Spasticity developing in the upper extremity in stroke patients causes disability by limiting movement and causing pain. This study investigates the effects of botulinum toxin injections on pain, functionality, spasticity, and range of motion in hemiplegic patients with post-stroke spasticity.
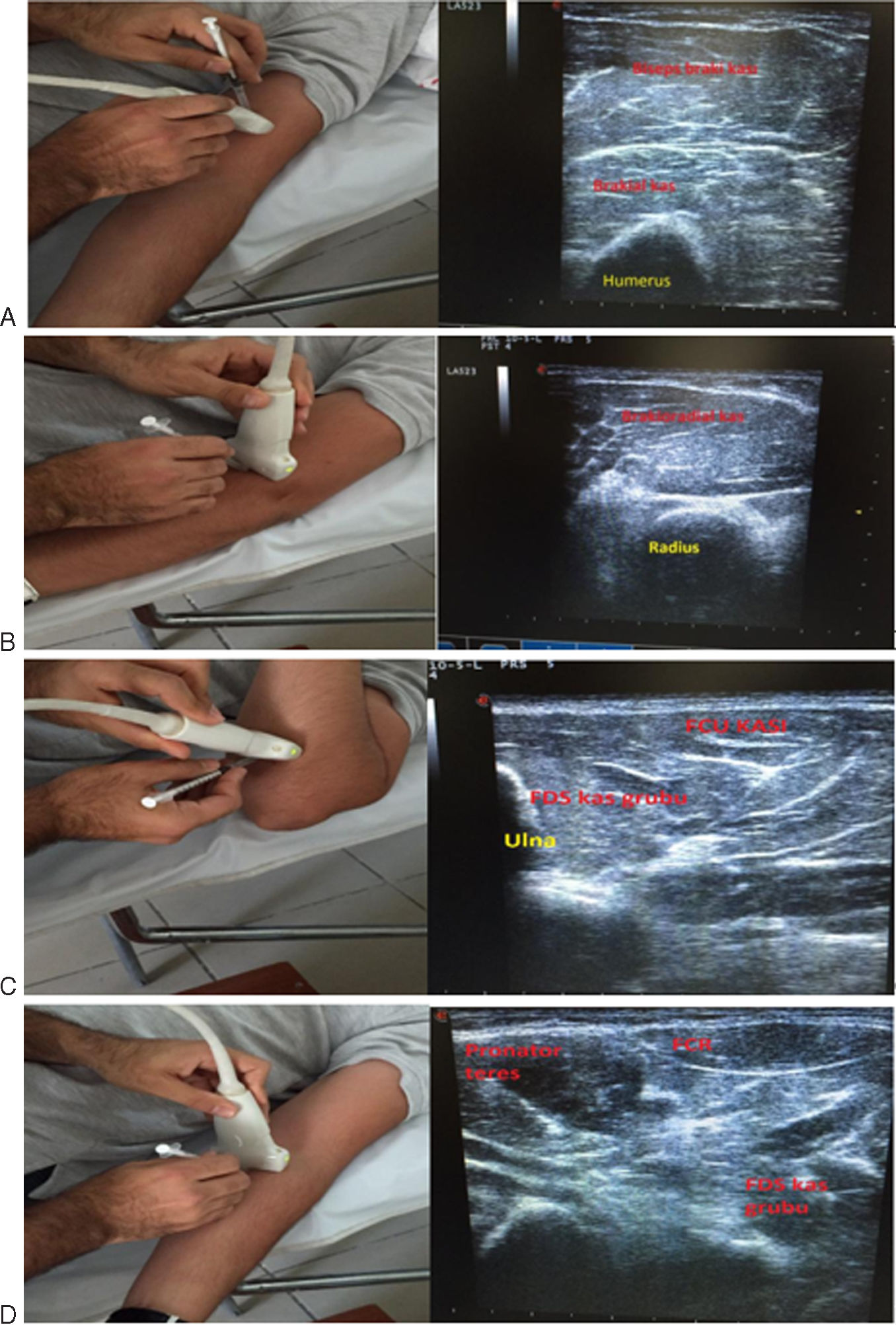
Materials and methodsThe study involved a double-blind, prospective, randomized controlled trial with thirty-one stroke patients aged 35–80 who developed upper extremity spasticity. The study group (n=16) received botulinum toxin-A (BT-A) injections in addition to conventional rehabilitation and stretching exercises, while the control group (n=15) received placebo injections. Evaluations were conducted before treatment, in the second week, and three months after treatment. The study evaluated pain relief through the Visual Analog Scale (VAS), assessed spasticity with the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), and measured functionality using the Fugl Meyer Assessment Scale (FMAS) and the Box Block Test (BBT).
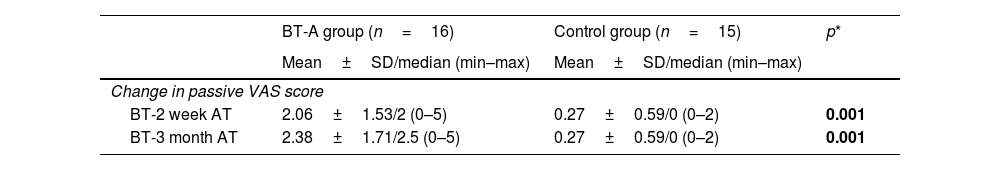
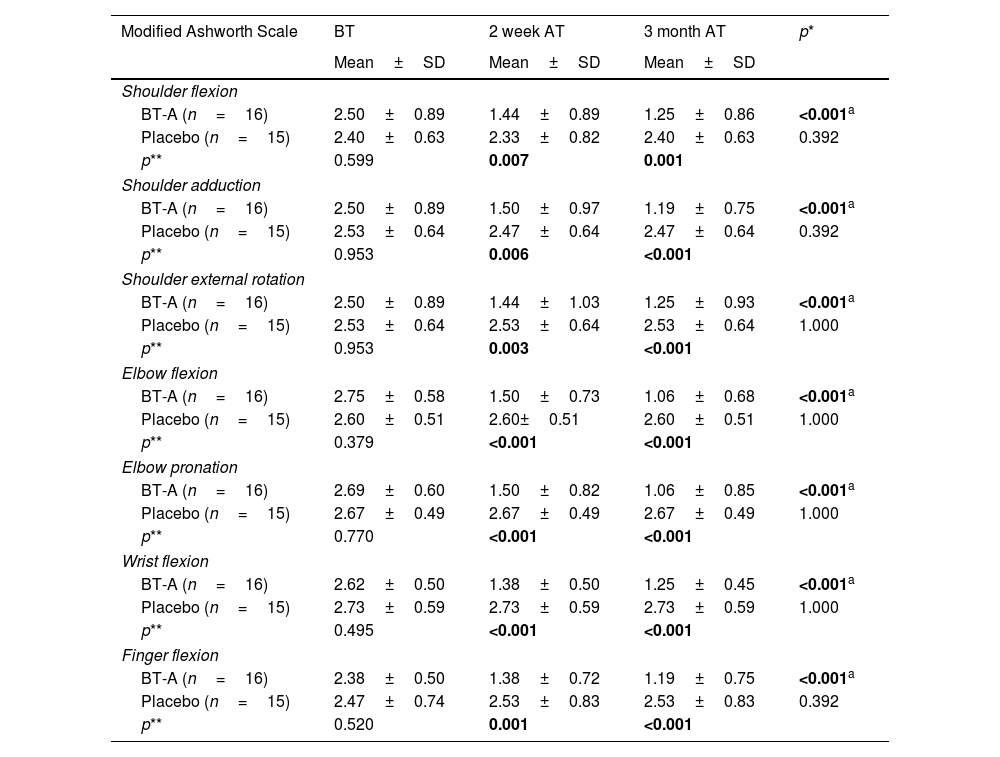
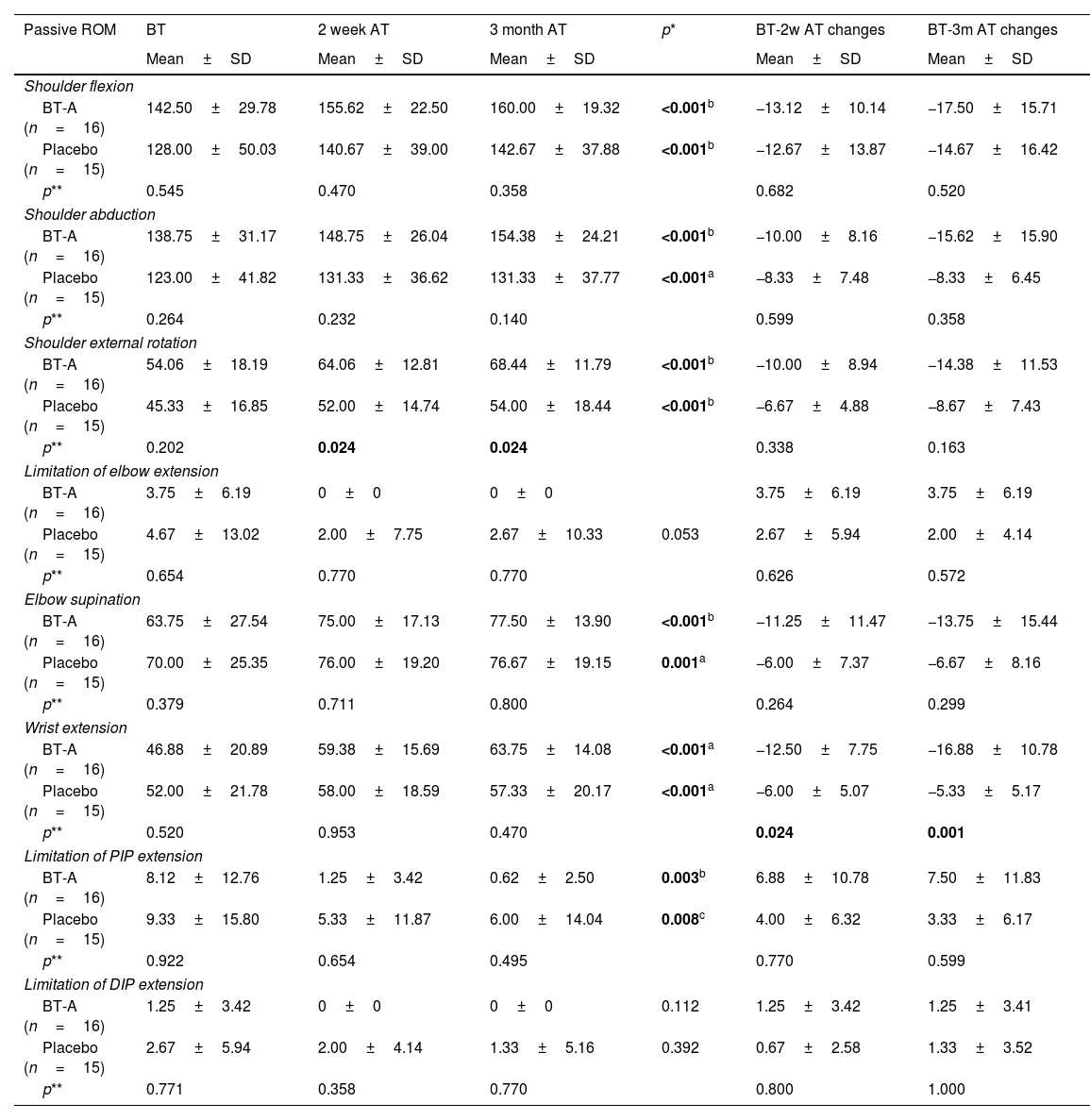
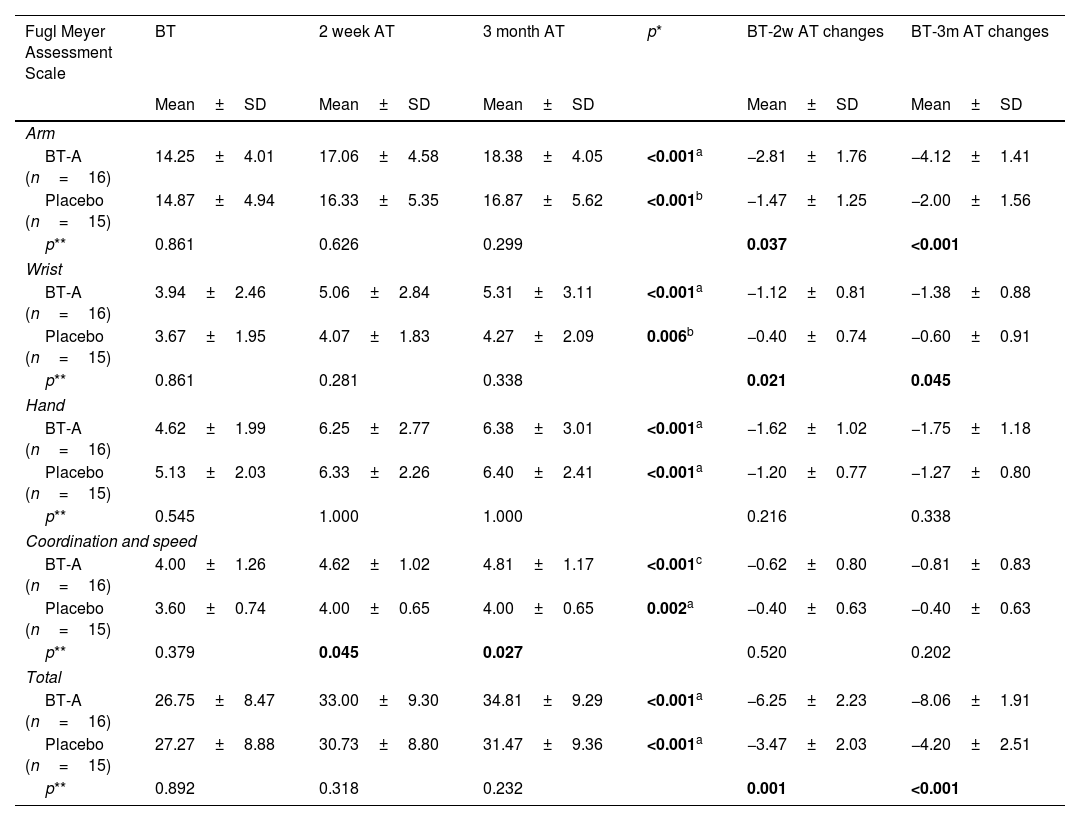
ResultsThe mean age of patients was 56.03±11.81. The median time after stroke was 24 months. The BT-A group demonstrated significantly lower VAS and MAS scores compared to controls at both 2 weeks and 3 months after treatment. Additionally, the BT-A group showed significantly higher changes in arm, wrist, and total FMAS scores compared to the control group. However, no significant difference was found in terms of hand, coordination, and speed FMAS score changes.
ConclusionsThe results of our study demonstrated that BT-A injection with ultrasonography guidance is an effective method for alleviating pain caused by passive shoulder movement, significantly reducing spasticity, and markedly improving motor functions.
La espasticidad que se desarrolla en la extremidad superior en pacientes con ictus causa discapacidad al limitar el movimiento y provocar dolor. Este estudio investiga los efectos de las inyecciones de toxina botulínica sobre el dolor, la funcionalidad, la espasticidad y la amplitud de movimiento en pacientes hemipléjicos con espasticidad postictus.
Materiales y métodosEl estudio consistió en un ensayo doble ciego, prospectivo, aleatorizado y controlado con 31 pacientes con ictus de entre 35 y 80 años que desarrollaron espasticidad en las extremidades superiores. El grupo de estudio (n=16) recibió inyecciones de toxina botulínica (BT-A) además de rehabilitación convencional y ejercicios de estiramiento, mientras que el grupo de control (n=15) recibió inyecciones de placebo. Se realizaron evaluaciones antes del tratamiento, en la segunda semana y 3 meses después del tratamiento. El estudio evaluó el alivio del dolor mediante la Escala analógica visual (EAV), valoró la espasticidad con la Escala de Ashworth modificada (EAM) y midió la funcionalidad mediante la Escala de valoración de Fugl Meyer (FMAS) y el Test de box block (BBT).
ResultadosLa edad media de los pacientes fue de 56,03±11,81 años. La mediana de tiempo tras el ictus fue de 24 meses. El grupo BT-A mostró puntuaciones significativamente más bajas en la EAV y la EAM en comparación con los controles, tanto a las 2 semanas como a los 3 meses después del tratamiento. Además, el grupo BT-A mostró cambios significativamente mayores en las puntuaciones de brazo, muñeca y FMAS total en comparación con el grupo de control. Sin embargo, no se encontraron diferencias significativas en cuanto a los cambios en las puntuaciones FMAS de mano, coordinación y velocidad.
ConclusionesLa inyección de BT-A con guía ecográfica puede aliviar eficazmente el dolor causado por el movimiento pasivo del hombro, reducir significativamente la espasticidad y mejorar en gran medida las funciones motoras.