The Colorectal Cancer Screening Program of Barcelona was implemented in December 2009 and involves pharmacies for the distribution and collection of screening tests. The aim of this article is to describe the main indicators of the first round of the Program (2010–2011), based on the ones suggested by the European Union.
Material and methodsThe target population of the Colorectal Cancer Screening Program of Barcelona includes men and women aged 50–69 years who live in the catchment areas of Hospital Clínic and Hospital del Mar. Screening consists of biennial immunochemical fecal occult blood testing, with colonoscopy as confirmatory procedure.
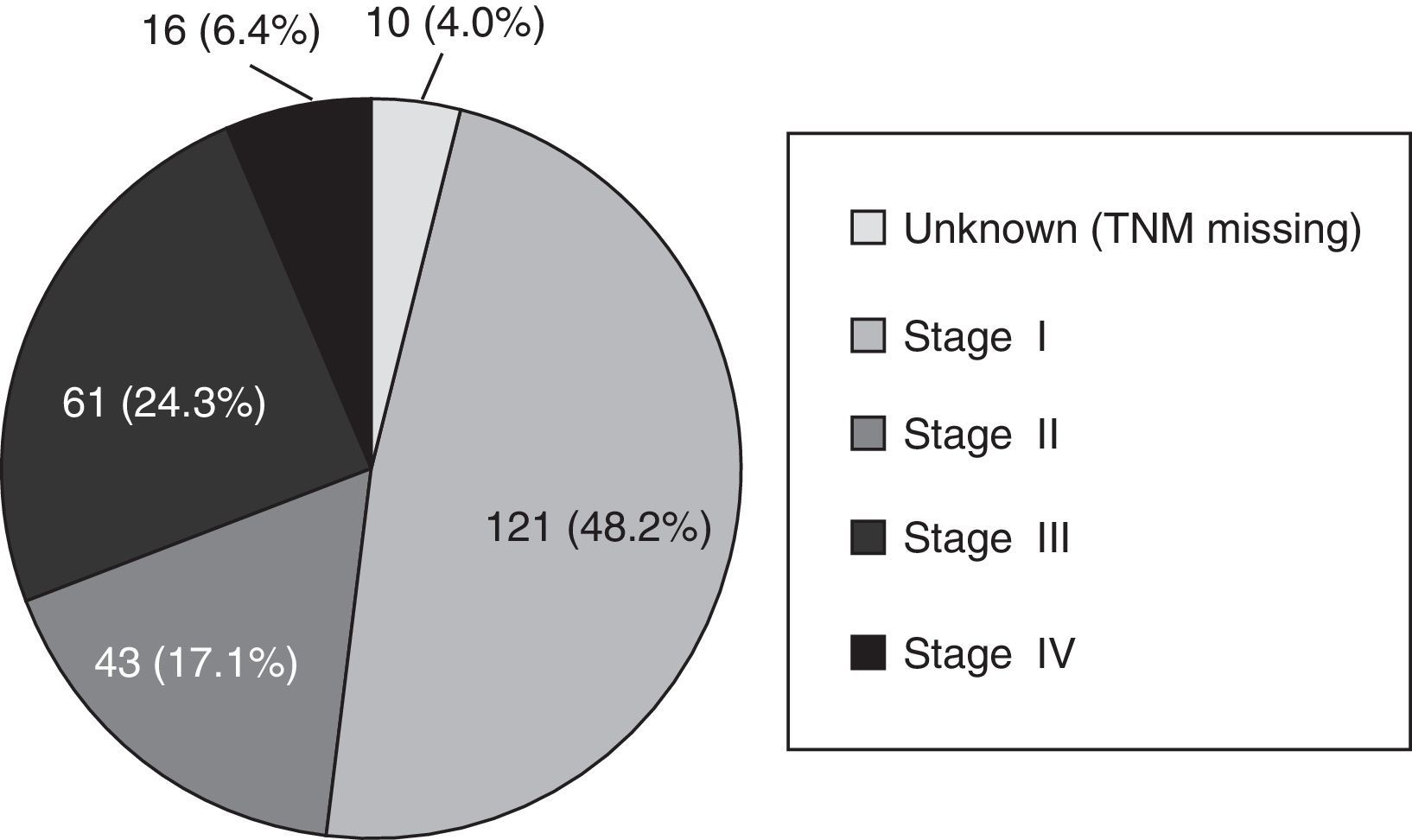
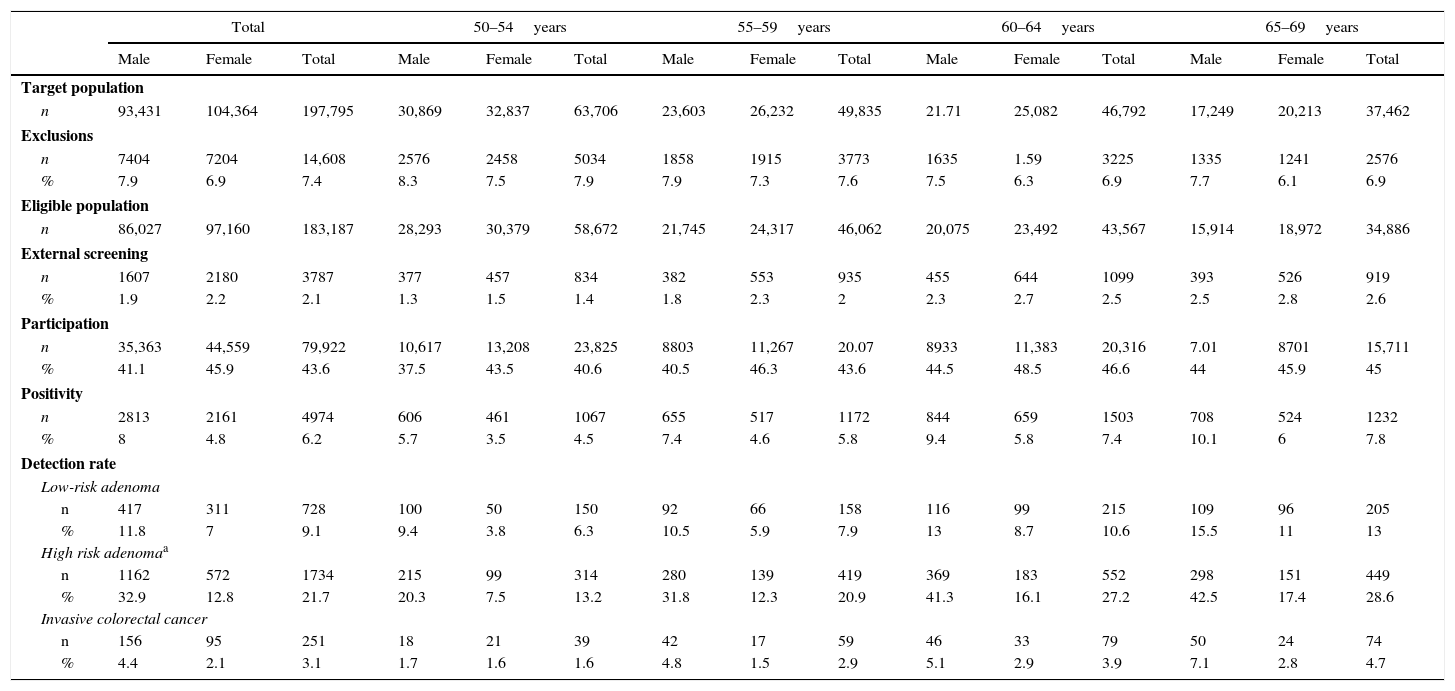
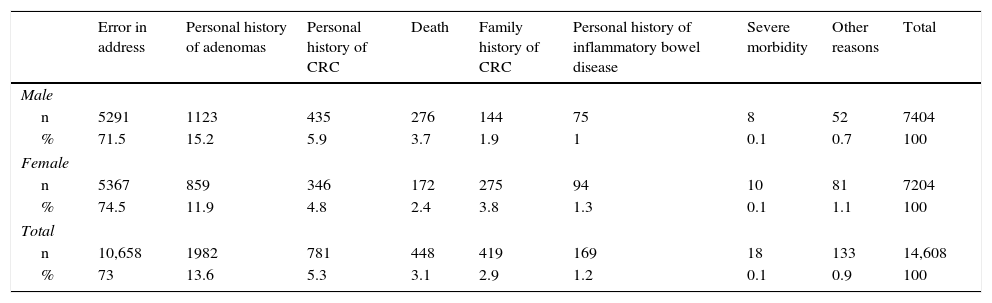
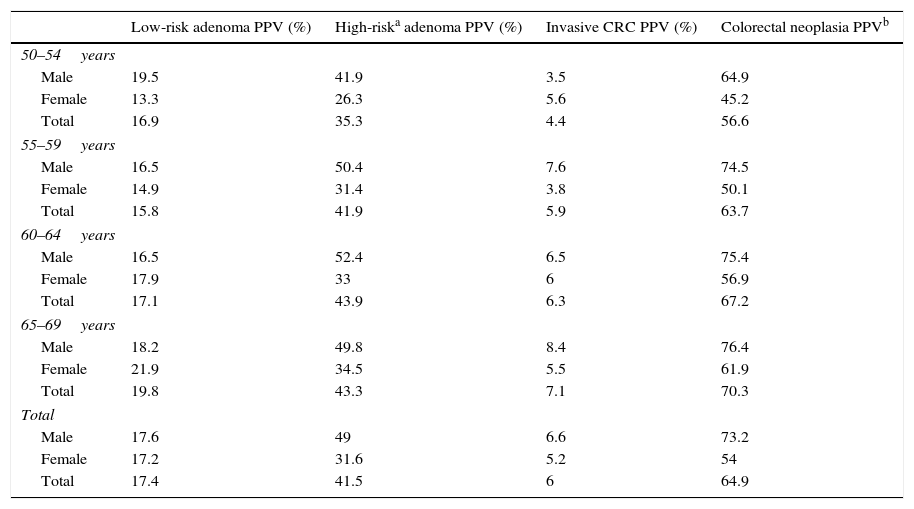
ResultsTarget population comprised 197,795 persons. Participation rate was 43.6%, was higher among women and among those aged 60 and older. 2.1% of the eligible population stated to have been already screened for colorectal cancer. Overall positivity rate was 6.2%, higher among men and with a broad variability among health care areas. The detection rates of low- and high-risk adenoma, and of invasive cancer were 9.1‰, 21.7‰ and 3.1‰, respectively. 48.2% of tumors were stage I.
ConclusionsThese results are considered satisfactory and consistent with those obtained in other programs and with European standards. Nevertheless, some areas for improvement have been identified. The high participation rate can be attributed, at least in part, to the type of test and to the involvement of community pharmacies.
El Programa de Detección Precoz del Cáncer de Colon y Recto de Barcelona se puso en marcha en diciembre de 2009 y cuenta con las oficinas de farmacia para la distribución y recogida del test de cribado. En este artículo se describen los principales indicadores de la primera ronda del Programa (2010–2011) según los propuestos por la Unión Europea.
Material y métodosEl Programa de Detección Precoz del Cáncer de Colon y Recto de Barcelona se dirige a varones y mujeres de 50 a 69 años residentes en las áreas de referencia del Hospital Clínic y del Hospital del Mar, tiene periodicidad bienal, y utiliza el test inmunológico de detección de sangre oculta en heces y posterior confirmación diagnóstica mediante colonoscopia.
ResultadosLa población diana fue de 197.795 personas. La tasa de participación fue del 43,6%, siendo mayor en mujeres y en mayores de 59 años. Un 2,1% de la población invitada declaró un cribado externo al Programa. La tasa de positividad fue del 6,2%, mayor en varones y con amplia variabilidad entre áreas básicas de salud. Las tasas de detección de adenoma de bajo y alto riesgo, y de cáncer invasivo fueron, respectivamente, del 9,1‰, del 21,7‰, y del 3,1‰. El 48,2% de los tumores fueron estadio I.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos se consideran satisfactorios y acordes con los de otros programas y estándares europeos, aunque se han identificado aspectos de mejora. La elevada participación puede atribuirse, al menos parcialmente, al test empleado y a la implicación de la red de oficinas de farmacia comunitaria.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora