To evaluate the need for surgical biopsy in patients diagnosed with radial scars without atypia by percutaneous biopsy.
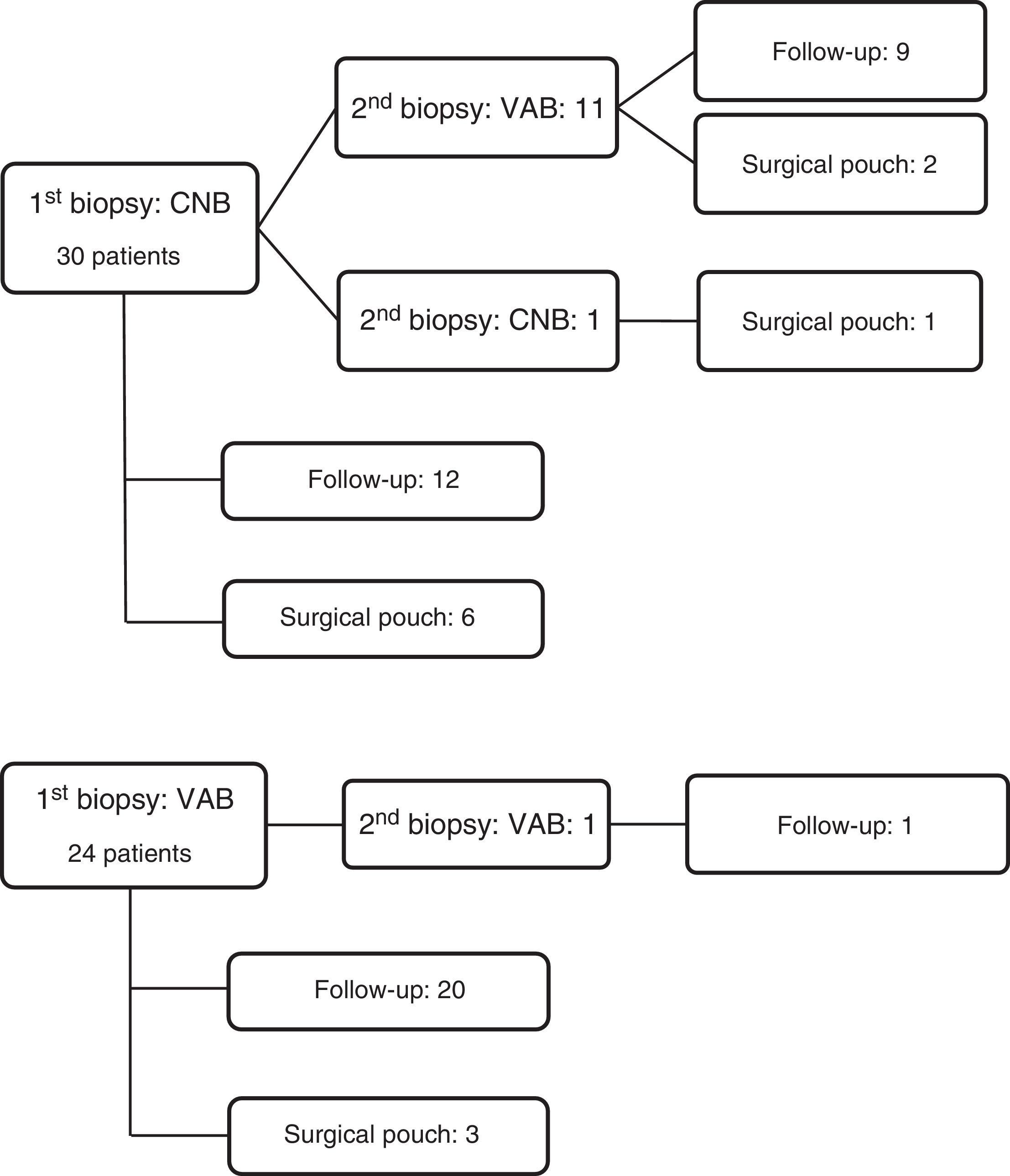
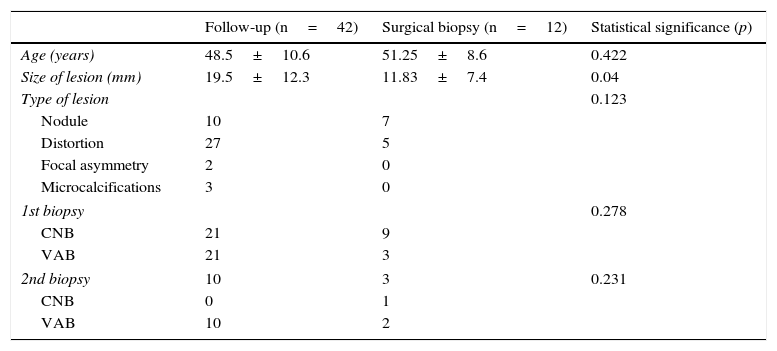
Material and methodsIn this retrospective observational study, we selected patients with a histological diagnosis of radial scar in specimens obtained by percutaneous biopsy during an 8-year period. The statistical analysis was centered on patients with radial scar without atypia (we assessed the radiologic presentation, the results of the percutaneous biopsy, and their correlation with the results of surgical biopsy and follow-up) and we added the patients with atypia and cancer in the elaboration of the diagnostic indices.
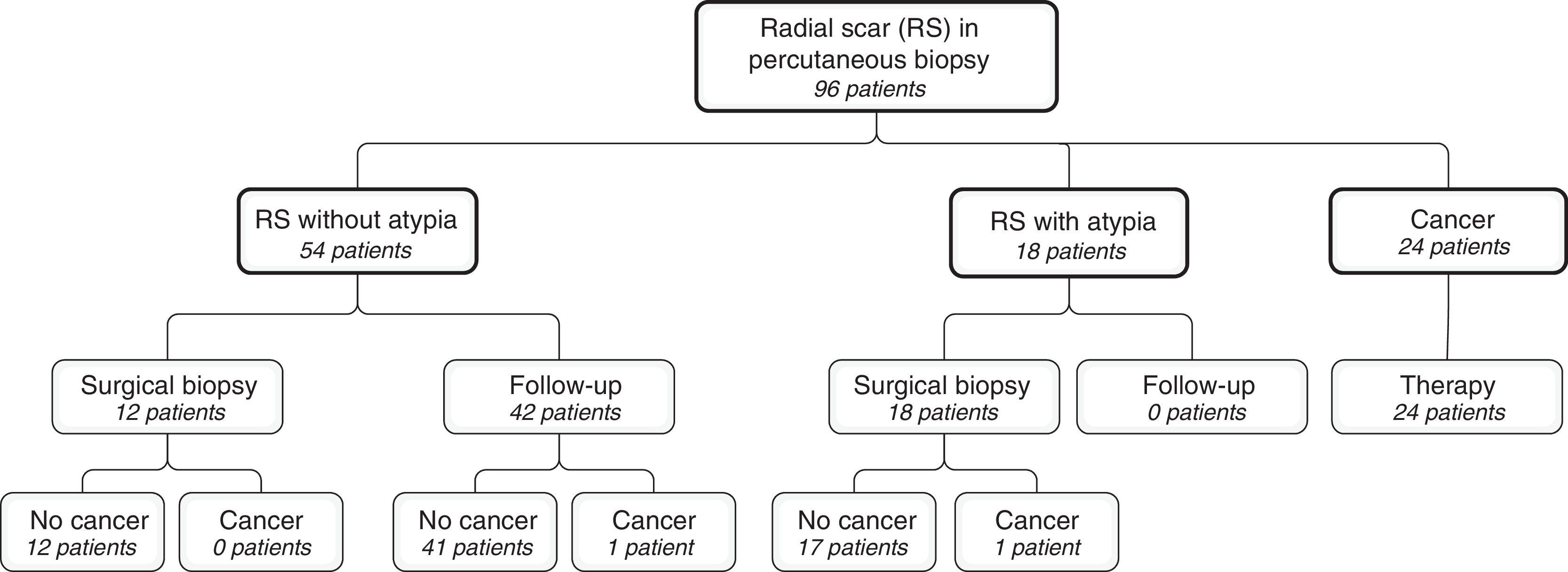
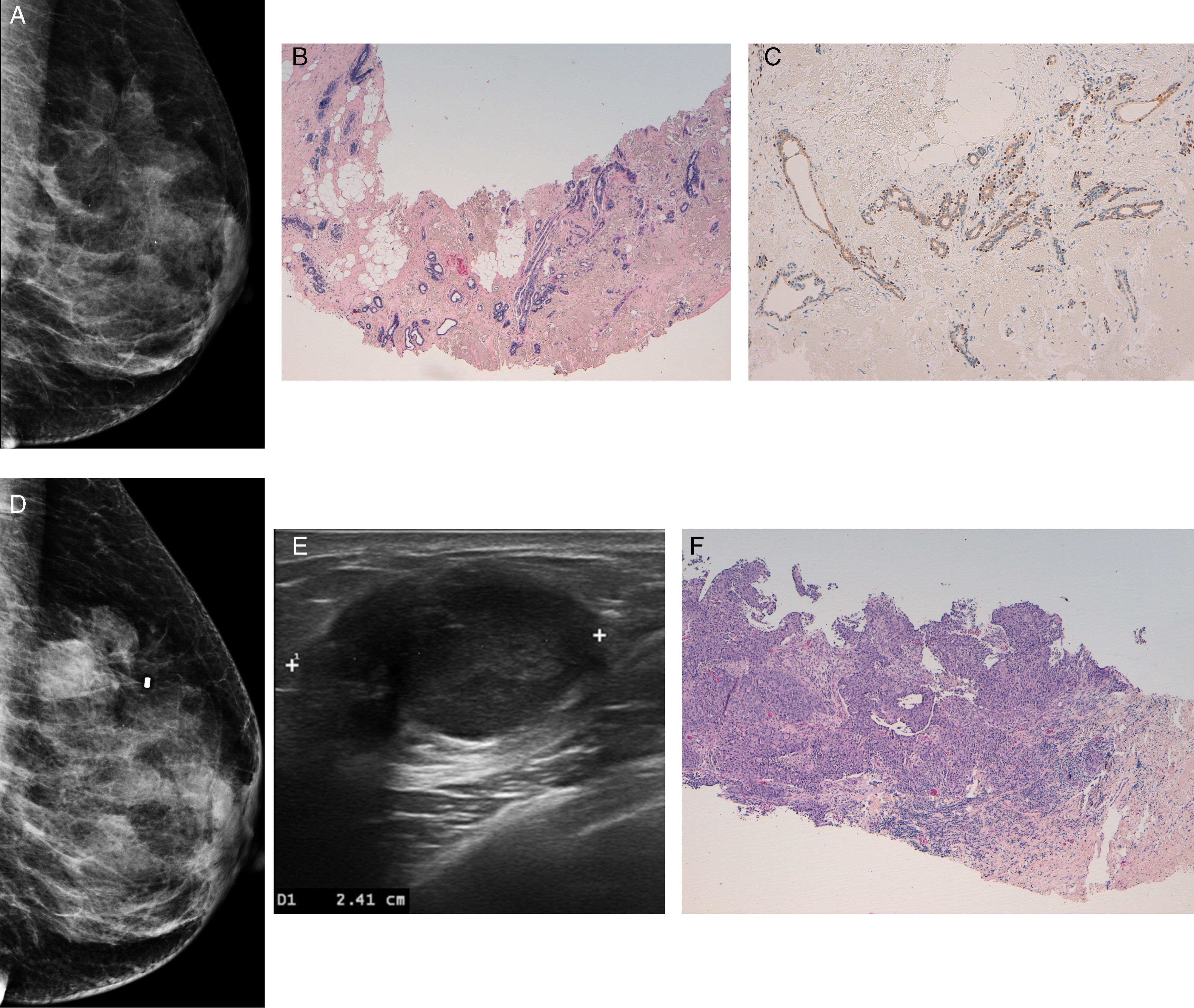
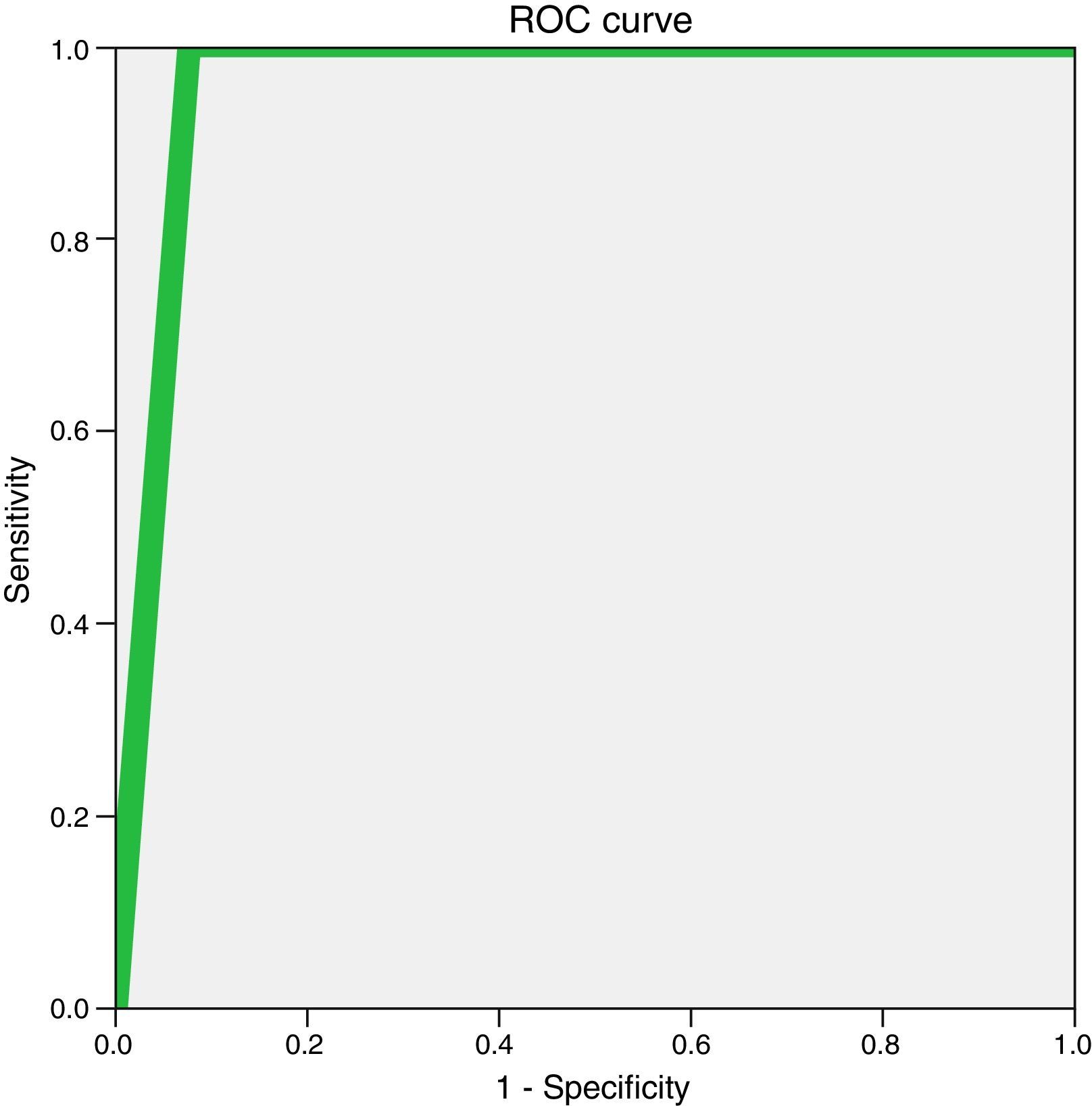
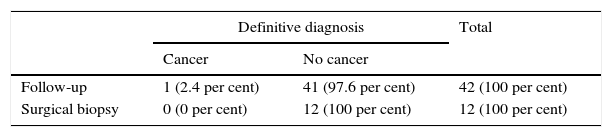
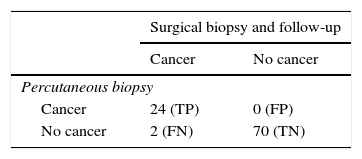
ResultsWe identified 96 patients with radial scar on percutaneous biopsy; 54 had no atypia, 18 had atypia, and 24 had cancer. Among patients with radial scar without atypia, there were no statistically significant differences between patients who underwent imaging follow-up and those who underwent surgical biopsy (p>0.05). The rate of underdiagnosis for percutaneous biopsy in patients without atypia was 1.9 per cent. The rates of diagnosis obtained with percutaneous biopsy in relation to follow-up and surgical biopsy in the 96 cases were sensitivity 92.3 per cent, specificity 100 per cent, positive predictive value 100 per cent, negative predictive value 97.2 per cent, and accuracy 97.9 per cent. The area under the ROC curve was 0.96 (p<0.001), and the kappa concordance index was 0.95 (p<0.001).
ConclusionsWe consider that it is not necessary to perform surgical biopsies in patients with radial scars without atypia on percutaneous biopsies because the rate of underestimation is very low and the concordance between the diagnosis reached by percutaneous biopsy and the definitive diagnosis is very high.
Evaluar la necesidad de biopsia quirúrgica en pacientes diagnosticadas por biopsia percutánea de cicatriz radial sin atipia.
Material y métodosRealizamos un estudio observacional retrospectivo y seleccionamos las pacientes con diagnóstico histológico en biopsia percutánea de cicatriz radial durante un periodo de 8 años. El análisis estadístico principal se centró en pacientes con cicatriz radial sin atipia (valoramos la presentación radiológica, los resultados de la biopsia percutánea y su correlación con la biopsia quirúrgica y seguimiento) y añadimos a las pacientes con atipia y cáncer en la elaboración de índices diagnósticos.
ResultadosIdentificamos 96 pacientes con cicatriz radial en biopsia percutánea. Cincuenta y cuatro no presentaban atipia, 18 asociaban algún tipo de atipia y 24, cáncer. No hubo diferencias estadísticas significativas al comparar las pacientes en seguimiento radiológico con aquellas que se sometieron a biopsia quirúrgica en el grupo sin atipia (p>0,05). La tasa de infraestimación de la biopsia percutánea en pacientes sin atipia fue del 1,9%. Los índices diagnósticos obtenidos para la biopsia percutánea en relación con el seguimiento y la biopsia quirúrgica en los 96 casos fueron: sensibilidad, 92,3%; especificidad, 100%; valor predictivo positivo, 100%; valor predictivo negativo, 97,2%; y exactitud, 97,9%. El área bajo la curva ROC fue de 0,96 (p<0,001) y el índice de concordancia kappa de 0,95 (p<0,001).
ConclusiónConsideramos que no es necesario realizar biopsia quirúrgica en pacientes diagnosticadas de cicatriz radial sin atipia en biopsia percutánea, ya que la tasa de infraestimación es muy baja y existe un elevado grado de concordancia entre la biopsia percutánea y el diagnóstico definitivo.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora