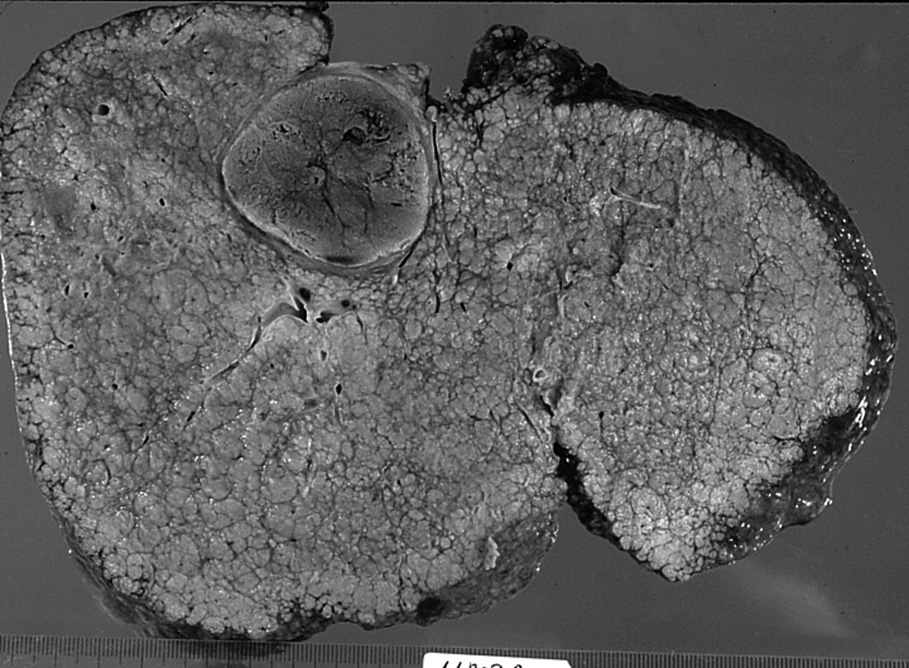
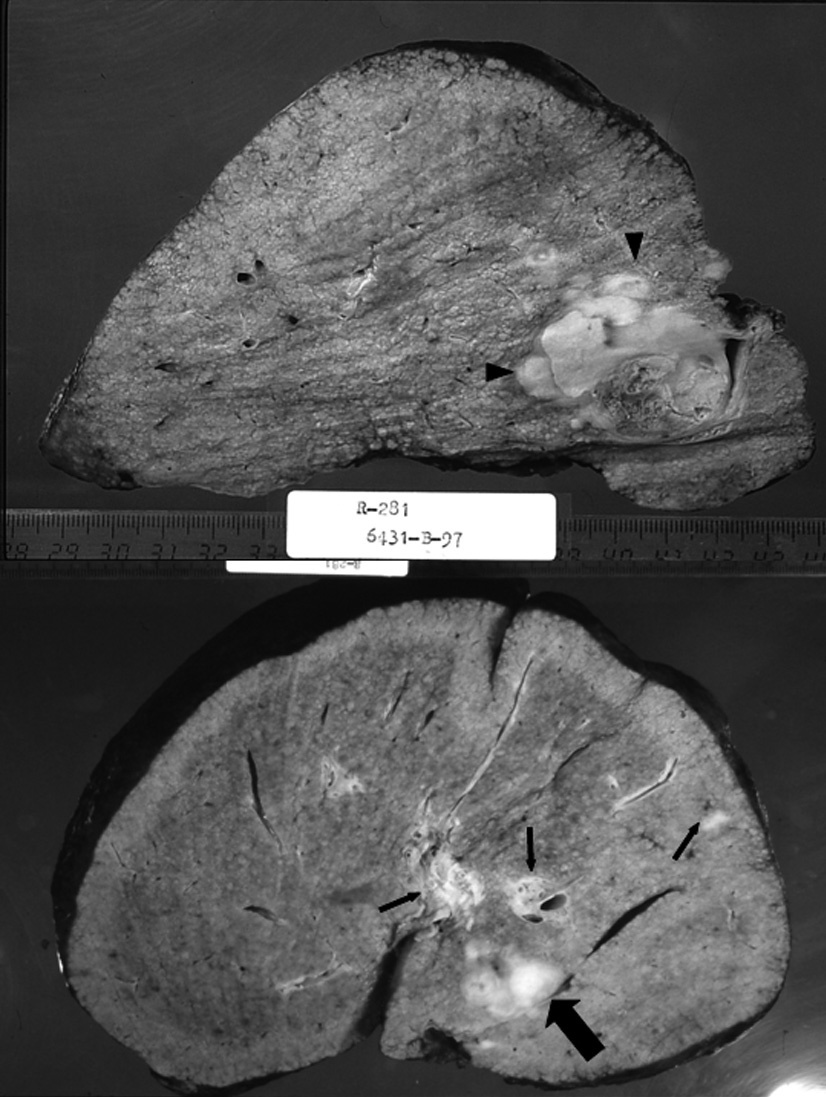
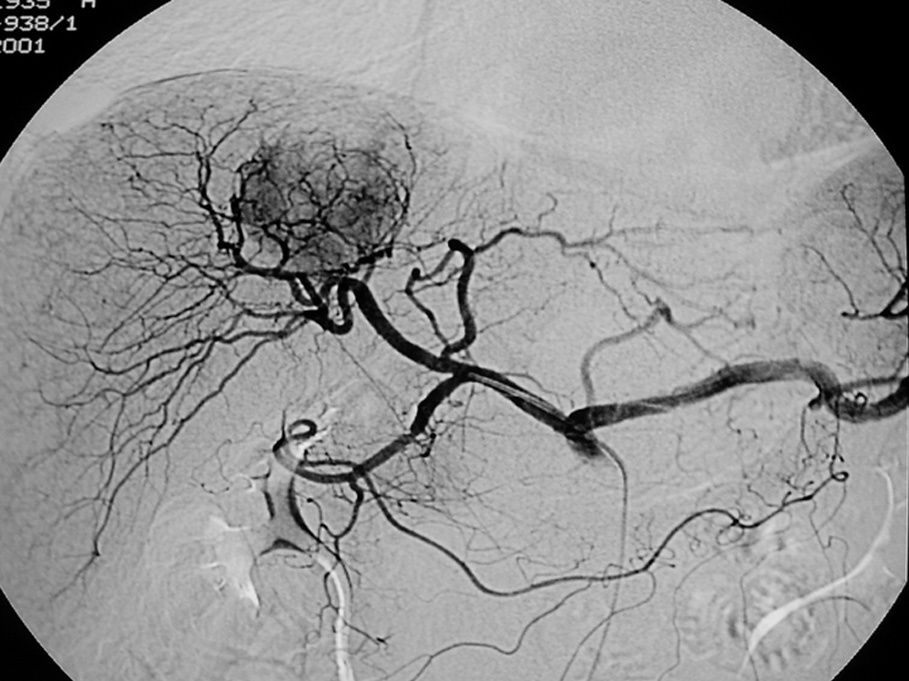
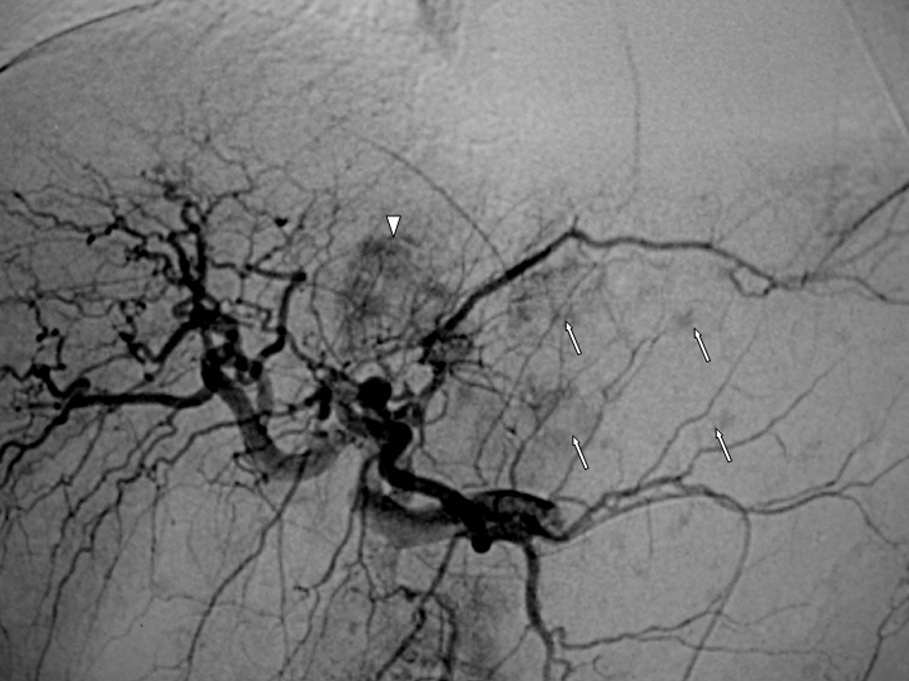
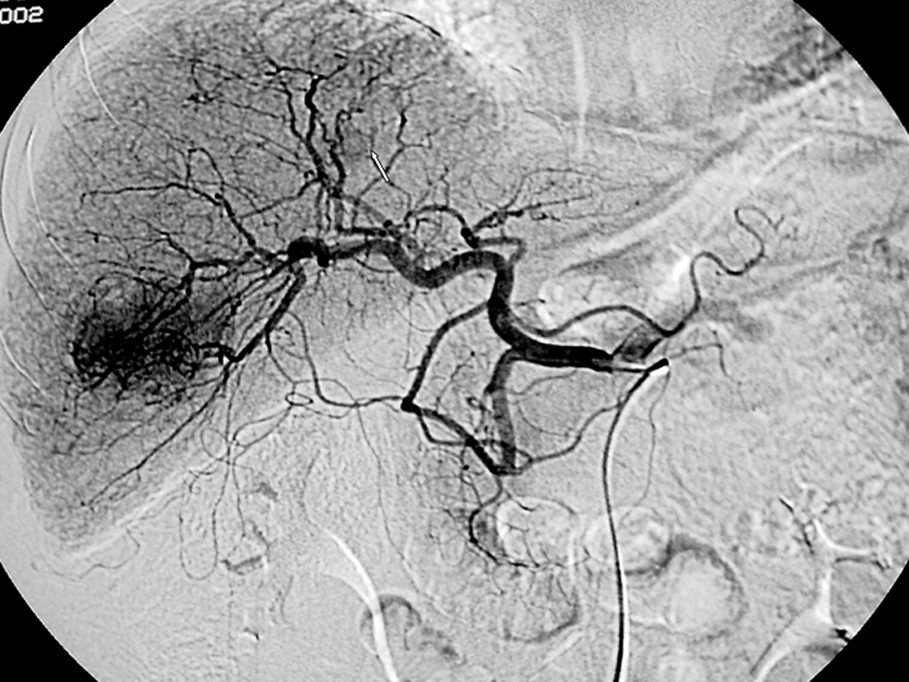
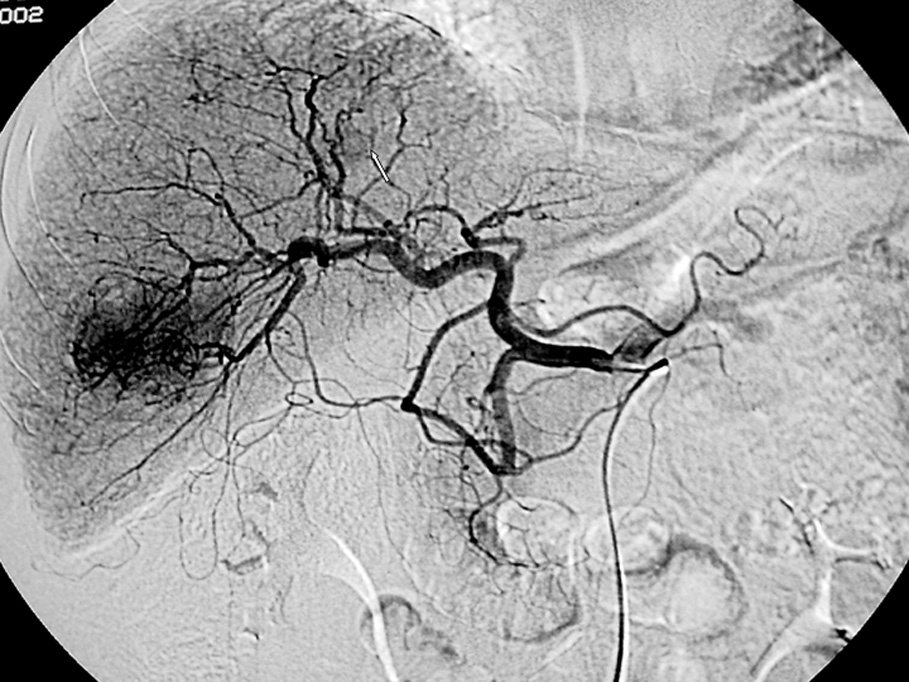
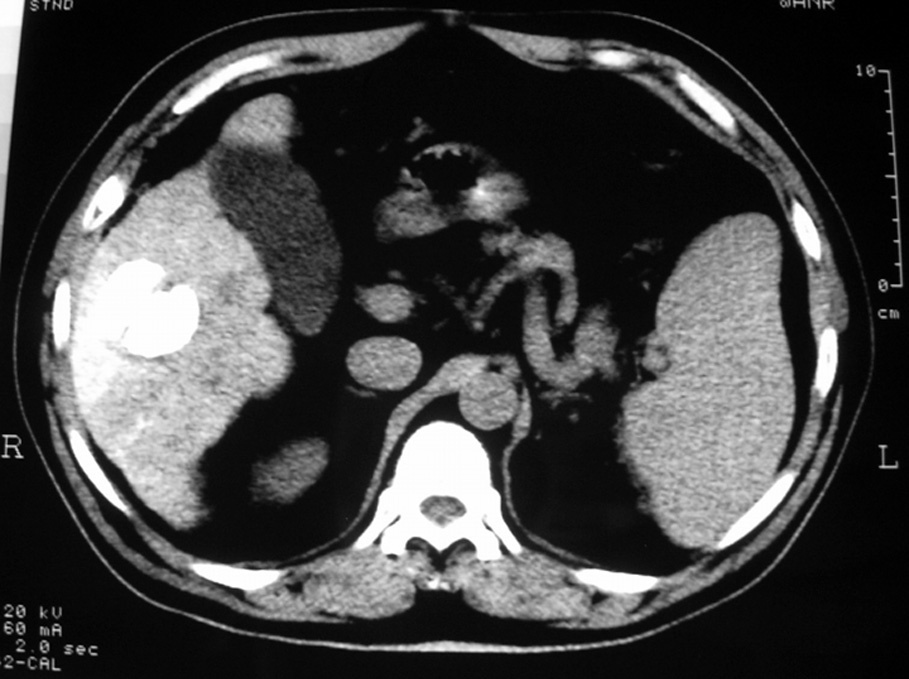
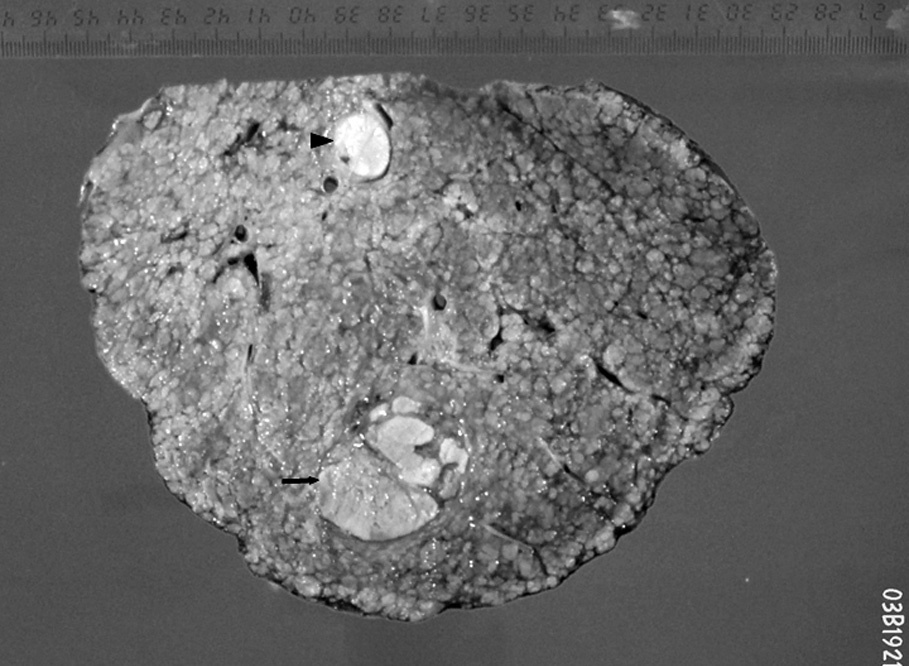
Radiología, fundada en 1912, es el Órgano de Expresión Científica Oficial de la Sociedad Española de Radiología Médica (SERAM).
Radiología, de periodicidad bimestral (6 números al año), publica dos ediciones una en español y otra en inglés. Todos los artículos son sometidos a un riguroso proceso de revisión doble ciego
Radiología focaliza su interés en la publicación de trabajos Originales, aunque también tienen cabida en ella Comunicaciones breves, Revisiones, Casos en imagen, Notas clínicas y Críticas de libros.
La revista está indexada entre otras en: Emerging Sources Citation Index (Clarivate), Medline, Scopus y EMBASE/Excerpta Médica.