Although the transradial approach had significantly reduced vascular complications, studies have demonstrated that it may be related to higher radiation exposure. The objective of this study is to compare radiation exposure in invasive cardiologic procedures using the transradial and transfemoral approaches.
MethodsProspective cohort study including patients undergoing diagnostic cardiac catheterization or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) between August 2010 and December 2011. Clinical, angiographic and radiation exposure characteristics were recorded in a dedicated database. Patients were analyzed according to the access route: femoral or radial.
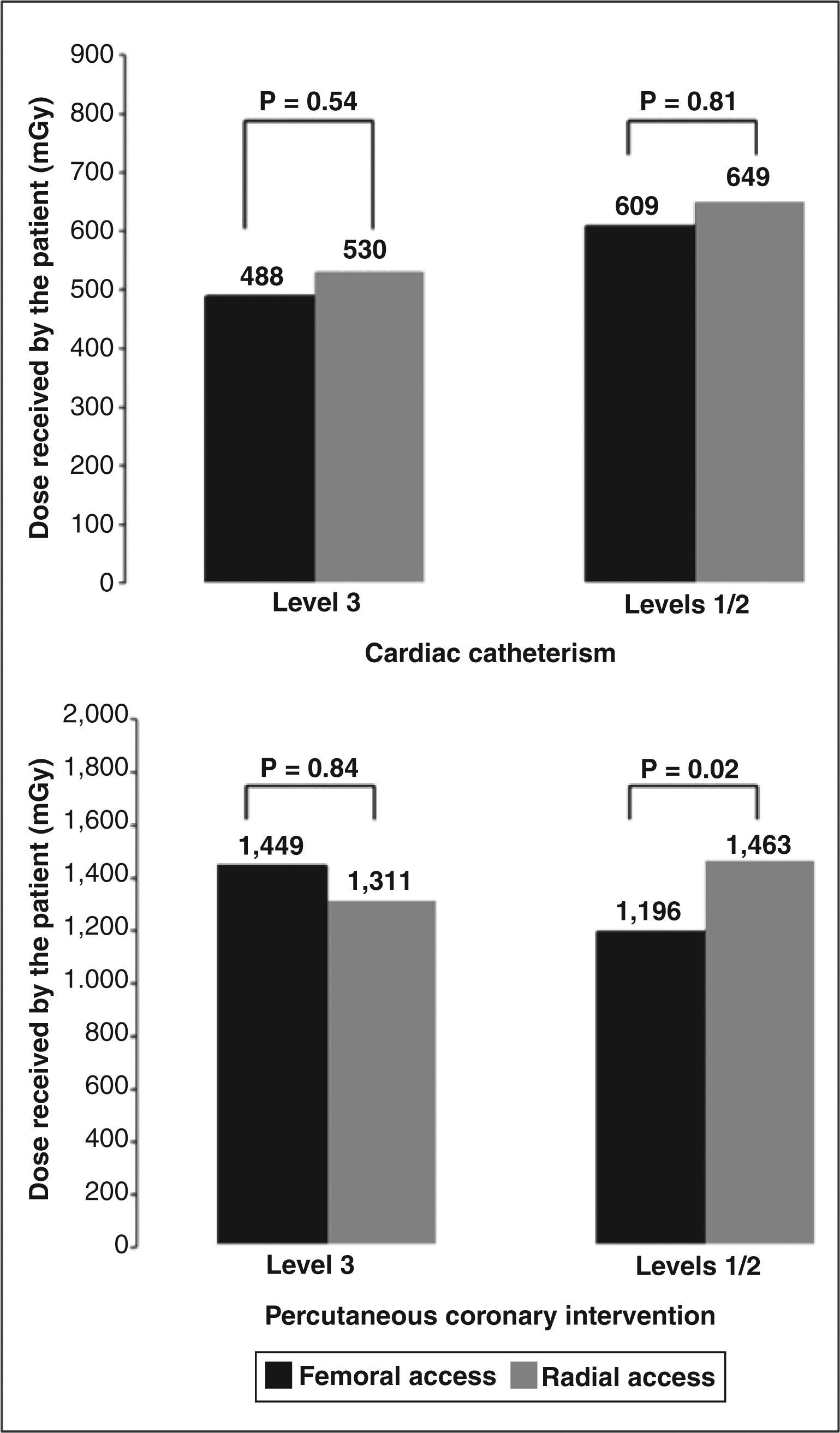
ResultsOf the 1,197 patients included in the study, 782 were submitted to procedures using the femoral access and 415 using the radial access. There was a lower prevalence of females (36.2% vs. 45.6%; P < 0.01), previous coronary artery bypass graft surgery (4% vs. 12.7%; P < 0.01) and severe valvular heart disease (0.3% vs. 1.4%; P=0.07) in the radial group. The median radiation dose received by the patients was higher with the radial approach, both for diagnostic (621.6mGy vs 445.7mGy; P < 0.01) and therapeutic procedures (1,241.6mGy vs 990.9mGy; P < 0.01). Less experienced operators in the radial approach exposed patients to higher radiation doses (1,463mGy vs 1,196mGy; P=0.02), which did not occur with the more experienced operators (1,311mGy vs 1,449mGy; P=0.84).
ConclusionsPatients undergoing invasive cardiologic procedures are exposed to higher radiation levels when the radial access is used. However, experienced operators may neutralize this disadvantage.
Exposição Radiológica em ProcedimentosCoronários Realizados pelas Vias Radial e Femoral
IntroduçãoEmbora a abordagem transradial tenha reduzido as complicações vasculares, estudos demonstram que pode estar relacionada a maior exposição radiológica. É objetivo deste estudo comparar os parâmetros de exposição radiológica em procedimentos cardiológicos invasivos pelos acessos radial e femoral.
MétodosEstudo de coorte prospectiva incluindo pacientes submetidos a cateterismo cardíaco diagnóstico ou intervenção coronária percutânea (ICP) entre agosto de 2010 e dezembro de 2011. Características clínicas, angiográficas e de exposição à radiação foram registradas em banco de dados específico. Os pacientes foram analisados de acordo com a via de acesso: femoral ou radial.
ResultadosForam incluídos 1.197 pacientes, 782 submetidos a procedimentos por via femoral e 415, a procedimentos por via radial. Observou-se menor prevalência de pacientes do sexo feminino (36,2% vs. 45,6%; P < 0,01), cirurgia de revascularização miocárdica prévia (4% vs. 12,7%; P < 0,01) e valvulopatia grave (0,3% vs. 1,4%; P=0,07) no grupo radial. A mediana da dose de radiação recebida pelos pacientes foi maior com a utilização da via radial, tanto para procedimentos diagnósticos (621, 6mGy vs. 445,7mGy; P < 0,01) como terapêuticos (1.241, 6mGy vs. 990,9mGy; P < 0,01). Operadores menos experientes no acesso radial expuseram pacientes a maior dose de radiação nas ICPs (1.463mGy vs. 1.196mGy; P=0,02), o que não ocorreu com os mais experientes (1.311mGy vs. 1.449mGy; P=0,84).
ConclusõesPacientes submetidos a procedimentos cardiológicos invasivos são expostos a níveis maiores de radiação pela via de acesso radial. No entanto, operadores experientes podem neutralizar essa desvantagem em relação à via femoral.
Since its introduction into interventional cardiology, 1,2 the use of the radial access has grown steadily in recent years.3 The advantages of the radial access route include lower rates of bleeding and vascular complications,4-8 as well as more comfort for patients, with a significant reduction in hospital costs and length of hospitalization.9 Some studies have even shown a reduction in mortality in certain subgroups of patients.10,11 Therefore, the radial access route is considered by some as the standard strategy for certain cardiac procedures.12,13
However, concerns about possible increased exposure to radiation with the radial access still exist, 14 and contradictory results have been reported.15-19 These studies demonstrate that the radial approach can increase the radiation dose received by both patients and interventionists.14,20 Given the continuing concerns related to ionising radiation, this may be a limitation of the radial access technique.
Thus, the present study aimed to evaluate the radiological exposure when using the radial and femoral access routes in a real-world population, subjected to diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
METHODSDesignThis was an observational study.
Study populationPatients referred for diagnostic cardiac catheterization or percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) were followed to record the radiological exposure patterns. Data on the clinical profile of patients were collected and prospectively analyzed. All patients signed an informed consent, and the protocol was approved by the local ethics and research committee.
Transradial and transfemoral proceduresThe procedures were performed by different surgeons, regardless of the access route. The choice of arterial access was made at the surgeon’s discretion, as well as the type of catheter, type of view used, and the number of radiographies. The procedures for both radial and femoral approaches followed the current guidelines. After the procedures, hemostasis of the radial artery was performed by Tensoplast® (BSN Medical Pty Ltd. – Pinetown, South Africa) pressure dressing. In femoral procedures, hemostasis was performed by manual compression.
Radiological exposure parametersThe radiological exposure of patients was measured by the amount of incoming radiation on the skin (cumulative air KERMA [Kinetic Energy Released per unit MAss]). Additionally, fluoroscopy time, number of frames and frames per radiography, and analysis of the dose-area product were measured to determine time of radiological exposure and the irradiated area.
Procedures were performed using Philips Allura Xper FD10 monoplane equipment (Einthoven, Netherlands), three lenses (15cm, 20cm, and 25cm), double filter (copper and aluminium), with standard programming for image acquisition at a rate of 15 frames per second.
Radiation overexposure was defined as total dose≥2Gy at the end of the procedure.
Statistical AnalysisData were prospectively collected and stored in a specific database using the ACCESS software. SPSS for Windows version 18.0 was used for the analysis.
Results were shown as mean and standard deviation, median and interquartile range, and percentage. The chi-squared test, Student’s t-test, and the Mann-Whitney test were used for comparison. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05 (two-tailed).
RESULTSBetween August 2010 and December 2011, a total of 1,197 invasive cardiological procedures were performed; 415 by radial and 782 by femoral access.
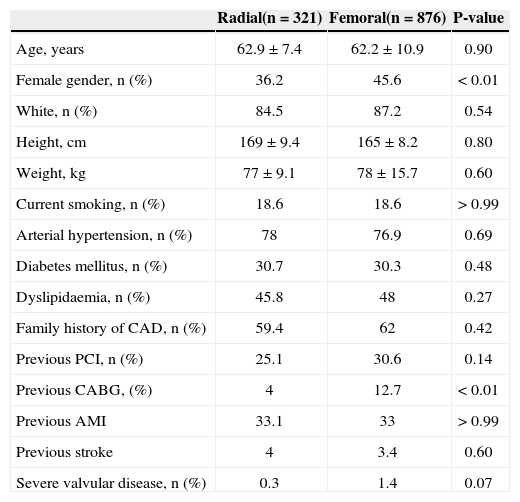
In general, the clinical profile was similar between the groups, but patients undergoing transradial procedures showed lower prevalence of female patients (36.2% vs. 45.6%; P < 0.01), previous coronary artery bypass grafting (4% vs. 12.7%; P < 0.01), or severe valvular disease (0.3% vs. 1.4%; P=0.07) (Table 1).
Characteristics of patients submitted to diagnostic and therapeutic procedures
| Radial(n=321) | Femoral(n=876) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 62.9±7.4 | 62.2±10.9 | 0.90 |
| Female gender, n (%) | 36.2 | 45.6 | < 0.01 |
| White, n (%) | 84.5 | 87.2 | 0.54 |
| Height, cm | 169±9.4 | 165±8.2 | 0.80 |
| Weight, kg | 77±9.1 | 78±15.7 | 0.60 |
| Current smoking, n (%) | 18.6 | 18.6 | > 0.99 |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 78 | 76.9 | 0.69 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 30.7 | 30.3 | 0.48 |
| Dyslipidaemia, n (%) | 45.8 | 48 | 0.27 |
| Family history of CAD, n (%) | 59.4 | 62 | 0.42 |
| Previous PCI, n (%) | 25.1 | 30.6 | 0.14 |
| Previous CABG, (%) | 4 | 12.7 | < 0.01 |
| Previous AMI | 33.1 | 33 | > 0.99 |
| Previous stroke | 4 | 3.4 | 0.60 |
| Severe valvular disease, n (%) | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.07 |
CAD, coronary artery disease; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; AMI, acute myocardial infarction.
Of the 782 patients undergoing diagnostic cardiac catheterization, 222 underwent the procedure by radial and 560 by femoral access route.
The fluoroscopy time (5.4±4.2min vs. 4.3±3.3minutes; P=0.001) was higher in the radial access group, but with a smaller number of radiographies (11±3 vs. 16±4; P=0.04). The total number of frames (778±228 vs. 736±169; P=0.08) and frames per radiography (81.2±14 vs. 91.2±24; P=0.14) were similar in radial and femoral access groups, respectively.
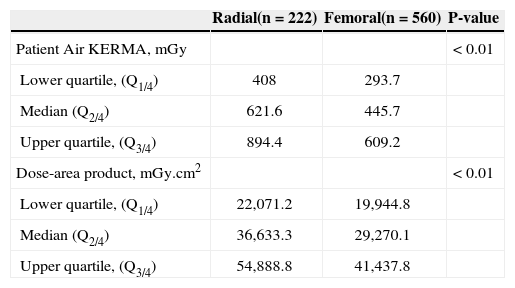
When analyzing the parameters of radiation exposure, it was observed that the medians of radiation dose on the skin (radial 621.6mGy vs. femoral 445.7mGy) and the dose-area product (radial 36,633.3mGy.cm2 vs. femoral 29,271.0mGy.cm2) were higher (P < 0.01) in patients submitted to radial access examination (Table 2).
Radiological exposure of patients submitted to diagnostic procedures
| Radial(n=222) | Femoral(n=560) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Air KERMA, mGy | < 0.01 | ||
| Lower quartile, (Q1/4) | 408 | 293.7 | |
| Median (Q2/4) | 621.6 | 445.7 | |
| Upper quartile, (Q3/4) | 894.4 | 609.2 | |
| Dose-area product, mGy.cm2 | < 0.01 | ||
| Lower quartile, (Q1/4) | 22,071.2 | 19,944.8 | |
| Median (Q2/4) | 36,633.3 | 29,270.1 | |
| Upper quartile, (Q3/4) | 54,888.8 | 41,437.8 |
KERMA, Kinetic Energy Release per unit Mass.
Of the 415 patients submitted to PCI, 99 patients underwent the procedure through radial and 316 by femoral approach.
PCI was performed in different clinical scenarios in both groups (P=0.02): elective PCI (55.5% radial vs. 55% femoral), PCI in acute coronary syndromes without ST-segment elevation (43.4% radial vs. 34.1% femoral), and primary PCI (radial 1.1% vs. femoral 10.9%).
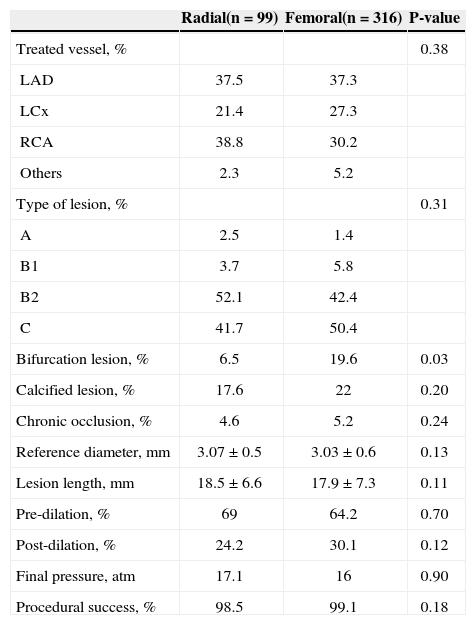
The procedural characteristics and angiographic characteristics of the treated lesions did not differ significantly between groups, except for a higher percentage of patients with bifurcation lesions treated through femoral approach (Table 3).
Angiographic characteristics of patients submitted to therapeutic procedures
| Radial(n=99) | Femoral(n=316) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treated vessel, % | 0.38 | ||
| LAD | 37.5 | 37.3 | |
| LCx | 21.4 | 27.3 | |
| RCA | 38.8 | 30.2 | |
| Others | 2.3 | 5.2 | |
| Type of lesion, % | 0.31 | ||
| A | 2.5 | 1.4 | |
| B1 | 3.7 | 5.8 | |
| B2 | 52.1 | 42.4 | |
| C | 41.7 | 50.4 | |
| Bifurcation lesion, % | 6.5 | 19.6 | 0.03 |
| Calcified lesion, % | 17.6 | 22 | 0.20 |
| Chronic occlusion, % | 4.6 | 5.2 | 0.24 |
| Reference diameter, mm | 3.07±0.5 | 3.03±0.6 | 0.13 |
| Lesion length, mm | 18.5±6.6 | 17.9±7.3 | 0.11 |
| Pre-dilation, % | 69 | 64.2 | 0.70 |
| Post-dilation, % | 24.2 | 30.1 | 0.12 |
| Final pressure, atm | 17.1 | 16 | 0.90 |
| Procedural success, % | 98.5 | 99.1 | 0.18 |
LDA, left anterior descending artery; LCx, left circumflex artery; RCA, right coronary artery.
Patients submitted to PCI via radial approach had higher fluoroscopy time (9.2±3.2minutes vs. 7.1±1.1minutes; P < 0.01) and higher number of radiographies per examination (17.4±2 vs. 14.6±1; P=0.03). The total number of frames (878±198 vs. 899±207; P=0.80) and frames per radiography (84.3±20 vs. 85.4±19; P=0.60) did not differ between groups.
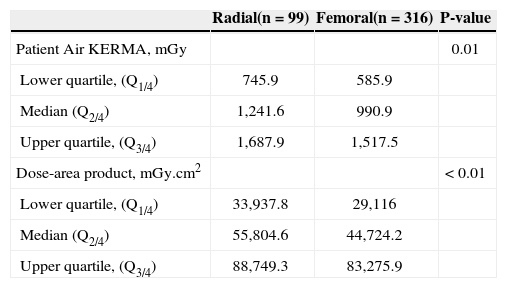
Similarly to patients submitted to diagnostic catheterization, the medians of radiation dose on the skin (radial 1,241.6mGy vs. femoral 990.9mGy) and dose-area product (radial 55,804.6mGy.cm2 vs. femoral 44,724.2mGy.cm2) were higher (P < 0.01) in the radial access group (Table 4).
Radiological exposure of patients submitted to therapeutic procedures
| Radial(n=99) | Femoral(n=316) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Air KERMA, mGy | 0.01 | ||
| Lower quartile, (Q1/4) | 745.9 | 585.9 | |
| Median (Q2/4) | 1,241.6 | 990.9 | |
| Upper quartile, (Q3/4) | 1,687.9 | 1,517.5 | |
| Dose-area product, mGy.cm2 | < 0.01 | ||
| Lower quartile, (Q1/4) | 33,937.8 | 29,116 | |
| Median (Q2/4) | 55,804.6 | 44,724.2 | |
| Upper quartile, (Q3/4) | 88,749.3 | 83,275.9 |
KERMA, Kinetic Energy Release per unit Mass.
The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI)21 proposes three skill levels for surgeons using the radial approach. Levels 1 and 2 correspond to surgeons with less experience, and level 3 corresponds to more experienced surgeons (qualified to perform all types of surgery in patients with complex anatomy and lesions). In a stratified analysis, it was observed that the surgeons with extensive experience using the radial approach (level 3) performed both diagnostic catheterization and PCI with similar radiological exposure between the two approaches. However, less experienced surgeons (levels 1 and 2) exposed patients to higher radiation levels during PCI (Figure 1).
Radiological overexposureRadiological overexposure (dose > 2Gy) did not differ between the radial and femoral access routes in diagnostic catheterization procedures (1.8% vs. 1.3%; P=0.32). However, a higher percentage of patients were exposed to doses > 2Gy in therapeutic procedures via radial access (20.2% vs. 14.4%; P=0.045).
DISCUSSIONThe present study demonstrates that the radial access route results in higher radiological exposure in diagnostic cardiac catheterization procedures and PCI. However, these results are strongly influenced by the surgeon’s experience.
The present study is one of the first to demonstrate, in the Brazilian literature, that the radial approach may be related to higher radiological exposure. It is a significant issue, as concerns regarding radiation are relevant and have been published by prominent scientific societies. In studies published in 201122 and 2012,23 the authors demonstrated that radiological overexposure (> 2Gy) is frequent in Brazil, in both diagnostic and therapeutic evaluations. In the 2011 publication,22 1.2% and 21% of diagnostic evaluations and PCIs exceeded the 2Gy dose, respectively. In the present study, similar levels of exposure were observed. However, experienced surgeons using the radial approach can match this exposure to that observed with the femoral access. Therefore, it is essential that interventionists and training centers carefully consider this aspect of the technique, and use their best efforts to implement all radiological protection measures in their services.
It is known that in the beginning of the learning process, the success rate,24 fluoroscopy time, and contrast volume are higher with the radial access. 22 The present results confirm these findings. Moreover, it is clear that the angiographic profile of patients undergoing the radial approach is less complex than those undergoing femoral access. In the present study, a lower prevalence of female patients, CABG, severe valve disease, and bifurcation lesions were observed in the PCI group. This selection bias has been frequent in studies comparing the two approaches. The Transradial Approach [LEft versus right] aNd procedural Times during percutaneous coronary procedures (TALENT)19 and RadIal Vs. FemorAL Access for Coronary Intervention (RIVAL) studies,25 for instance, either excluded patients with CABG (TALENT) or limited the number of mammary artery grafts (RIVAL). It appears, therefore, that even in large studies, the clinical/angiographic profile of patients undergoing radial access is less severe.
The learning curve plays an essential role in any procedure. In the present study, higher surgeon’s experience was directly related to lower radiological exposure. The RIVAL10 study has reported similar findings. Although the radial approach has not shown superiority in relation to the femoral access in the primary outcome analysis, a subgroup analysis demonstrated that surgeons with high experience can even reduce mortality in acute myocardial infarction. Due to the unequivocal evidence of reduction in cardiovascular outcomes, current studies exploring the influence of the learning curve and its relation to radiation exposure are being performed. The Transradial and Transfemoral Approach by EXPERienced Operators in Daily rouTine (EXPERT – www.clinicaltrials.gov; NCT01794325) study will randomly assess whether surgeons with high experience in the radial approach can perform diagnostic catheterization with radiation exposure similar to that of the femoral approach. Thus, it will be possible to determine whether the higher dose of radiation during radial procedures is the result of the surgeon’s experience or of the technique itself.
Study limitationsThe present study has limitations that should be considered. It is a single-center and observational analysis. Patients were selected for either route of access at the surgeon’s discretion. Possible technical difficulties strongly related to radiological exposure were not discriminated. The fact that the radiological exposure referred only to the radiation dose received by the patient precludes any inference about the dose received by surgeons in this study.
CONCLUSIONSThis study demonstrated that patients undergoing invasive cardiac procedures, both diagnostic and therapeutic, are exposed to higher radiation levels via radial access. However, surgeons who have experience with the technique can counteract this disadvantage in relation to the femoral access.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.