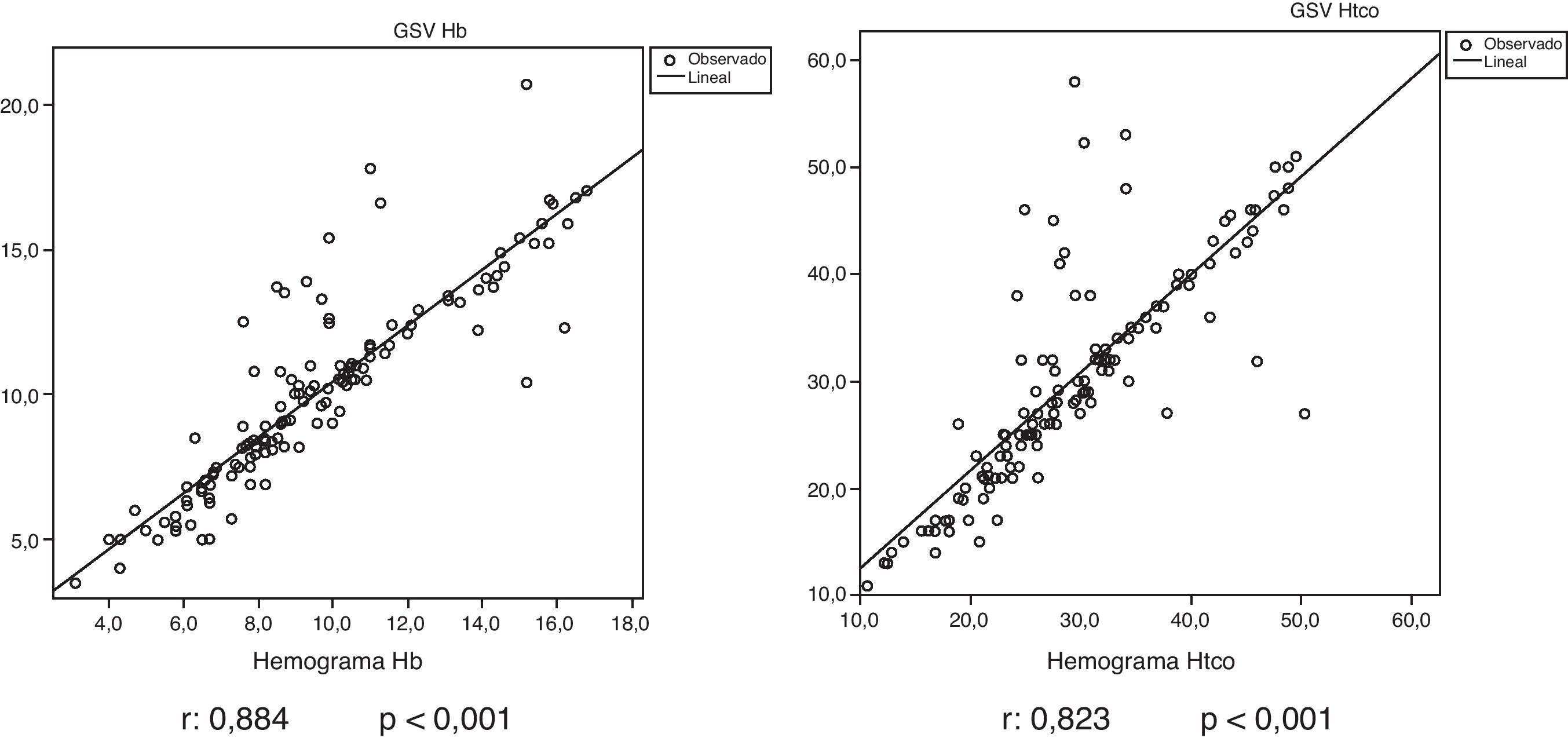
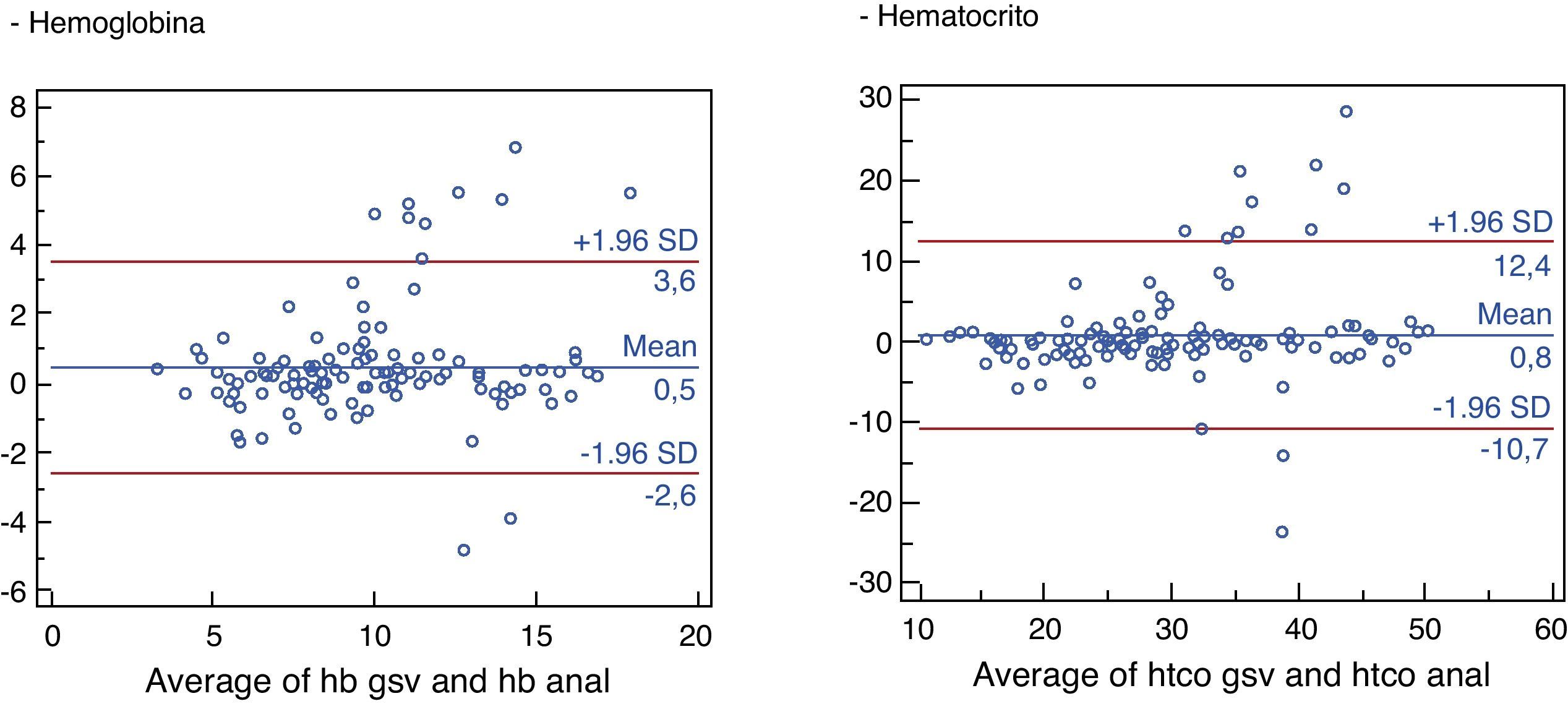
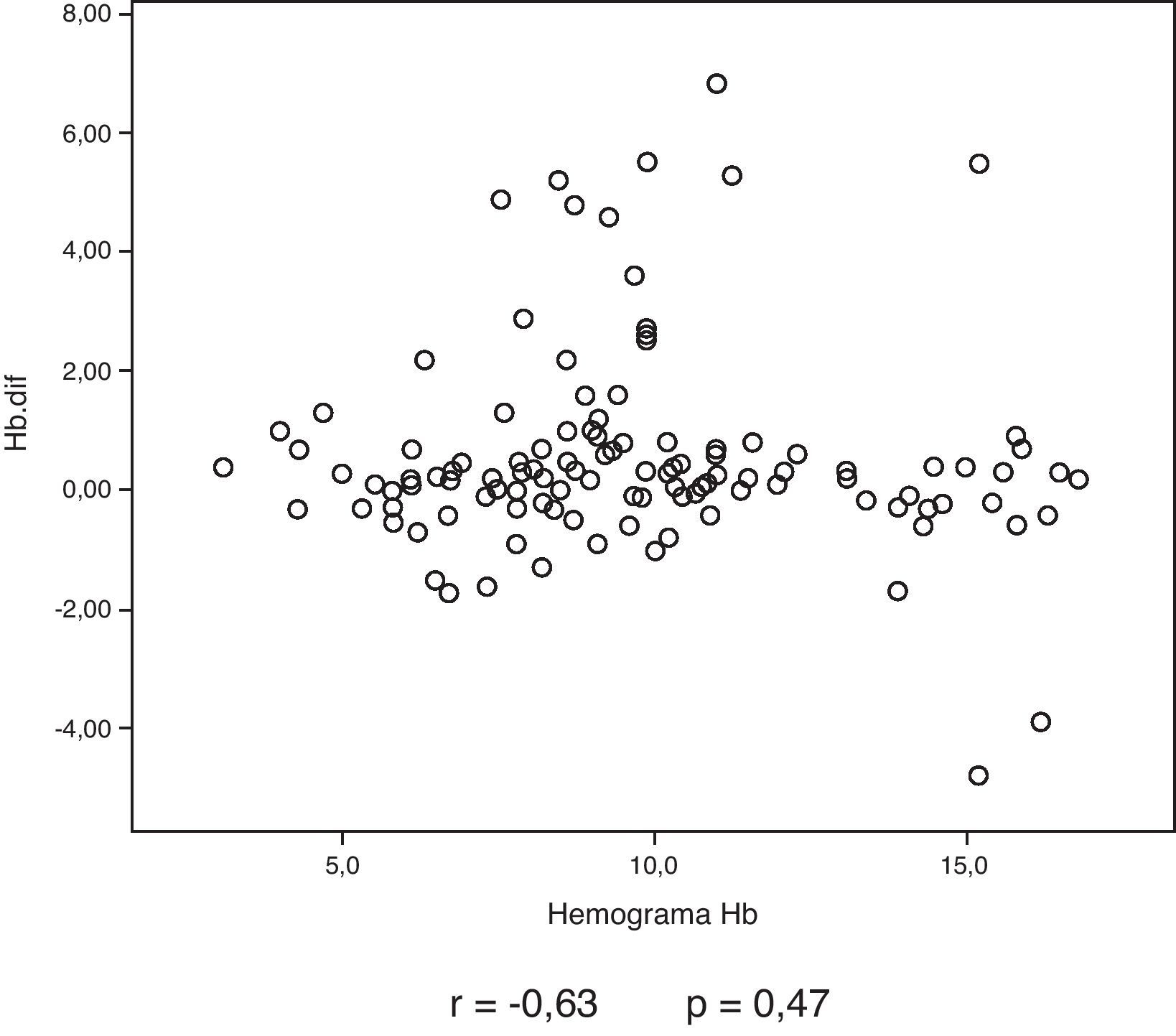
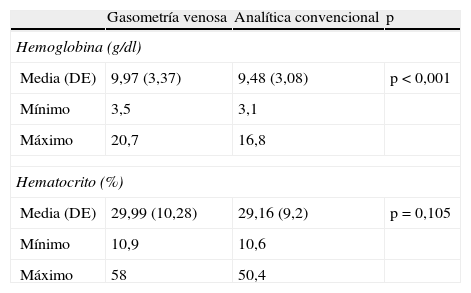
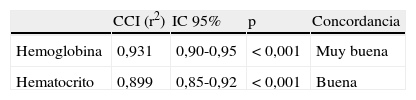
ResultadosSe incluyeron 132 pacientes. Un total de 87 (65,9%) eran varones y la edad media fue de 66,8 años. La GSV sobreestimó la Hb en 0,49g/dl (intervalo de confianza del 95% 0,21-0,76) respecto al LAB. La concordancia fue muy buena en la Hb (CCI 0,931) y buena en el HTC (CCI 0,899), mostrando las gráficas de Bland-Altman tanto la concordancia como la sobreestimación de la determinación de la Hb por GSV. En 19 pacientes (14,39%) la Hb por GSV superó en más de 1g/dl la determinación final obtenida por LAB.
ConclusionesLa determinación precoz de Hb y HTC en pacientes con HD aguda mediante GSV resulta fiable en la valoración inicial de la anemia. La GSV sobreestima sistemáticamente el valor de Hb en al menos 0,5g/dl, por lo que la evaluación clínica y hemodinámica del sangrante debe prevalecer sobre el resultado analítico.
Evaluation of patients with acute gastrointestinal bleeding (AGB) requires early clinical evaluation and analysis. The aim of this study is to evaluate early concordance of hemoglobin (Hb) and hematocrit (HTC) levels determined by conventional venous blood gas analysis (VBG) and by conventional Laboratory in Emergencies (LAB).
Patients and methodsObservational and prospective study of patients admitted in the Gastrointestinal Haemorrhage Unit with both high and low AGB. Demographic and clinical variables and simultaneous venous blood samples were obtained to determine Hb and HTC by VBG and LAB. Concordance in both methods was analysed by intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman analysis.
ResultsOne hundred and thirty-two patients were included: 87 (65.9%) males, average age 66.8 years. VBG overestimated Hb in 0.49g/dl (95% confidence interval: 0.21-0.76) with respect to LAB. Concordance was very high in Hb (ICC 0.931) and high in HTC (0.899), with the Bland-Altman graphs showing both concordance and overestimation of Hb levels determined by VBG. In 19 patients (14.39%), Hb by VBG exceeded in more than 1g/dL the final determination obtained by LAB.
ConclusionsEarly determination of Hb and HTC in patients with AGB by VBG provides reliable results in the initial evaluation of anaemia. VBG systematically overestimates Hb values by less than 0.5g/dl, and therefore clinical and hemodynamic evaluation of the bleeding patient should prevail over analytical results.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora