El síndrome de Baxter consiste en una neuropatía por atrapamiento de la primera rama del nervio plantar lateral o calcáneo inferior que cursa con dolor, imposibilidad para la abducción del 5.° dedo y, en algunos casos, parestesias.
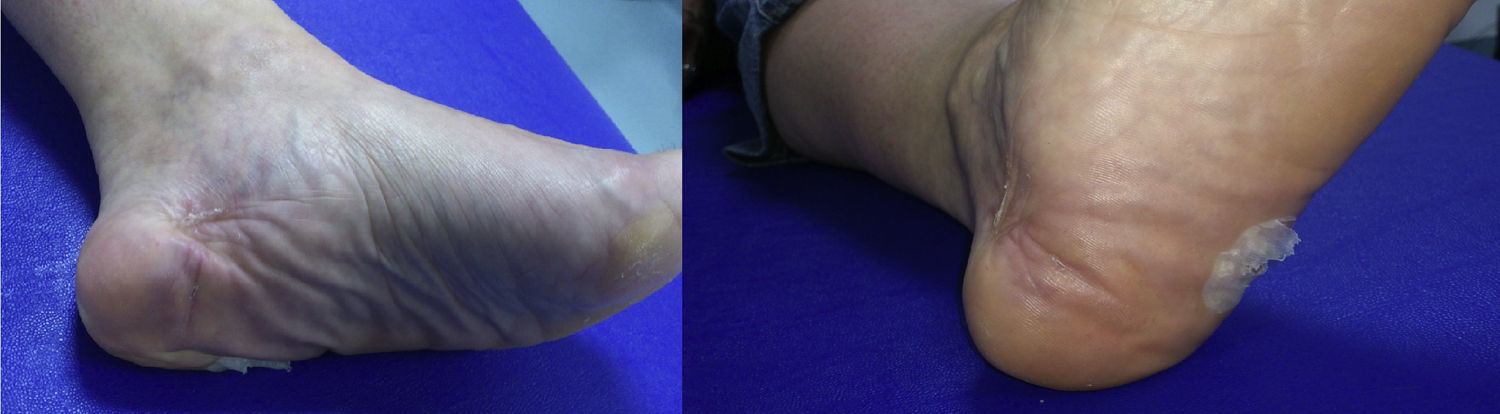
Se presenta el caso de una paciente de 44 años diagnosticada de fascitis plantar, tratada quirúrgicamente con fasciectomía tras el fracaso del tratamiento conservador. Durante el postoperatorio presentó pérdida de la movilidad del 5.° dedo, parestesias difusas y dolor moderado con dificultad para la deambulación.
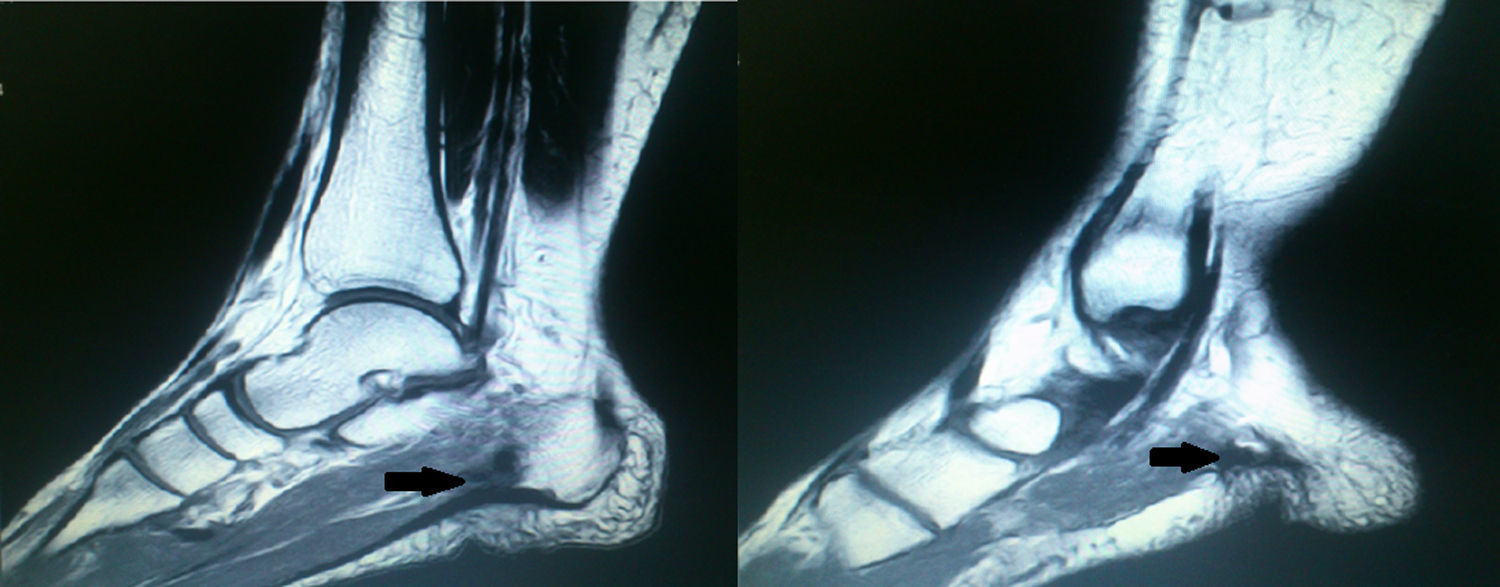
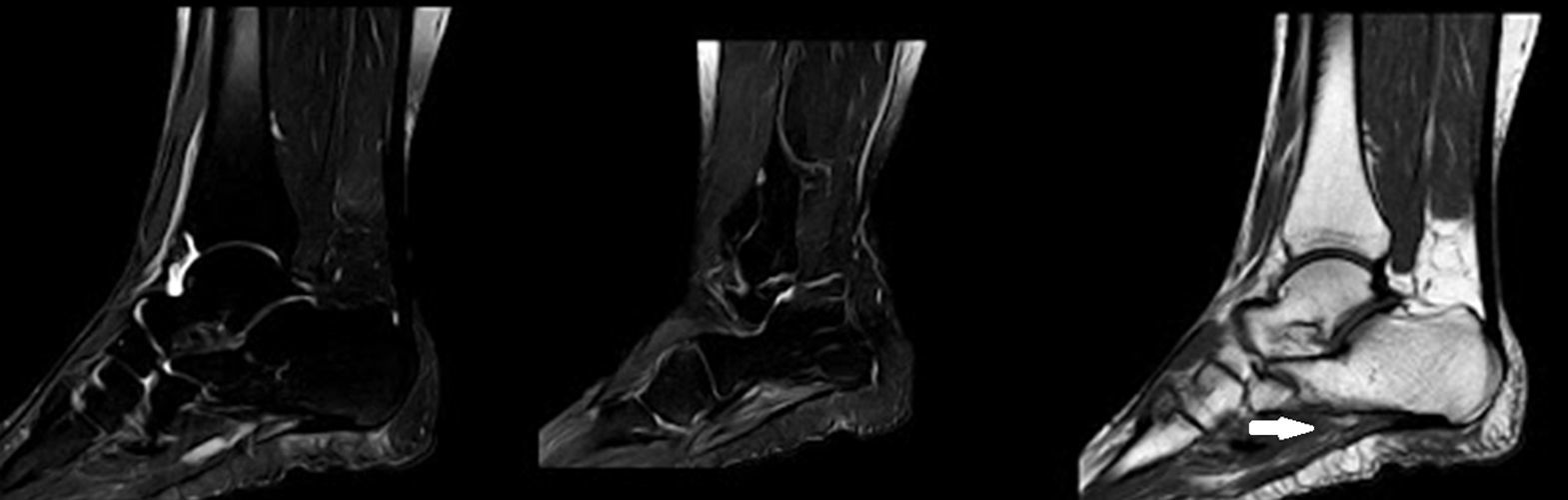
Tras la realización de resonancia magnética y electromiograma es diagnosticada de síndrome de Baxter.
Inició tratamiento de rehabilitación obteniendo mejoría de la alodinia a nivel de la cicatriz y adquirió marcha sin ayudas técnicas, con menor dificultad para puntillas y talones. Sin embargo mantuvo parestesias ocasionales y ausencia de movilidad del 5.° dedo.
Baxter syndrome is an entrapment neuropathy of the first branch of the lateral plantar nerve or inferior calcaneal nerve that causes pain, inability to abduct the fifth toe and, in some cases, paraesthesia.
We report the case of a 44-year-old woman with a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis, treated surgically with fasciectomy after failure of conservative treatment. During the postoperative period, the patient showed loss of mobility of the fifth toe, moderate diffuse pain, numbness, and difficulty walking.
After the performance of magnetic resonance imaging and electromyography, the patient was diagnosed with Baxter syndrome.
She began rehabilitation, which improved allodynia of the scar and allowed her to walk without technical aids and with less difficulty in heel toe walking. However, there was persistence of occasional numbness and lack of mobility of the fifth toe.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora