Número especial: Avances y retos en la psiquiatría regional en Latinoamérica
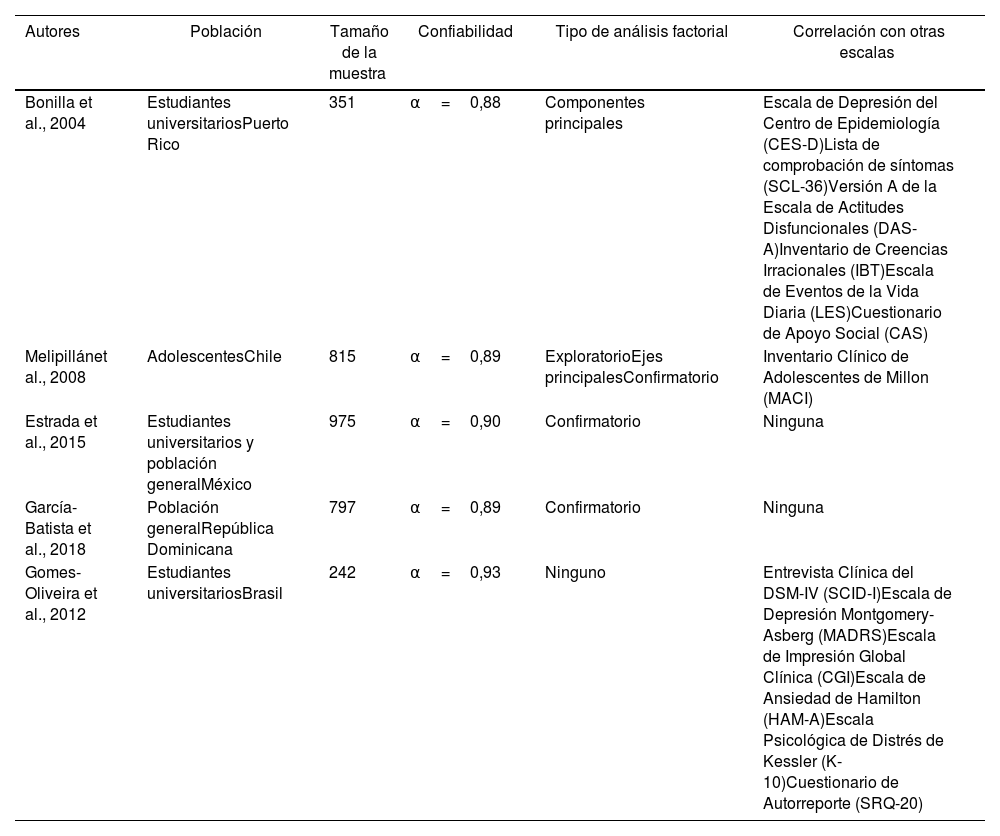
Más datosEl Inventario de Depresión de Beck-II (BDI-II) es uno de los instrumentos más utilizados en la práctica clínica e investigadora para medir síntomas depresivos; no obstante, se desconocen sus propiedades psicométricas en población colombiana. El objetivo de este estudio es hallar evidencia de dichas propiedades en universitarios, entre los que se da una alta prevalencia de depresión.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio instrumental para evaluar la confiabilidad y conocer la evidencia de validez de estructura interna y de relación con otras variables del BDI-II en una muestra de 409 estudiantes de una universidad privada de Bogotá.
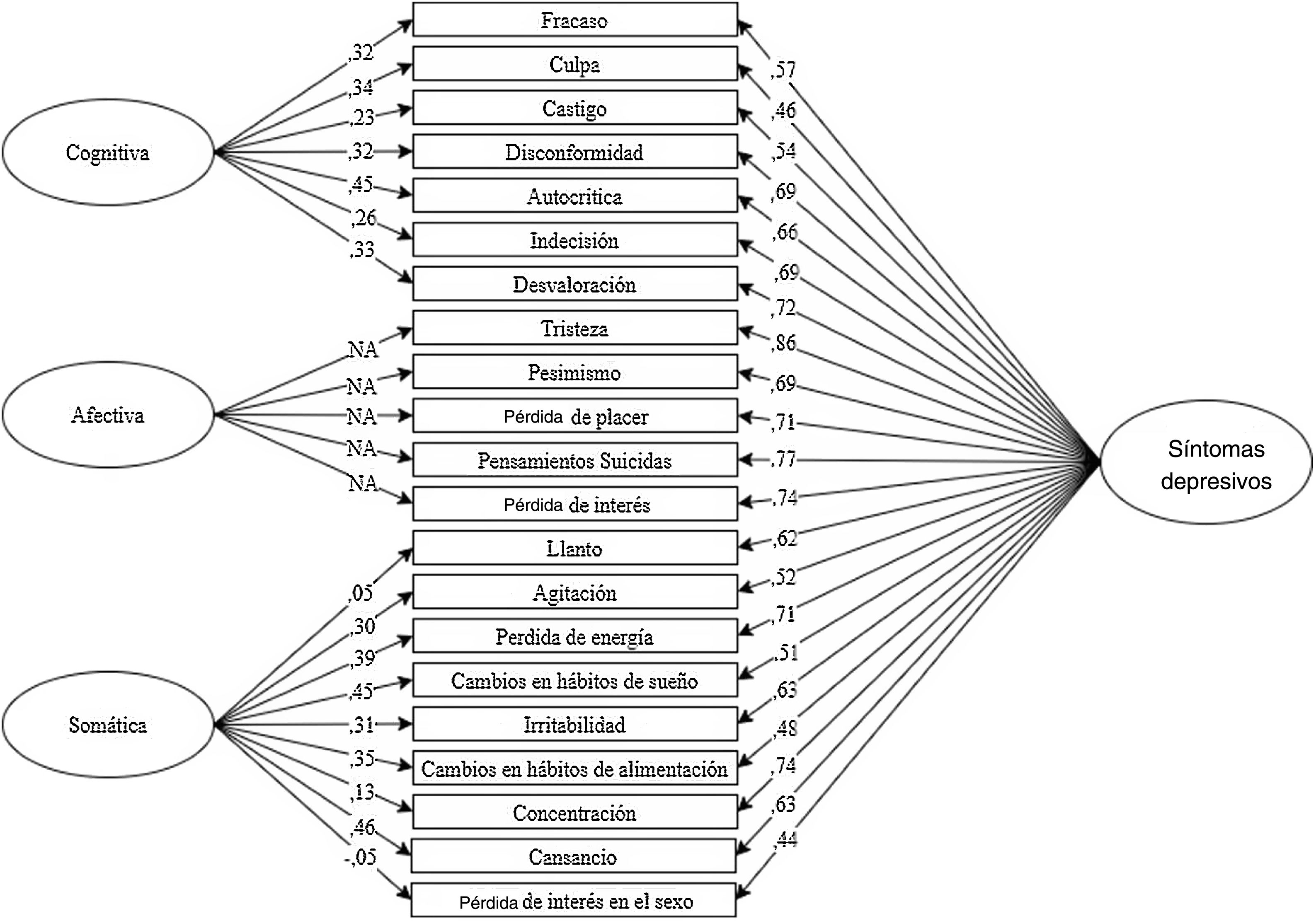
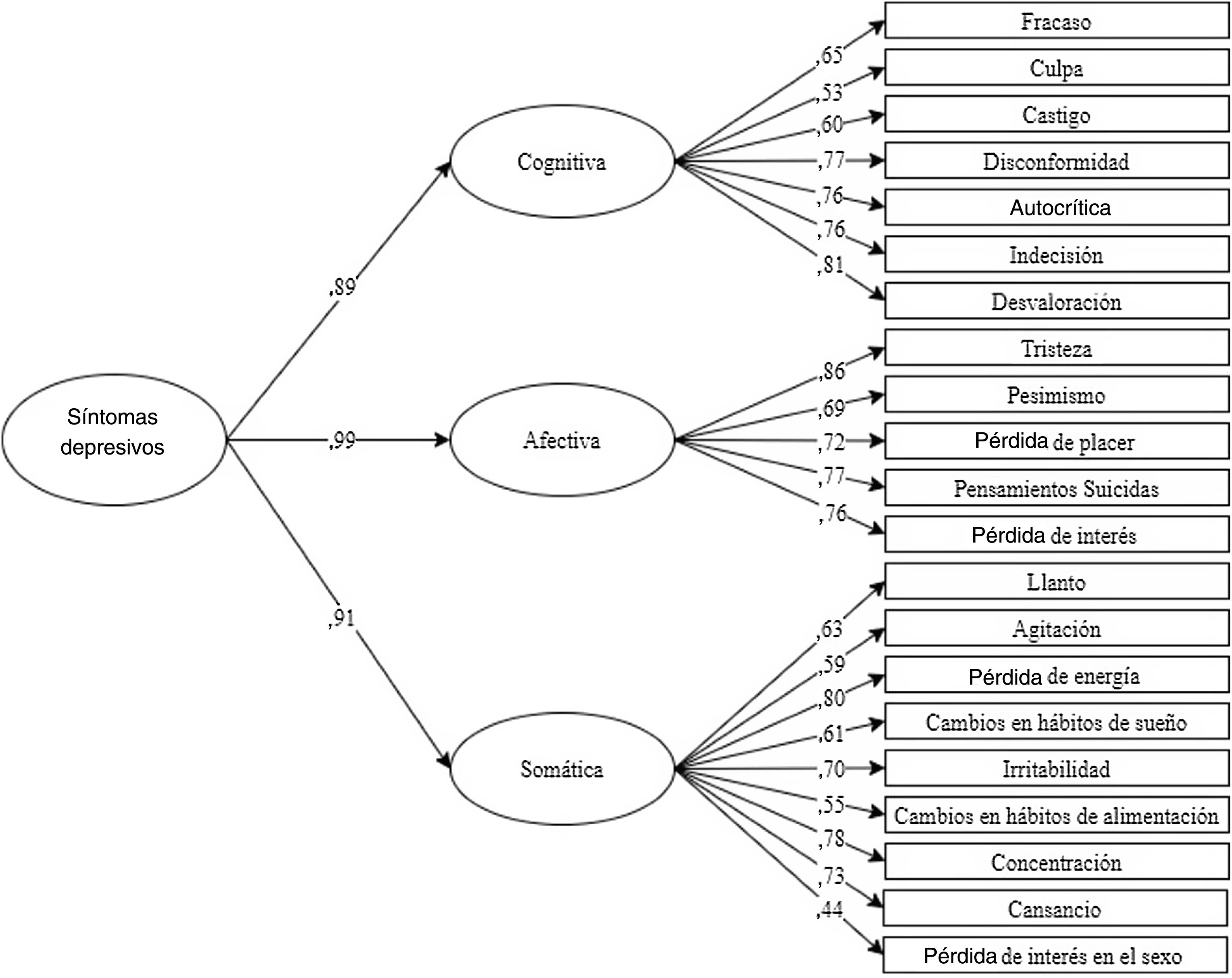
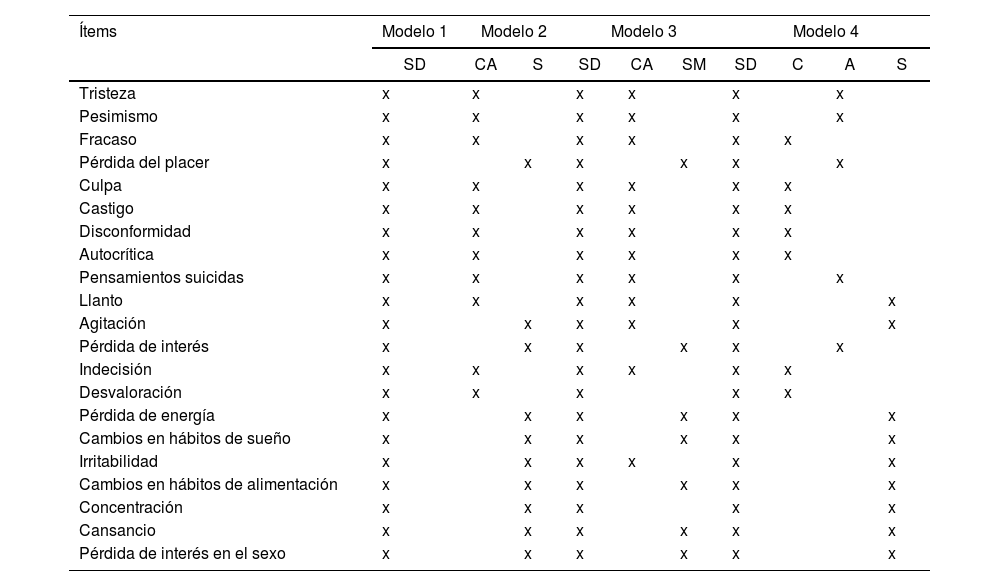
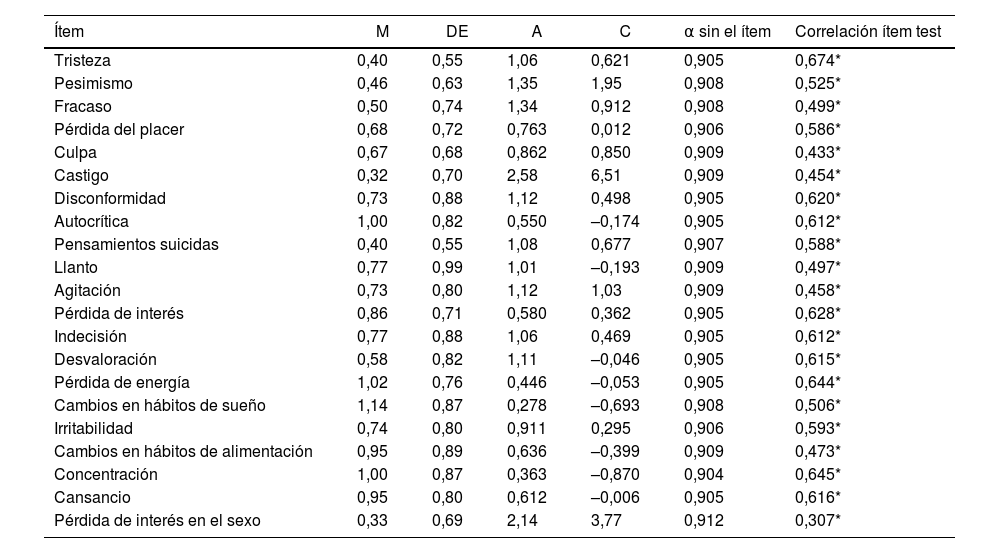
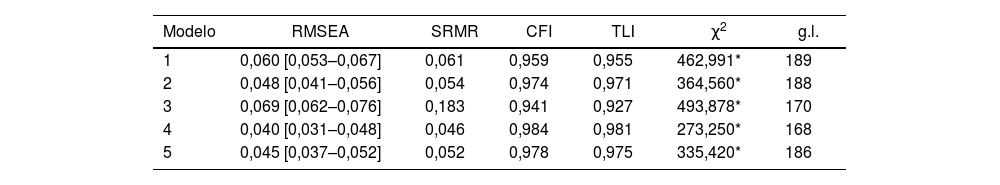
ResultadosEn cuanto a la fiabilidad, se obtuvo alfa de Cronbach=0,91. Como prueba de validez, se encontraron correlaciones ítem-test que oscilaron entre 0,31 y 0,67, todas ellas estadísticamente significativas (p<0,0001) y un buen ajuste de un modelo bifactorial (RMSEA=0,040; SRMR=0,046; CFI=0,984; TLI=0,981) y de un modelo de segundo orden a los datos. (RMSEA=0,045; SRMR=0,045; CFI=0,978; TLI=0,975). En la relación con otras variables, se encontró una correlación directa y estadísticamente significativa con los factores de riesgo (rSB =0,65) e inversa con los factores protectores (rSB =–0,519) del Inventario de Ideación Positiva y Negativa (PANSI).
ConclusionesLa evidencia sustenta que las puntuaciones obtenidas en el BDI-II permiten inferir los síntomas depresivos en esta población y se recomienda su uso clínico e investigador. Sin embargo, son necesarios más estudios confirmatorios en poblaciones con mayor variabilidad.
The Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) is one of the most frequently used instruments in clinical and research practice for depression symptoms. However, its psychometric properties in the Colombian population are unknown. The objective of this study was to find evidence of these properties in university students, who have a high prevalence of depression.
MethodAn instrumental study was carried out to evaluate the reliability, and to know the evidence of validity of the internal structure and the relationship with other variables of the BDI-II in a sample of 409 students of a private university in Bogotá.
ResultsRegarding reliability, a Cronbach's alpha=0.91 was obtained. As evidence of validity, item-test correlations were found that ranged from 0.31 to 0.67, all of them statistically significant (P<0.0001) and a good fit of a bifactorial model (RMSEA=0.040; SRMR=0.046; CFI=0.984; TLI=0.981) and of a second-order model to the data. (RMSEA=0.045; SRMR=0.045; CFI=0.978; TLI=0.975). In relation to other variables, a direct and statistically significant correlation was found with risk factors (=0.65) and inverse with the protective factors (=–0.519) of the Positive and Negative Suicide Ideation Inventory (PANSI).
ConclusionsThis evidence indicates that the BDI-II scores obtained enable depression symptoms to be inferred in this population and its clinical and research use is recommended. However, more confirmatory studies are needed in populations with greater variability.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora