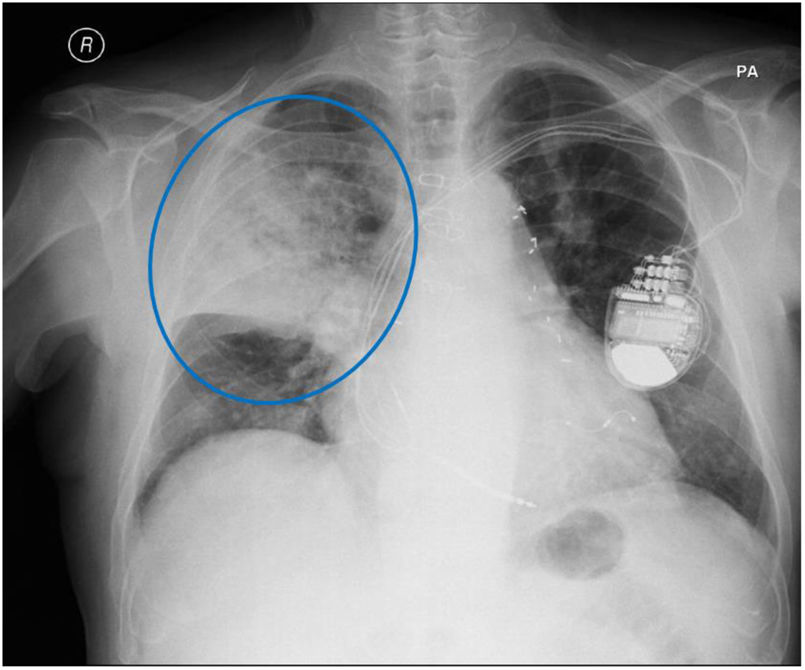
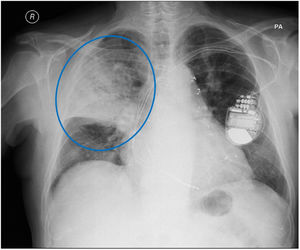
A 73-year-old man with a background of atrial fibrillation and pacemaker presented to the hospital with fever and cough for over 4 days. On physical examination he was hypotensive, pyretic and had decreased breathing sounds on the right with crepitations. Blood tests showed leukocytosis (16,900/μL), neutrophilia (16,150/μL) and CRP:306mg/dl. Arterial blood gases showed hypoxemia (pO2:58mmHg) and on chest radiography he had lung consolidation on the right (Fig. 1).
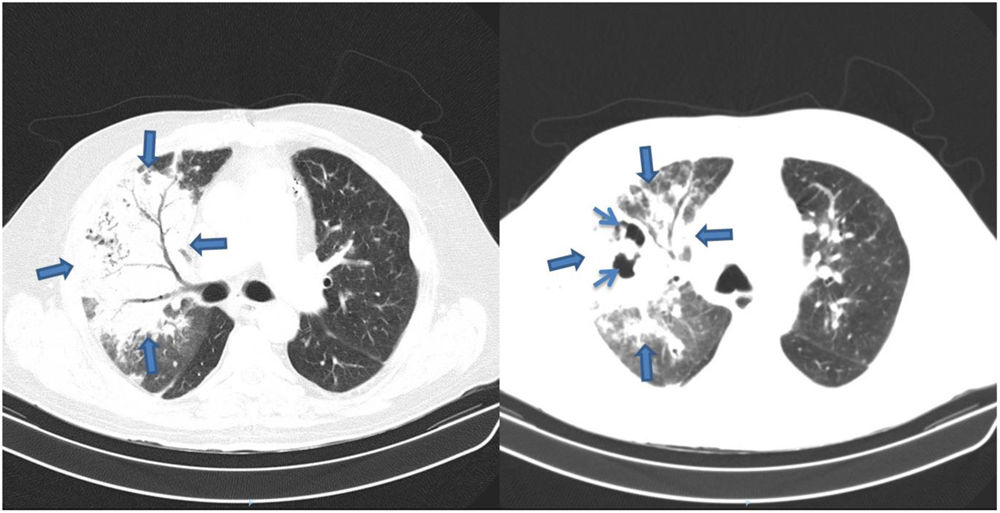
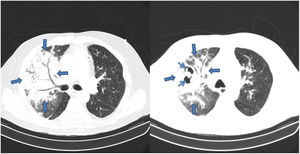
He was admitted to hospital for community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), was given ceftriaxone, showed improvements until the sixth day of treatment, but afterwards got worse analytically, radiologically and developed pyrexia. He underwent chest tomography that showed areas of consolidation and cavitation on the right (Fig. 2). He was prescribed piperacillin-tazobactan for fourteen days. The cultures and the bronchofibroscopic study didn’t isolate microorganisms and the biopsy was compatible with Necrotizing Pneumonia (NP). The patient had a positive response after treatment.
NP is a rare complication of CAP. Its early recognition and therapeutic optimization are associated with decreased morbidity and mortality. Severe complications are associated with the causal microorganism; seen in 51% of cases. The diagnosis of NP is based on clinical information, imaging and histology, therefore treatment should include a broad-spectrum of antibiotics with anaerobic coverage.