We present two groups of cases of atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) caused by Coxsackievirus A6 (CV-A6) detected in Argentina in 2015. The first group involved 14 patients from Chubut province and the second group affected 12 patients from San Luis province. Molecular analysis of the complete VP1 protein gene revealed the circulation of E2 sublineage, the most predominant worldwide. To our knowledge, this is the first report of CV-A6 infections associated with atypical HFMD in Argentina and South America.
Se describen dos grupos de casos de enfermedad de mano-pie-boca (HFMD) atípica causada por el virus Coxsackie A6 (Coxsackievirus A6, CV-A6) detectados en Argentina en el año 2015. El primero de los grupos involucró a 14 pacientes de Chubut y el segundo a 12 pacientes de San Luis. El análisis molecular del gen de la proteína VP1 completa reveló la circulación del sublinaje E2, el predominante a nivel global. Hasta donde sabemos, este es el primer reporte de infecciones CV-A6 asociadas con HFMD atípica en Argentina y Sudamérica.
Classical hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is an acute febrile infection characterized by vesicular exanthema on the palmsor soles and oral mucosa, typically occurring in young children and infants. More than 90% of HFMD cases are caused by Enterovirus A71 (EV-A71) and Coxsackievirus A16 (CV-A16), both members of Enterovirus A species (EV-A), Picornaviridae family. However, sporadic cases of the atypical form of HFMD can also be caused by other EV-A viruses19. We present two groups of atypical HFMD cases caused by Coxsackievirus A6 (CV-A6) detected in Argentina in 2015.
The first group of 14 cases was reported in Chacay Oeste (a rural population of 89 inhabitants in Chubut province) between September 2nd 2015 and October 1st 2015. All patients were treated at the Gan Gan Rural Hospital, Chubut. The Department of Epidemiology of the province of Chubut reported the cases. Patients presented with fever with 48h of evolution and the characteristic vesiculobullous and erosive eruption, which primarily affected palms and soles. To a lesser extent, the rash affected the folds of the large joints, cheeks, perianal region and in some cases the whole body. Several patients presented onychomadesis on the fingernails. The second group cases occurred in General San Martín, San Luis province, a town with a population of 697 inhabitants. Twelve cases of atypical HFMD were reported between November 11th 2015 and November 22nd 2015 through the National System of Epidemiological Surveillance of measles and rubella. Initially, the patients were screened for these viral agents, being all the patients negative.
A total of eight stool samples from the 14 patients in Chubut and six from the 12 patients in San Luis were obtained. Viral RNA was extracted from stool suspensions using the QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). After that, a generic PCR for enterovirus detection was performed as previously described4. For the positive enterovirus cases, we used primer pairs 222/224 and 88/89 for partial VP1 sequencing for the identification of the enterovirus type. We subjected the sequences to BLAST search (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST) and defined the virus type using the criteria of ≥75% nucleotide and ≥85% amino acid similarity in the VP1 region15. A complete VP1 gene of representative strains of both groups was obtained using nested primers specific for CV-A6 as previously described18. Moreover, the isolation of human enteroviruses in the human rhabdomyosarcoma (Rd) cell line was attempted for all specimens17.
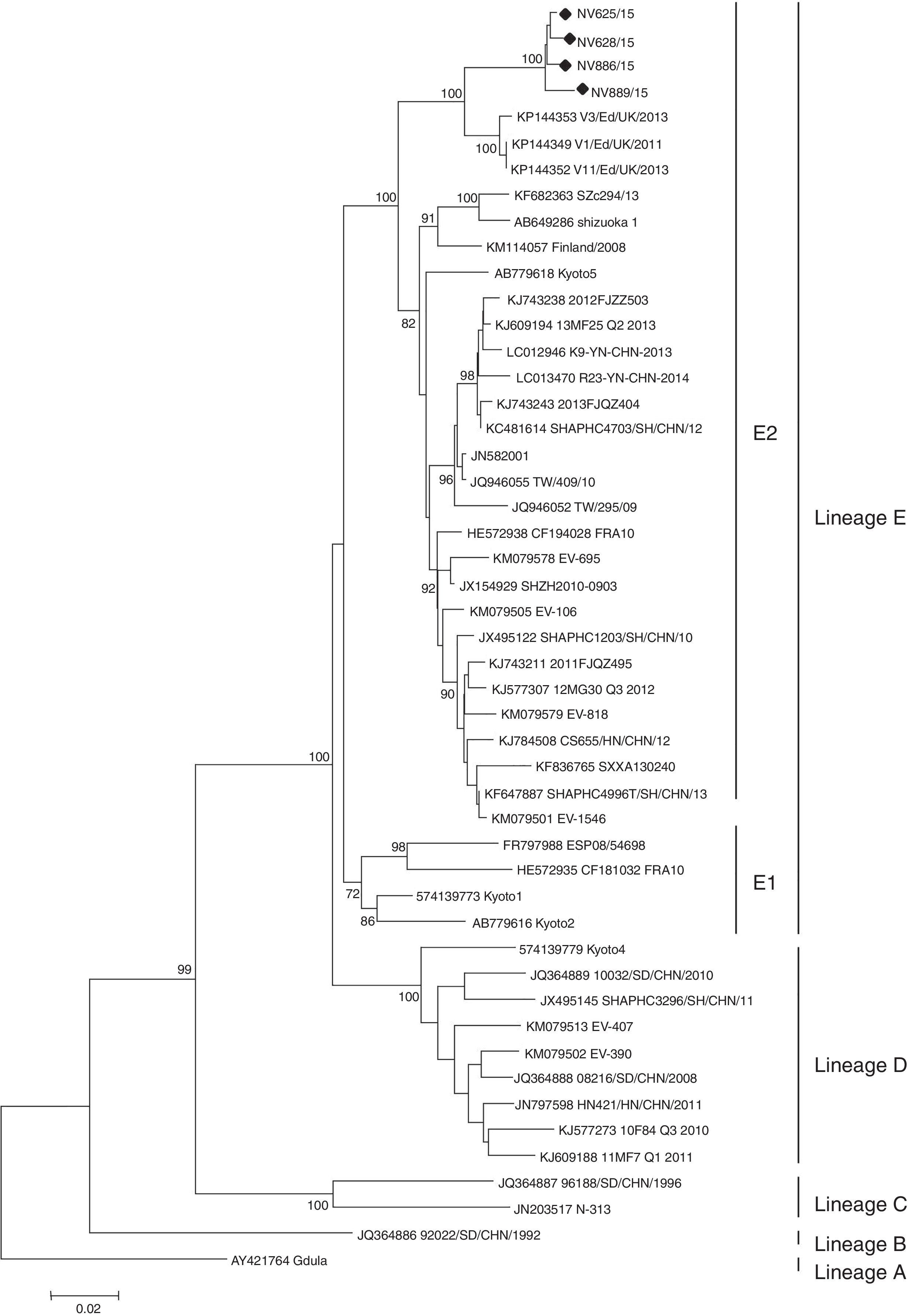
Enteroviruses were detected in five (62.5%) of eight patients from Chubut and in four (66.7%) of six patients from San Luis. CV-A6 was identified in all enterovirus-positive samples. No virus was isolated in any of the samples tested. Partial sequencing of VP1 (position 2560–2865, based on strain Gdula, GenBank accession No. AY421764) of the nine strains detected showed a high nucleotide similarity between them (99.1–99.7%), which suggests that both groups of cases are related. Phylogenetic analysis of the complete VP1 gene shows that CV-A6 strains are grouped into five lineages (A–E), with two sublineages E1 and E22. In our study, it was possible to obtain complete VP1 sequences of four strains (two from each cluster), which revealed that they belong to the E2 lineage (Fig. 1). This information is consistent with the latest notifications that showed that strains of the sublineage E2 are predominant worldwide2,10.
Phylogenetic tree of the complete VP1 gene of Argentinean Coxsackievirus A6 strains from atypical hand, foot and mouth disease, 2015. For lineage classification, other selected strains from GenBank were included (accession numbers are given in the phylogenetic tree). The maximun likehood method was used to construct the tree using MEGA version 6.0 (https://www.megasoftware.net). The phylogenetic tree was determined for 1000 replicates with random seeds. Only strong bootstrap values (>70%) were shown; (black dot) indicates Argentinean strains (GenBank accession No. KX575862-65).
HFMD outbreaks caused by CV-A6 have been reported in Singapore (2009), Taiwan (2009–2010), Japan (2011), Thailand (2012) and China (2013). In North America, CV-A6-associated HFMD outbreaks were reported in the USA and Cuba from 2011 to 20132. In Europe, CV-A6 was responsible for HFMD outbreaks in Finland, France and Spain from 2009 to 20113,13 and more recently in Edinburgh, United Kingdom, in 2011–201318. Argentinean CV-A6 strains show 95.5% similarity to strains detected in Scotland, suggesting a European source.
Classical HFMD has the highest incidence in infants and children. However, during the outbreak of atypical HFMD in Finland in 2008, a high incidence in adults was notified16. In Europe and North America, no significant differences in age were found among the CV-A6 cases. In our patients, the age range in Chacay Oeste and General San Martín was 2–28 years (average=10.1) and 1–58 years (average=12.2) respectively. We observed a wide age distribution although it would be necessary to study a larger population to estimate the real impact of this virus infection.
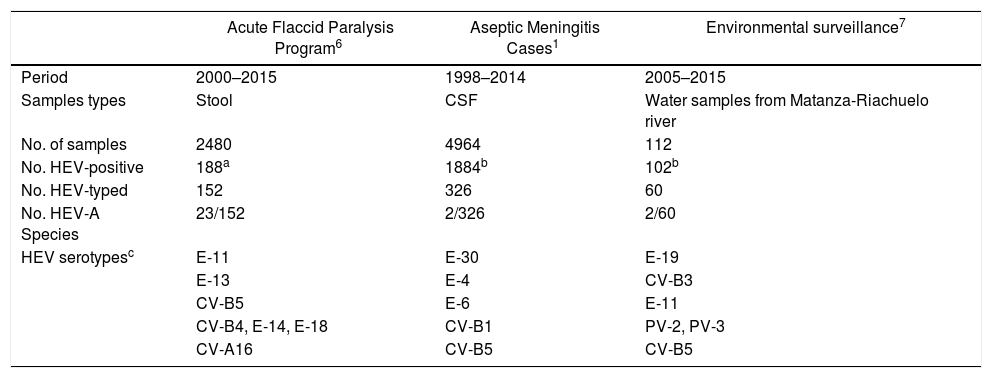
In this study, it was not possible to investigate material obtained from vesicular lesions and only stool samples were available. No virus was isolated in any of the samples tested possibly because Coxsackie A viruses are difficult to recover in cell culture systems11. In Argentina, there is no active public health surveillance for HFMD and it is not a notifiable disease. Studies conducted in patients with meningitis, sepsis and in environmental samples in our country highlight the predominant role of Enterovirus B species (EV-B), mainly represented by Echovirus 30 (E-30), E-9, E-14, E-6, E-16, CV-A9 and CV-B1-38,9,14. Epidemiological information generated in our laboratory confirms that the circulation of EV-A is poorly detected (Table 1). Consequently, CV-A6 infections are probably underdiagnosed as a result of the lack of active public health surveillance for HFMD. Finally, the understanding of the variability of this atypical form of HFMD should help to avoid confusion with other skin conditions such as eczema herpeticum or chickenpox5,12. In patients with non-specific clinical manifestations, it is important to rule out the presence of enteroviruses, which would avoid unnecessary treatment with acyclovir and possible hospitalization.
Detection and typing of human enterovirus serotypes from Argentina
| Acute Flaccid Paralysis Program6 | Aseptic Meningitis Cases1 | Environmental surveillance7 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Period | 2000–2015 | 1998–2014 | 2005–2015 |
| Samples types | Stool | CSF | Water samples from Matanza-Riachuelo river |
| No. of samples | 2480 | 4964 | 112 |
| No. HEV-positive | 188a | 1884b | 102b |
| No. HEV-typed | 152 | 326 | 60 |
| No. HEV-A Species | 23/152 | 2/326 | 2/60 |
| HEV serotypesc | E-11 | E-30 | E-19 |
| E-13 | E-4 | CV-B3 | |
| CV-B5 | E-6 | E-11 | |
| CV-B4, E-14, E-18 | CV-B1 | PV-2, PV-3 | |
| CV-A16 | CV-B5 | CV-B5 |
E: Echovirus, CV: Coxsackievirus, PV: Poliovirus.
To our knowledge, this is the first report of CV-A6 infections associated with atypical HFMD in Argentina and South America. This information could be useful to establish an adequate surveillance system for enteroviral disease to implement more appropriate public health interventions.
FundingThis work was supported by INEI-ANLIS “Dr. Carlos G. Malbrán”, Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
We thank to Gabriela Elbert, DiNaCEI, Ministerio de Salud de la Nación for collecting cases from San Luis province.