The objective of this study is to describe the frequency of dysphagia and the associated factors in stroke patients hospitalised in the Neurology Unit of the Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa, in Zaragoza, as well as to analyse the PPV and NPV of the volume-viscosity swallow test (V-VST).
MethodA cross-sectional descriptive study was conducted on stroke patients in order to assess the detectability of dysphagia using the V-VST and to track their progress for 7 days.
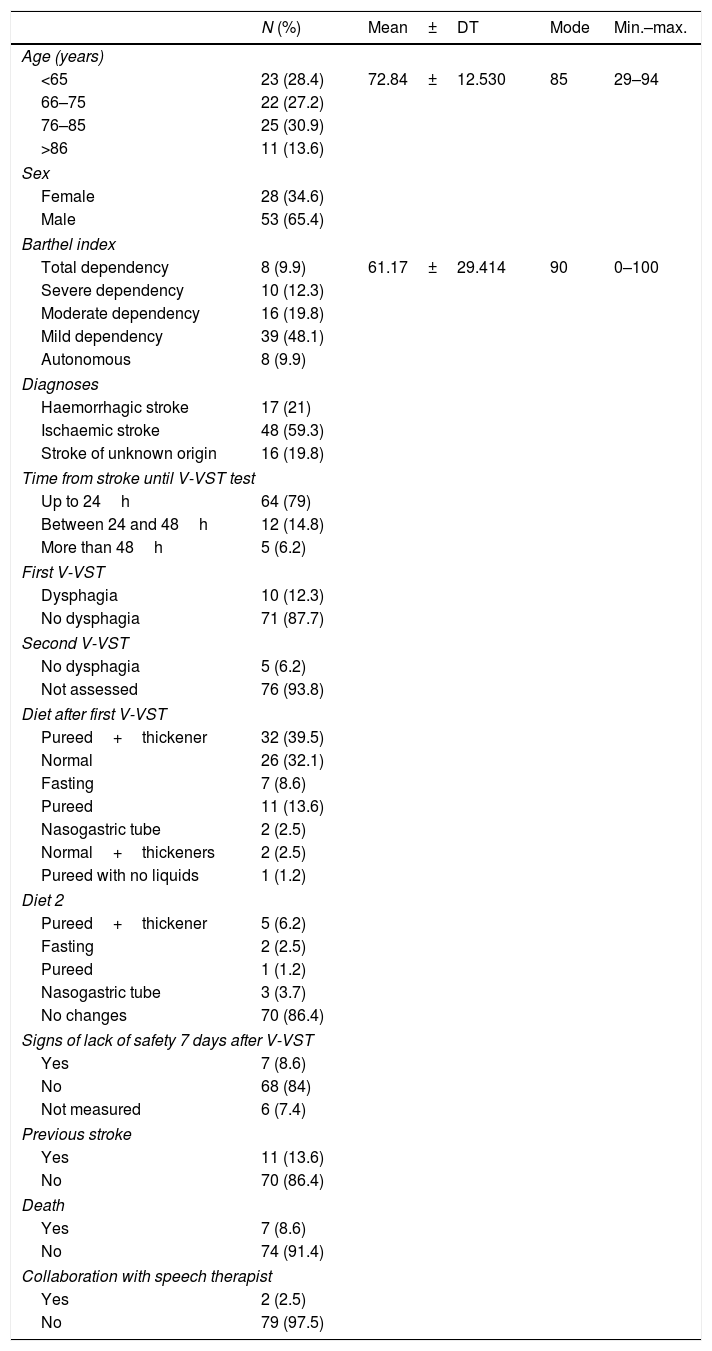
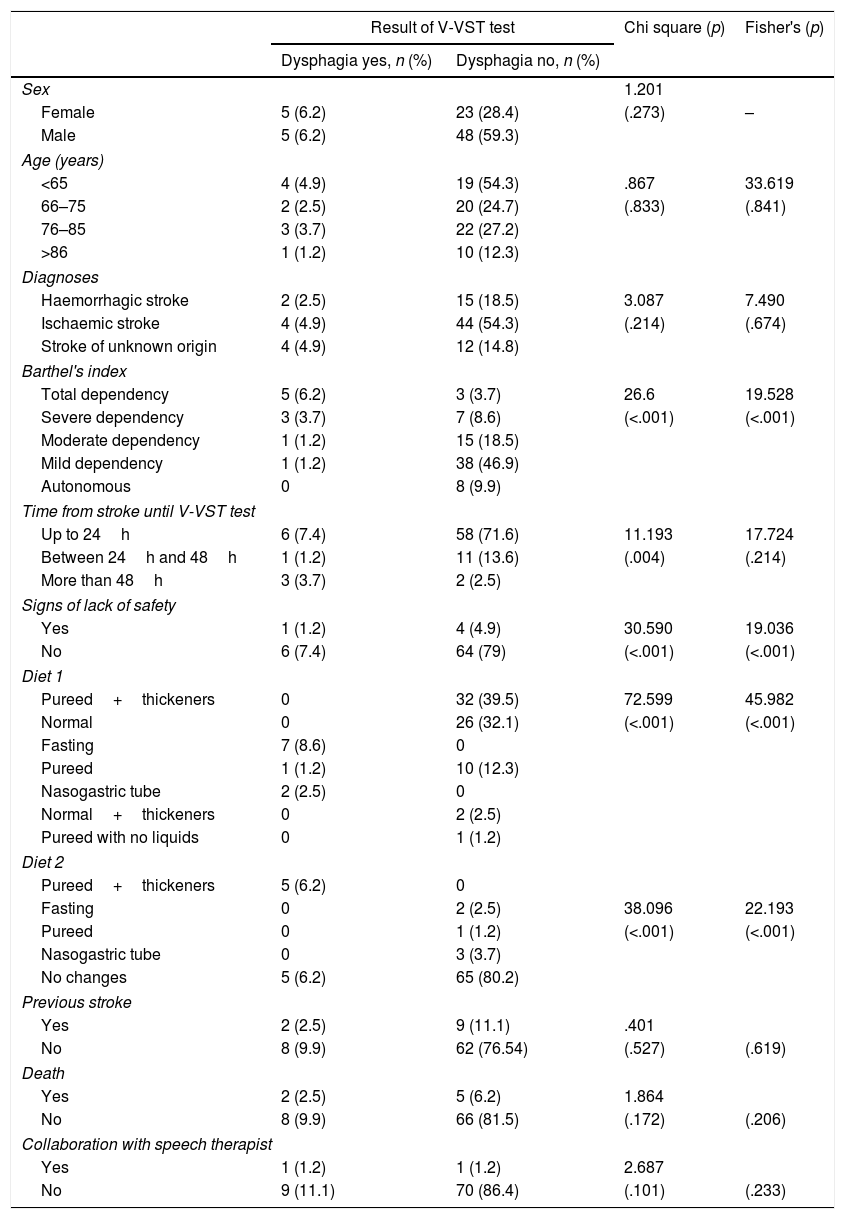
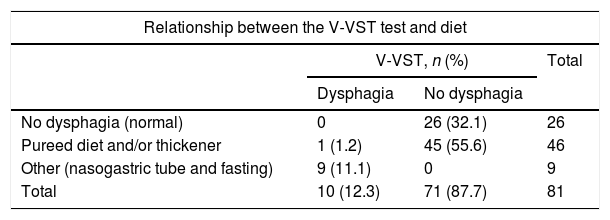
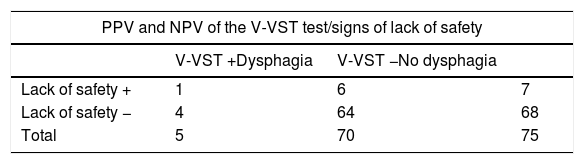
ResultsThe large majority (87.7%) of the patients did not have dysphagia. The study population included 81 subjects, of which 65.4% were men with a mean age of 72.84 years. The stroke was ischaemic type in 59.3% of cases, with no previous history of stroke in 86.4%, and with a slight dependence in 48.1% measured with Barthel index. The test was performed in the first 24h in 79% of the population, with preventive dietary measures being introduced in 56.8% of patients. Some signs of lack of security were observed in 7 patients (8.6%) in the first week. Significant statistical relationships were found between the dysphagia and the dependence, signs of lack of security during the intake in the following days, and the type of diet. The PPV and NPV for V-VST in our patients was 14.28 and 94.11%, respectively.
ConclusionsThe majority of patients did not have swallowing disorders due to their early detection with the V-VST, along with the dietary measures that appeared to reduce the risk of complications associated with dysphagia.
Describir la frecuencia y los factores asociados de disfagia en los pacientes ingresados por ictus en la Unidad de Neurología del Hospital Clínico Universitario Lozano Blesa (Zaragoza), y analizar el VPP y el VPN del método de exploración clínica volumen-viscosidad (MECV-V).
MétodosEstudio descriptivo transversal para evaluar la capacidad de detección de la disfagia del test MECV-V, y seguimiento de su evolución durante 7 días.
ResultadosEl 87,7% de nuestros pacientes no presentaban disfagia; la población estaba formada por 81 sujetos, 65,4% hombres, con una media de edad de 72,84 años, ACV de origen isquémico en el 59,3%, sin antecedentes de ACV en el 86,4% y nivel de dependencia leve en el 48,1% medido con Barthel. El test fue realizado en las primeras 24h al 79% de los sujetos, y se adoptaron medidas dietéticas en el 56,8%. Siete pacientes (8,6%) presentan signos de falta de seguridad la primera semana. Se encontró asociación estadísticamente significativa entre la disfagia y la dependencia, con los signos de falta de seguridad durante la ingesta en los días posteriores, y con la dieta. El VPP y el VPN para el test MECV-V en nuestros pacientes fueron de 14,28 y 94,11%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesLos pacientes no presentaron en su mayoría problemas de deglución, debido a la detección precoz con el test MECV-V y las medidas dietéticas que parece que reducen el riesgo de presentar complicaciones asociadas a la disfagia.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEDENE, (https://sedene.com/revista-de-sedene/ ) y autentifíquese.
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora