Breast radiology: New horizons in times of pandemics
Más datosThere have always been concerns about the secondary effects of diagnostic methods that use ionizing radiation. During mammography, the parameters to be concerned about are the mean glandular dose and the scatter dose. We evaluated the dose of radiation to the breast, thyroid gland, and lens in digital mammography in women with and without implants, in tomosynthesis in women with and without implants, and in contrast-enhanced mammography.
Materials and methodsThe study included 212 women with and without disease who were attended at the Centro Clínico de Estereotaxia, CECLINES, in Caracas, Venezuela, between June 2017 and August 2017; the women were classified into five groups according to the mammographic modality used to evaluate them and whether or not they had implants. The statistical analysis included descriptive statistics for the study population. We used the Mann-Whitney U to compare the mean glandular dose and dose in the thyroid gland and lens between groups.
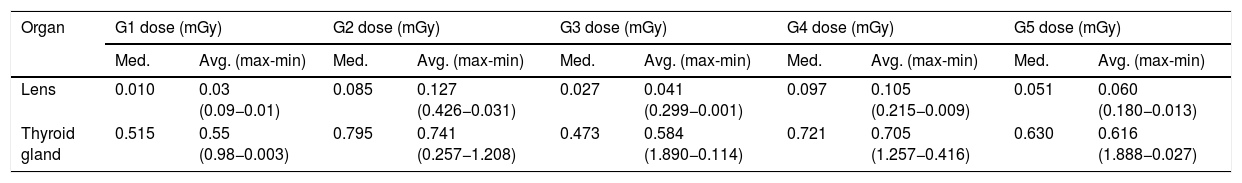
ResultsThe mean glandular dose and the dose of radiation received in the thyroid and lens were within the acceptable range. In a few exceptions, the mean glandular dose per view was slightly higher than 3 mGy. The scatter dose to the thyroid gland and the lens during mammography has a very small contribution to the annual dose equivalent.
ConclusionThe mean glandular dose and the scatter dose to the thyroid gland and lens delivered during tomosynthesis and 2D mammography in women with implants were higher than those delivered during other mammographic techniques in women without implants.
Siempre ha existido preocupación por los efectos secundarios de métodos diagnósticos que utilizan radiaciones ionizantes. Durante una mamografía preocupa la dosis glandular promedio y la dosis de radiación dispersa. Evaluamos la dosis de radiación a la mama, glándula tiroides y cristalino con mamografía digital sin y con implante, tomosíntesis sin y con implante y mamografía con contraste.
Materiales y métodosEl estudio incluyó 212 mujeres sanas y con patología que fueron divididas en 5 grupos dependiendo de la modalidad mamográfica y de la presencia o no de implantes. Acudieron al Centro Clínico de Estereotaxia, CECLINES, en Caracas, Venezuela, entre junio y agosto de 2017. El análisis estadístico contempla una descripción de la población en estudio. Se comparó la dosis glandular promedio y la dosis en glándula tiroides y cristalino entre los grupos, utilizando el estadístico U de Mann Whitney.
ResultadosLa dosis glandular promedio y la dosis de radiación recibida en la glándula tiroides y el cristalino están dentro de los valores aceptables. En pocas excepciones, la dosis glandular promedio por proyección estaba discretamente por encima de los 3 mGy. La radiación dispersa a glándula tiroides y cristalino durante una mamografía tiene una contribución muy pequeña a la dosis anual equivalente.
ConclusiónLas pacientes con implante (tomosíntesis y mamografía 2D) tuvieron la mayor mediana de dosis glandular promedio y dosis a glándula tiroides y cristalino mayor que las modalidades mamográficas sin implantes.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora