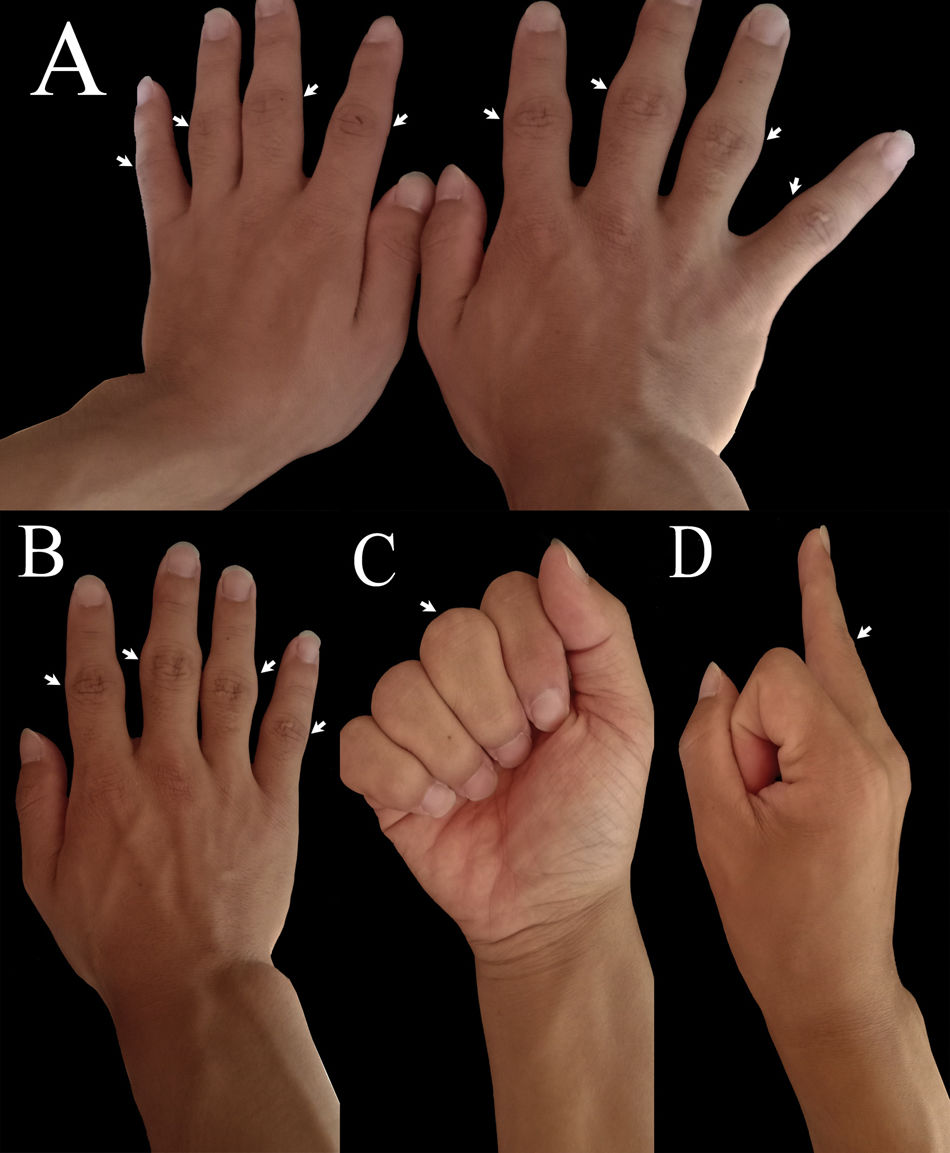
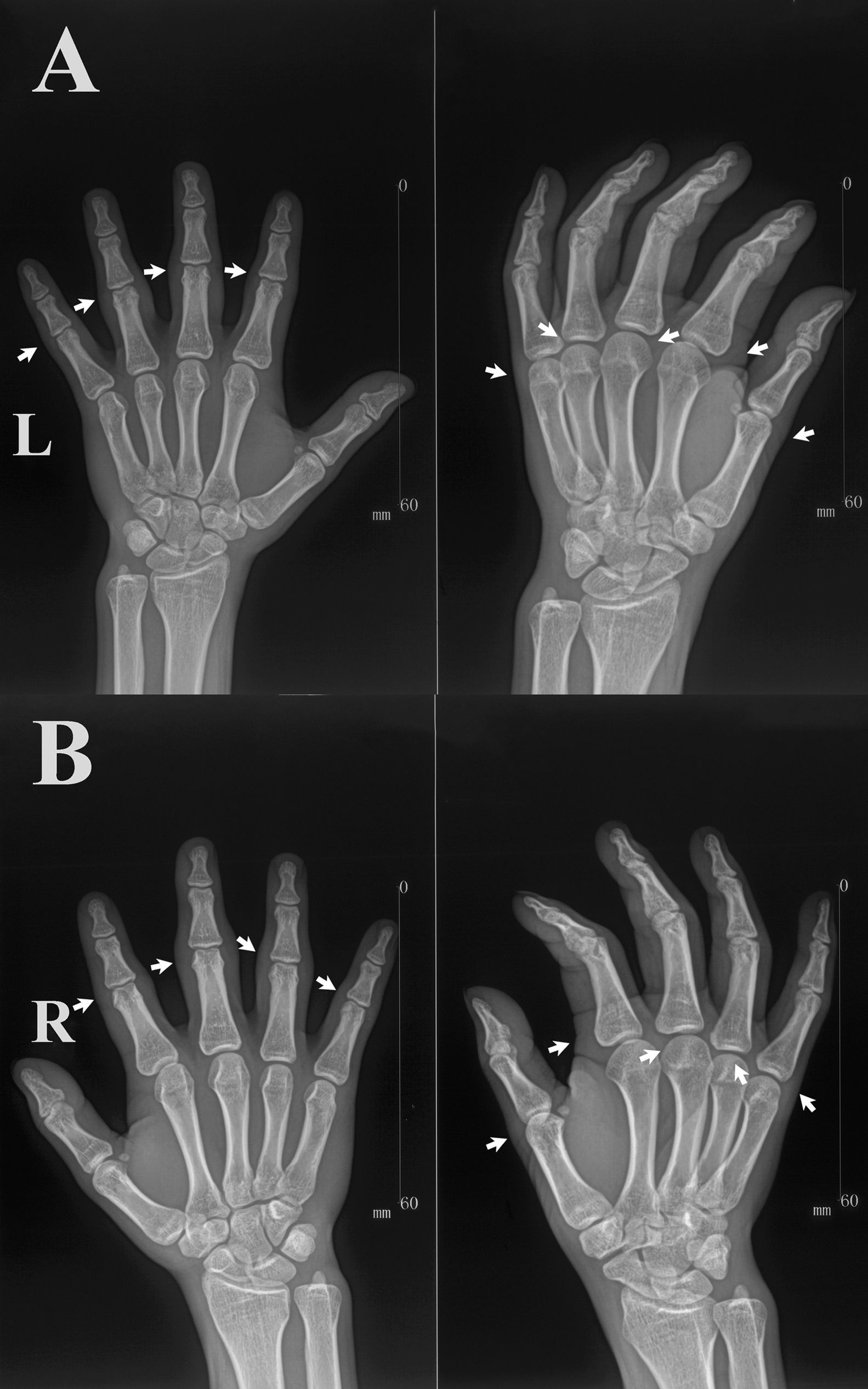
A 21-year-old young man was referred to our hospital with swelling fingers. The patient described the gradual appearance of swelling fingers since 3 years ago, without pain, joint stiffness, and local redness. Such a disturbance affected mainly proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints of 2nd to 5th finger and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints of 1st to 5th finger (Fig. 1). No history of evident trauma locally was reported. Rheumatoid factor, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein and anti-streptolizin O (ASO) were found to be within normal range. The radiograph of hands revealed soft tissue swelling around PIP and MCP joints, without erosion of bone or other structural abnormalities (Fig. 2). These findings were confirmed by ultrasonography. The diagnosis of pachydermodactyly (PDD) is made clinically, and can be supported by radiological studies and histopathologic examination. Thus, a diagnosis of PDD was made, which was usually seen in young males, with a ratio of 3.9 to 1.4 (male to female).1 PDD was a rare digital fibromatosis characterized by asymptomatic, progressive swelling of lateral aspects of PIP joint of fingers.2 No clinical progress was observed during these 3 years.
Ethics and consentThe use of human subjects for this study was approved by the Peking Union Medical College Hospital Ethical Review Board.
We thank the family members for their great cooperation.