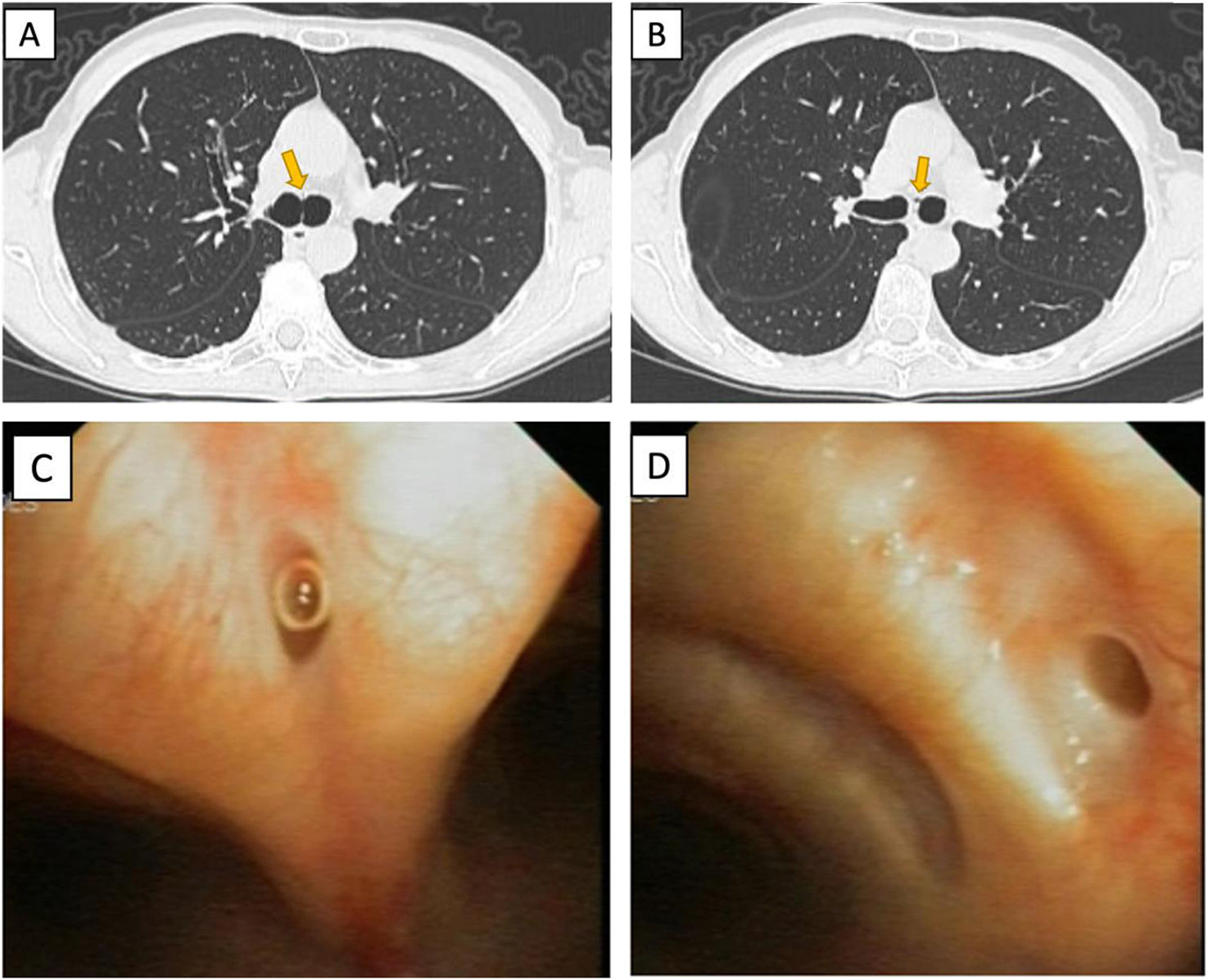
A 65-year-old female patient with dyslipidemia and never smoker, asymptomatic, recently diagnosed with a lung nodule is submitted to a CT scan and a flexible bronchoscopy as part of the study. In both tests, various tracheal and bronchial diverticula were discovered (Fig. 1).
(A) Chest CT scan shows an air cyst collection which communicate with the anterior wall of the carina (yellow arrow). (B) Chest CT scan shows two evaginations of small air collection communicating with the lumen of the left main bronchus (yellow arrow). (C) Bronchoscopy picture where a tracheal diverticulum in the anterior wall of the carina is seem. (D) Bronchoscopy picture where a bronchial diverticulum in the medial wall of the principal left bronchial is seem.
The tracheobronchial diverticula are evaginations or air cysts arising from the tracheal or bronchial walls with a direct communication with the lumen. They may be classified as congenital or acquired diverticula. Congenital diverticula usually arise on the right posterolateral part of the membranous tracheal wall, 5cm below the vocal cords and above the carina and are considered a true diverticulum with all layers of the tracheobronchial wall. They are thought to represent vestigial supernumerary lung or aborted division of the primary lung bud. Acquired diverticula can arise at any level and consist of a mucosal herniation caused by an intraluminal increased pressure through a weak portion of the bronchial walls like chronic cough.1,2
Both tracheal or bronchial diverticula are generally asymptomatic; however, they can serve as mucus reservoirs and cause recurrent respiratory infections. Also, they may be present concomitantly and are usually discovered incidentally when a CT scan or bronchoscopy is completed for another reason.2
Informed consentWritten informed consent given by the patient.
FundingThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors have participated in the elaboration of this article.
Conflicts of interestsThe authors declare not to have any conflicts of interest that may be considered to influence directly or indirectly the content of the manuscript.