Evaluar la relación entre el material recogido en filtros distales tras angioplastia y colocación de stent carotídeo (ASC) y la aparición de lesiones isquémicas cerebrales en la RM potenciada en difusión (RMD).
Determinar la influencia que tienen variables demográficas, clínicas y del procedimiento en el proceso embolígeno y en la isquemia post-ASC.
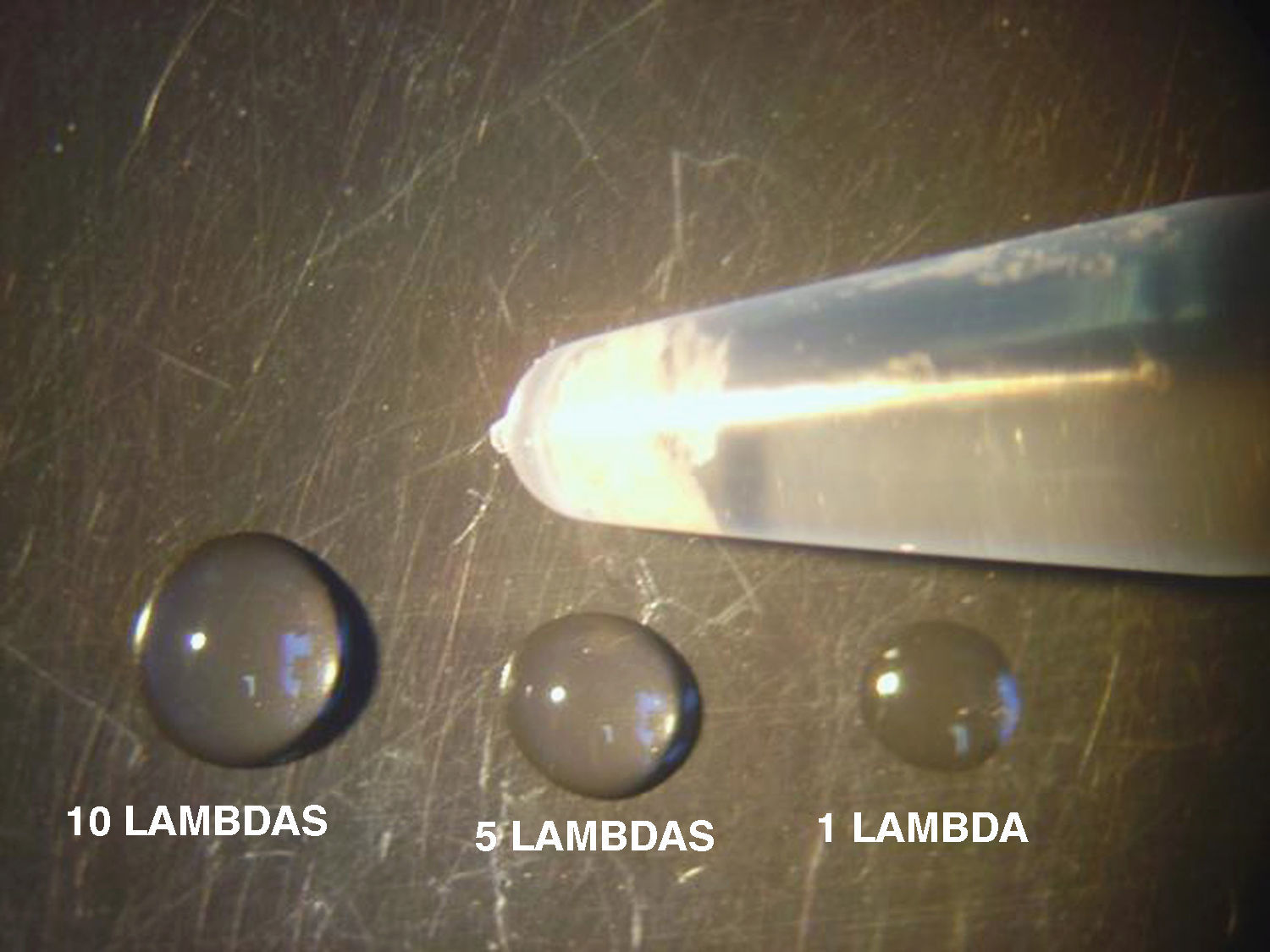
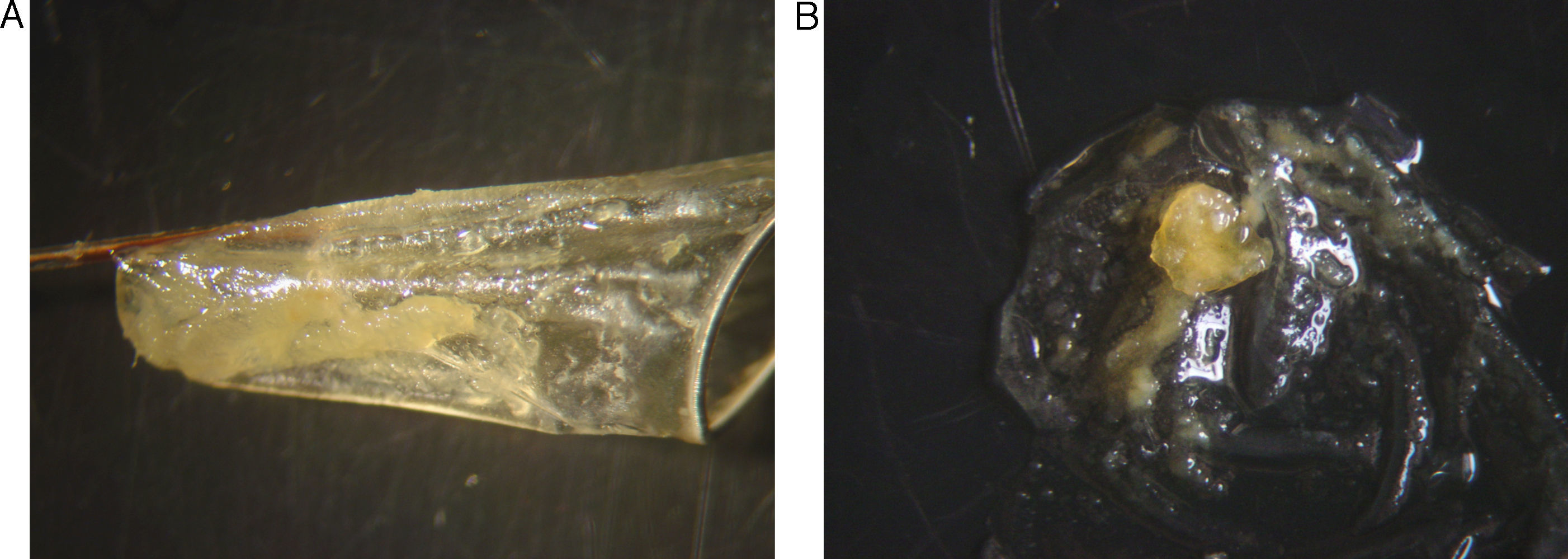
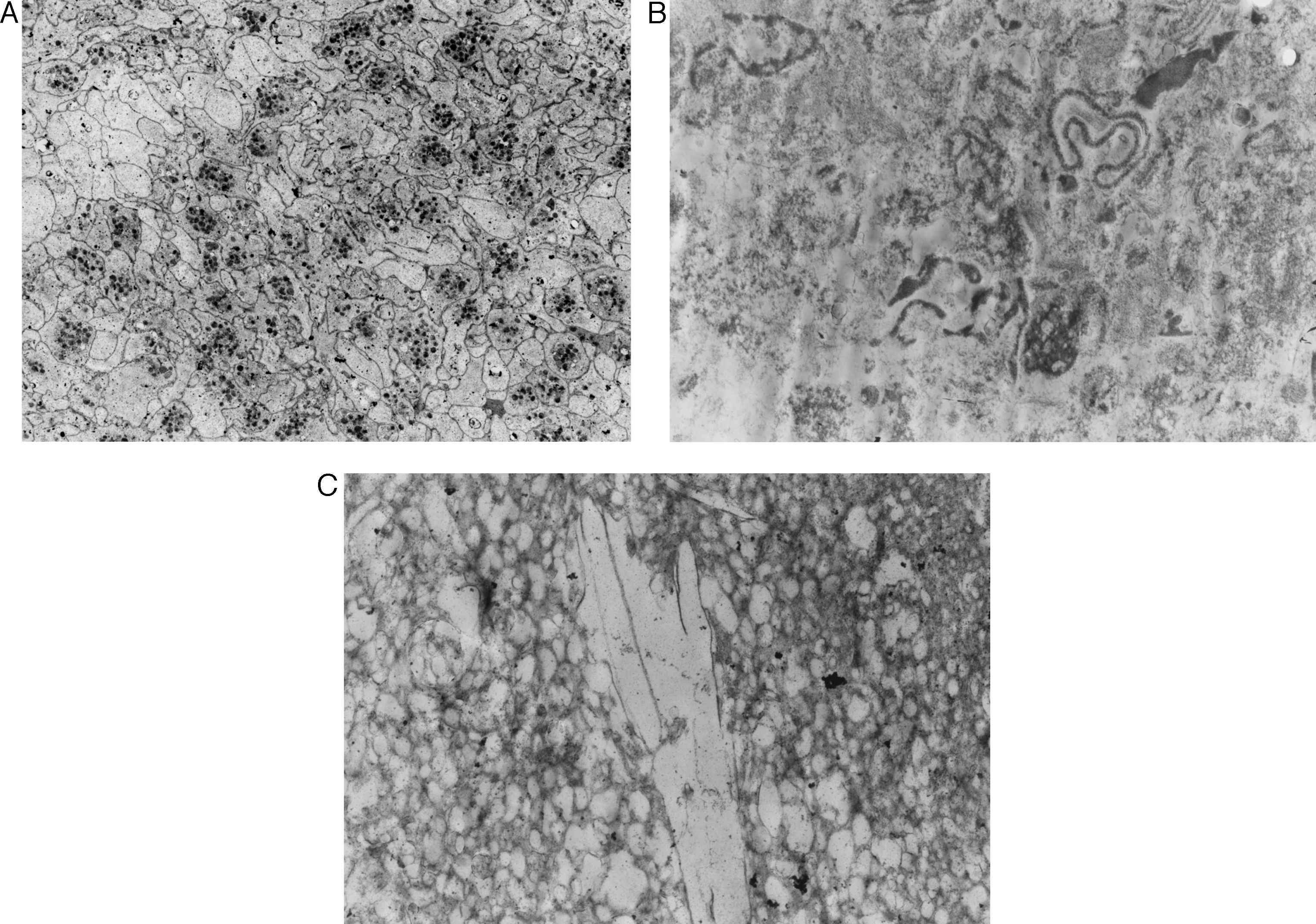
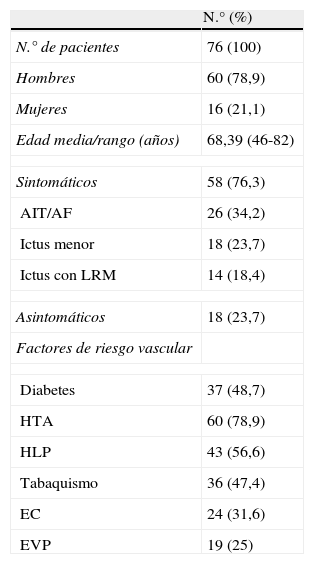
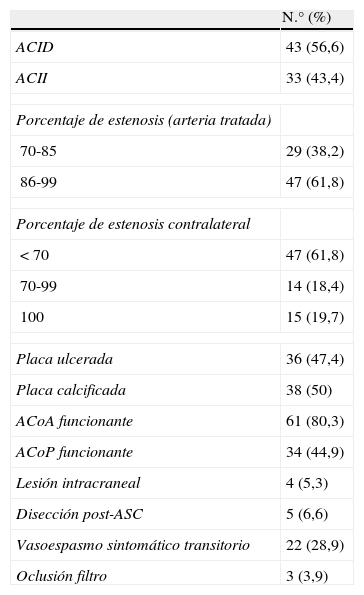
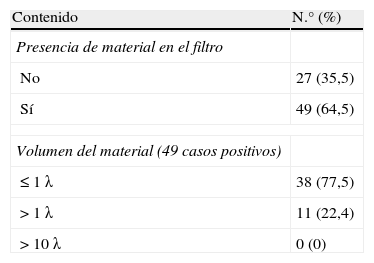
Material y métodoSe analizó histológicamente el contenido de los filtros de 76 pacientes sometidos a ASC por estenosis grave de la arteria carótida interna (ACI) (60 hombres; edad media 68,39 años; rango: 46-82), valorándose el volumen (< 1 λ=0,001 ml=1μl; 1-10 λ; y > 10 λ) y la composición de las partículas. Se realizó RMD previa y 24h después del procedimiento, recogiéndose la aparición de lesiones, número, tamaño y distribución. Se correlacionaron estadísticamente los datos anteriores y con variables demográficas, clínicas y del procedimiento.
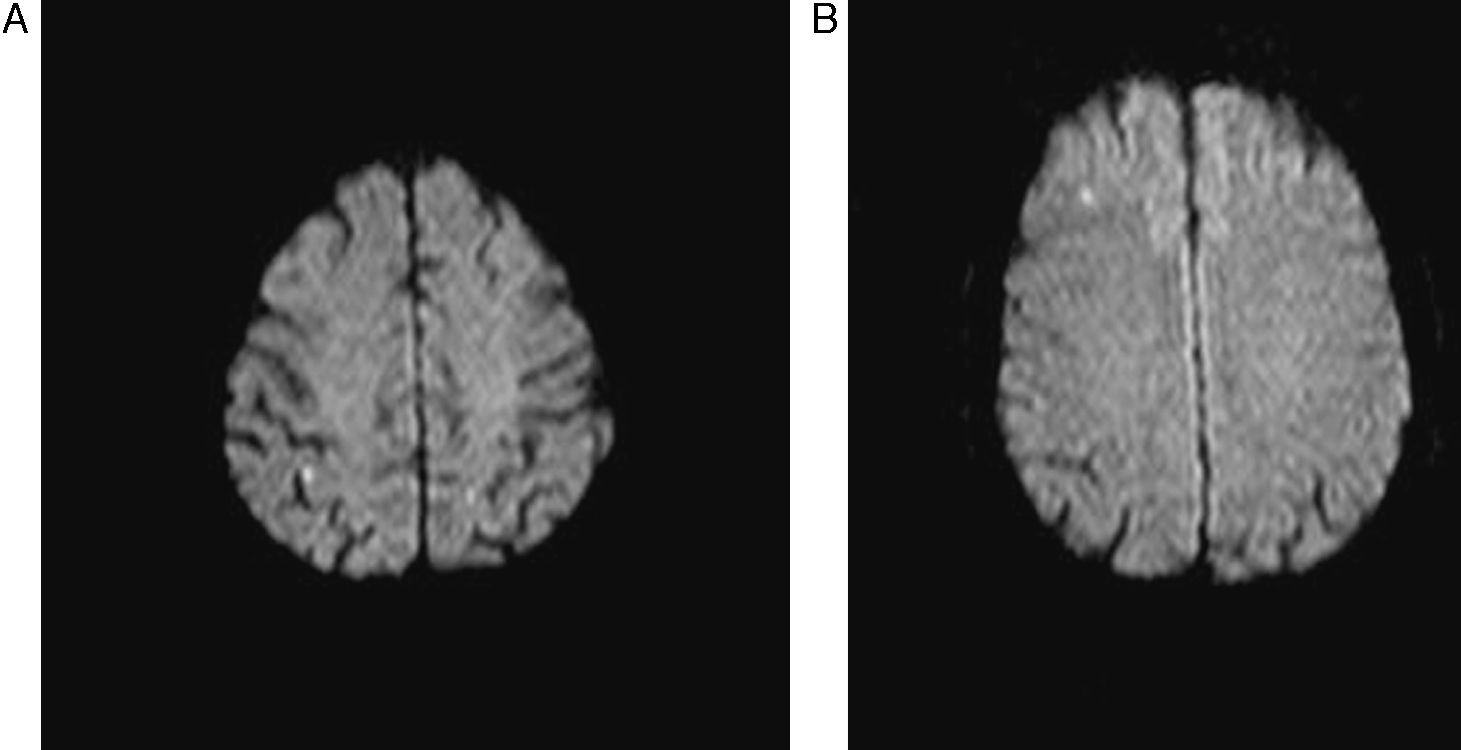
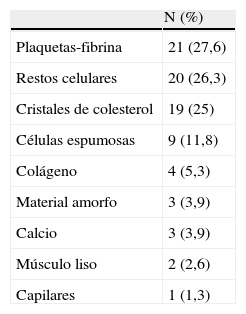
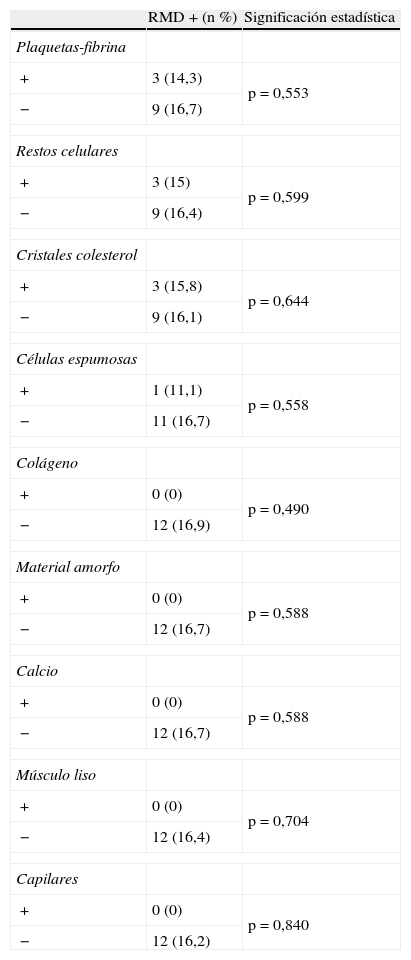
ResultadosCincuenta y ocho pacientes (76,3%) presentaron sintomatología previa al procedimiento. El 64,5% de los filtros (49) presentó partículas, la mayoría menores de 1 λ (77,5%), predominando los agregados fibrinoplaquetarios, restos celulares y cristales de colesterol. Doce pacientes (15,8%) demostraron lesiones en la RMD post-ASC, sin relación con el contenido en los filtros. No se encontró correlación estadística entre la presencia de material en los filtros y otras variables.
ConclusionesLa isquemia post-ASC no depende únicamente de la carga embolígena y su naturaleza. La menor prevalencia de lesiones post-ASC en nuestra serie en comparación con otras indica que la adecuada selección de pacientes y la experiencia minimizan la influencia negativa de algunas variables, como la edad, en su aparición.
To evaluate the relation between the material retrieved from distal filters after carotid angioplasty and stenting and the development of ischemic brain lesions in diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI).
To determine the influence of demographic, clinical, and procedural variables in the pathogenesis of emboli and in ischemia after carotid angioplasty and stenting.
Material and methodsWe submitted the contents of the filters of 76 patients (60 men; mean age, 68.39years; range, 46-82) who had undergone angioplasty and stenting for severe stenosis of the internal carotid artery for histologic analysis evaluating volume (< 1 λ=0.001ml = 1μl; 1-10 λ; and > 10 λ) and the composition of the particles. All patients underwent DWI before and 24hours after the procedure; we recorded whether lesions appeared and their number, size, and distribution. We correlated the findings with demographic, clinical, and procedural variables.
ResultsSymptoms were present before the procedure in 58 (76.3%) patients. Particles were present in 49 (64.5%) of the filters; most particles (77.5%) were 1 λ with a predominance of fibrin-platelet aggregates, cell remnants, and cholesterol crystals. DWI after the procedure detected lesions in 12 (15.8%) patients. We found no statistically significant correlation between filter contents and lesion detection after the procedure or between filter contents and other variables.
ConclusionsIschemia after carotid angioplasty and stenting does not depend solely on the embolic load and its nature. We consider that the lower prevalence of postprocedural lesions in our series compared to others suggests that appropriate patient selection and experience minimize the negative influence of some variables like age in their development.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora