Fabry disease (FD) causes glycosphingolipid accumulation in the vascular endothelium, with predominantly cardiac and renal involvement. Its prevalence in patients with concomitant involvement of these two organs is unknown. The objective of the study was to determine the prevalence of FD in patients with left ventricular hypertrophy and any degree of chronic kidney disease.
Patients and methodsPatients with ventricular thickness ≥ 13 mm and kidney disease from 29 Spanish hospitals were included. Sociodemographic variables and target organ involvement of FD were collected. Laboratory determinations of EF were carried out, with an enzymatic activity test ± genetic test in men and direct genetic test in women.
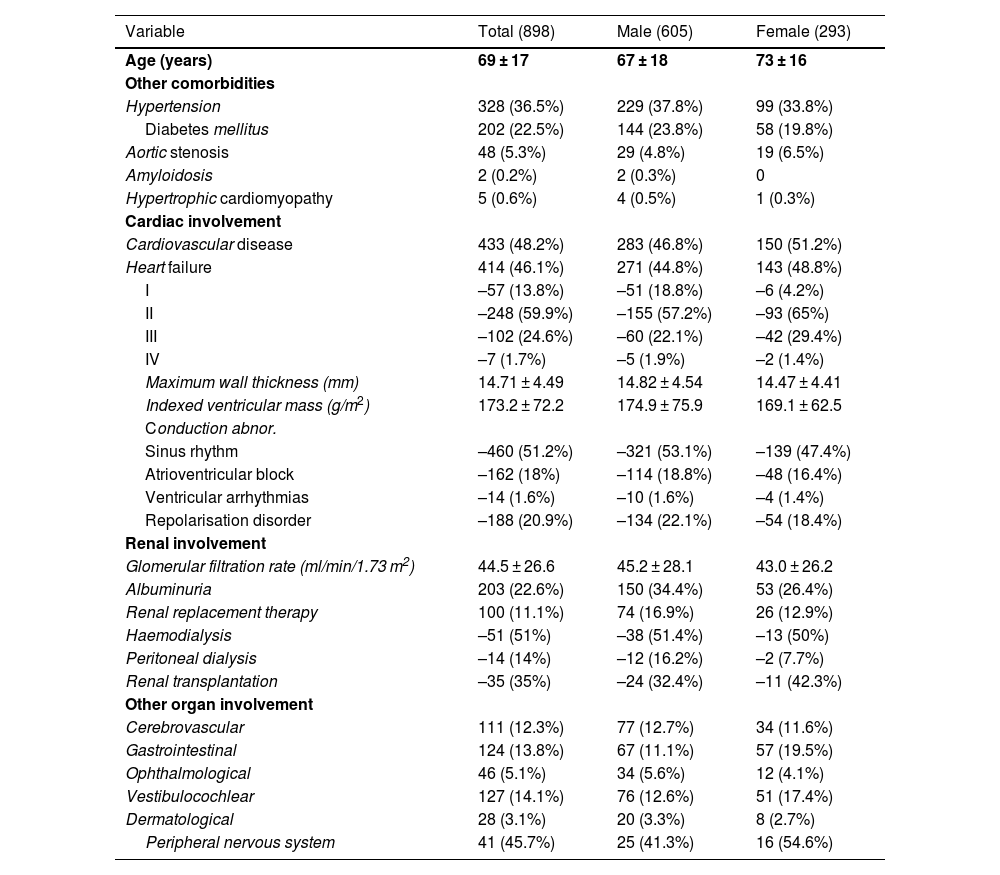
ResultsEight hundred ninety-eight patients with left ventricular hypertrophy and chronic kidney disease were included. The presence of heart failure and cardiorenal syndrome was common (46.1% and 40.1%). 3 patients (2 men and 1 woman) were diagnosed with FD, based on the presence of a pathogenic variant in the GLA gene and classic signs of FD, resulting in a prevalence of 0.33% (CI 95% 0.06%–1%). 6 patients (0.66%) presented genetic variants of unknown significance, without showing classic signs of FD, while in 13 patients (3.2%) performing the blood test was impossible.
ConclusionsFD is an important cause of left ventricular hypertrophy and chronic kidney disease. Genetic diagnosis is crucial for avoiding biases and ensuring accurate identification of FD, especially in women. The results support the inclusion of this disease in the differential diagnosis of patients with ventricular hypertrophy ≥ 13 mm and chronic kidney disease.
La enfermedad de Fabry (EF) produce acúmulo glicoesfingolípidos en el endotelio vascular, con afectación predominantemente cardíaca y renal. Su prevalencia en pacientes con afectación concomitante de estos dos órganos es desconocida. El objetivo del estudio fue determinar la prevalencia de EF en pacientes con hipertrofia ventricular izquierda y cualquier grado de enfermedad renal crónica.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron pacientes con grosor ventricular ≥ 13 mm y enfermedad renal de 29 hospitales españoles. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas y afectación de órganos diana de la EF. Se realizó estudio analítico de EF, con test de actividad enzimática ± test genético en varones y test genético directo en mujeres.
ResultadosSe reclutaron 898 pacientes con hipertrofia ventricular izquierda y enfermedad renal crónica. La presencia de insuficiencia cardíaca y síndrome cardiorrenal fue frecuente (46,1% y 40,1%). 3 pacientes (2 varones y 1 mujer) fueron diagnosticados de EF en base a la presencia de una variante patogénica del gen GLA y signos clásicos de EF, suponiendo una prevalencia del 0,33% (IC 95% 0,06%–1%). 6 pacientes (0,66%) presentaron variables de significado incierto, sin presentar estos pacientes signos clásicos de EF, y en 13 pacientes (3,2%) fue imposible realizar el estudio analítico.
ConclusionesLa EF es una causa importante de hipertrofia ventricular izquierda y enfermedad renal crónica. El diagnóstico genético es crucial para evitar sesgos y asegurar una identificación precisa de la EF, especialmente en mujeres. Los resultados respaldan la inclusión de esta enfermedad en el diagnóstico diferencial de pacientes con hipertrofia ventricular ≥ 13 mm y enfermedad renal crónica.