Hombre de 68 años con cuadro subagudo de irritabilidad, abulia, anhedonia, apatía, anorexia y pérdida de peso.
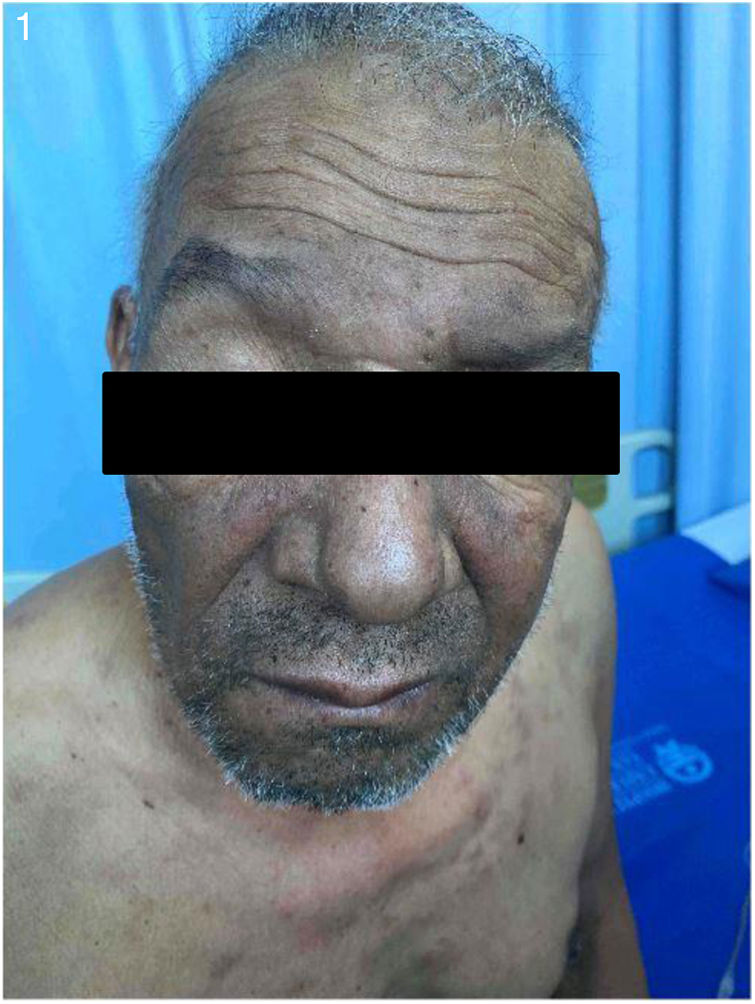
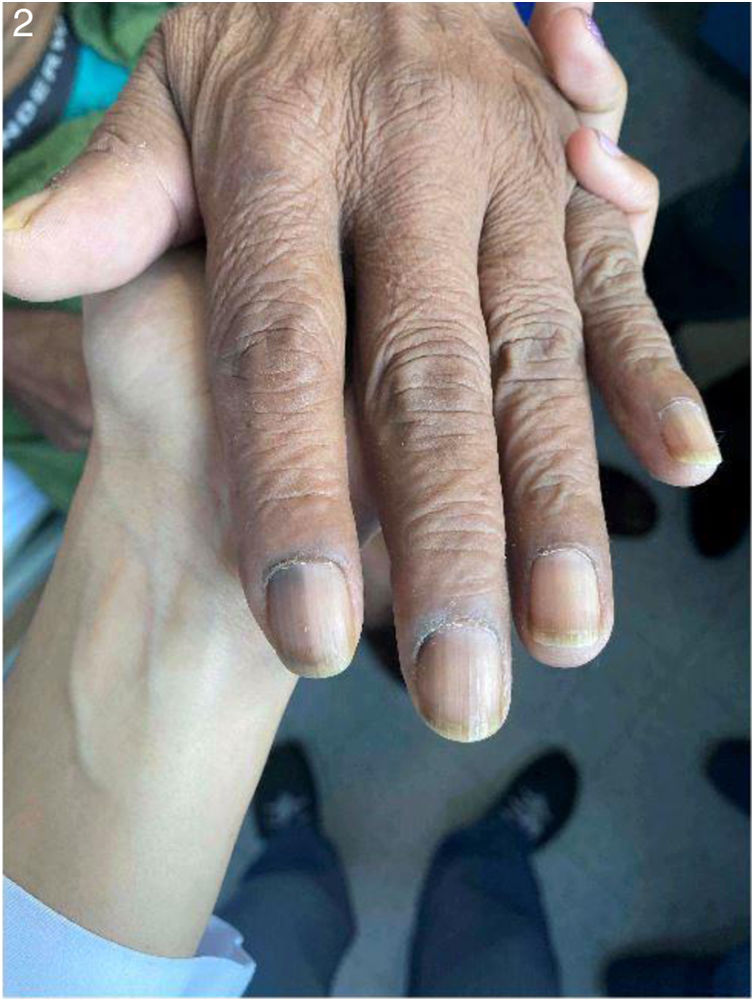
Hallazgos clínicosPresentaba placas eritemato-violáceas, irregulares, en rostro, tronco y brazos; poiquilodermia en miembros inferiores, livedo reticular, acropaquia y melanomiquia. Al examen mental presentaba una actitud apática e indiferente y un afecto plano.
Se documentó pancitopenia y colestasis intrahepática. Se descartaron causas infecciosas, carenciales e infiltrativas, así como patología neoplásica o alteraciones estructurales en hígado o sistema nervioso central que explicaran la sintomatología.
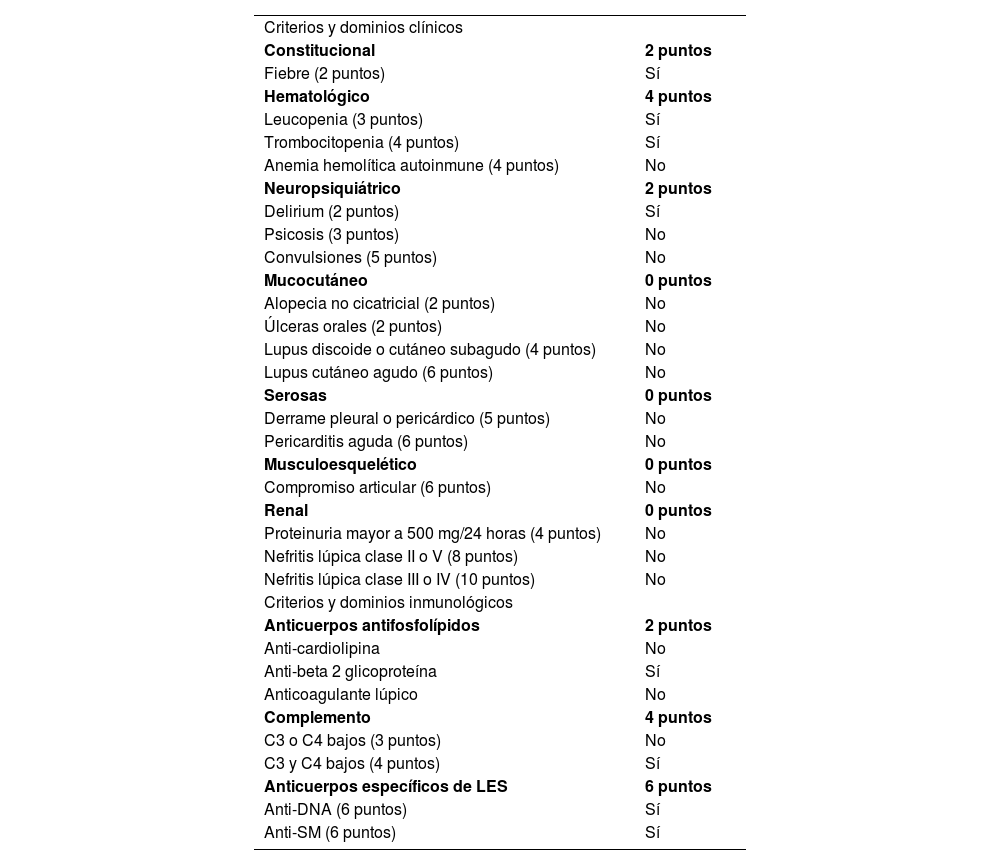
Tratamiento y desenlaceLos estudios de autoinmunidad, junto con la biopsia de piel, llevaron al diagnóstico de lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES). Ante sospecha inicial de síndrome confusional versus depresión con síntomas psicóticos, recibió manejo secuencial con múltiples antipsicóticos; el inicio del esteroide sistémico llevó a la resolución del cuadro clínico.
Relevancia clínicaEl LES afecta principalmente a mujeres jóvenes; en adultos mayores es infrecuente y debe descartarse siempre patología neoplásica subyacente. Las manifestaciones neuropsiquiátricas son atípicas en este grupo, observándose deterioro cognitivo y trastornos comportamentales en 1-5% de casos. Es importante considerarlo como diagnóstico diferencial en pacientes con síntomas neuropsiquiátricos refractarios al manejo convencional, teniendo en cuenta que puede haber mejoría clínica con tratamiento inmunomodulador.
A 68-year-old man with subacute symptoms of irritability, abulia, anhedonia, apathy, anorexia, and weight loss.
Clinical FindingsHe had erythematous-violaceous plaques on the face, trunk and arms; poikiloderma in lower limbs, livedo reticularis, clubbing and melanomichia. On mental examination he presented apathetic and indifferent with a flat affect.
Pancytopenia and intrahepatic cholestasis were documented. Infectious, nutritional and infiltrative causes were ruled out, as well as malignancy or structural alterations in the liver or central nervous system that could explain the symptoms.
Treatment and OutcomeAutoimmunity studies together with skin biopsy led to the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Given the initial suspicion of confusional syndrome versus depression with psychotic symptoms, he received sequential management with multiple antipsychotics; the start of the systemic steroid led to resolution of symptoms.
Clinical RelevanceSLE mainly affects young women; in older adults it is uncommon and underlying malignancy must always be ruled out. Neuropsychiatric manifestations are atypical in this group, with cognitive impairment and behavioral disorders observed in 1-5% of cases. (1) It is important to consider it as a differential diagnosis in patients with symptoms refractory to conventional management, giving that there may be improvement with immunomodulatory treatment.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora