Nailfold capillaroscopy is relatively little known tool outside the areas of rheumatology and dermatology. It is used to observe the shape, number and organization of the capillaries in the nail bed. It has not been widely used in the past, partly as it required specialized training and equipment, as well as the poor standardization of this diagnostic method. However, in recent years, thanks to renewed interest and research effort of the academic community, these problems have been able to be overcome, turning capillaroscopy into real resource for the study of microcirculation, being especially useful in differentiating primary from secondary Raynaud's phenomenon. These benefits have enabled capillaroscopy to gain importance in the rheumatology field, specifically in the early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis, a disease with significant microcirculation involvement, where the change in capillaroscopy pattern also helps to predict the onset of complications, such as digital ulcers and organ compromise.
La capilaroscopia del lecho ungular es una herramienta relativamente poco conocida fuera de las áreas de reumatología y dermatología, que permite observar la forma, cantidad y organización de los capilares en el lecho ungular. Históricamente, su uso ha sido poco difundido, en parte, por el requerimiento de entrenamiento y equipo especializado, así como la pobre estandarización de este método diagnóstico. No obstante, en los últimos años y gracias al renovado interés y esfuerzo investigativo de la comunidad académica, se han podido superar estos problemas, convirtiendo la capilaroscopia en un recurso real para el estudio de la microcirculación, siendo especialmente útil en la diferenciación del fenómeno de Raynaud primario del secundario. Estas bondades le han permitido a la capilaroscopia ganar importancia en el ámbito reumatológico, específicamente en el diagnóstico temprano de la esclerosis sistémica, enfermedad con importante afección de la microcirculación, donde la alteración del patrón capilaroscópico permite, además, predecir la aparición de complicaciones como úlceras digitales y compromiso orgánico.
Capillaroscopy is an in vivo technique which, using an instrument of optical magnification, allows the study of microcirculation.1 While it can be carried out in any of the anatomical locations in which the terminal capillaries take an orientation parallel to the skin (ocular conjunctiva, periareolar region and labial mucosa), the capillaries of the nailfold of the hands are those that, due to their accessibility, are routinely studied; for this reason, this technique is called nailfold capillaroscopy (NC).2,3 This study of the description of the quantitative and morphological characteristics of the capillaries allows to differentiate the primary Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) from the secondary and, in turn, when the underlying cause is an autoimmune disease (AD), to define the presence of vascular alterations characteristic of this type of diseases.4–6 Different optical instruments can be used for this procedure such as: the dermatoscope,7–9 ophthalmoscope, light microscope (stereoscope) and USB microscopes; however, the most indicated is the digital videocapillaroscope, which allows the dynamic assessment of the microvascular abnormalities with an adequate optical magnification (200×), as well as the computerized study of the different capillary parameters.10–13
MethodologyA non-systematic narrative review of the literature in English and Spanish was conducted in the databases: PubMed, Embase and Lilacs.
The PubMed search was developed with the following terms and descriptors: (“Microscopic Angioscopy” [Mesh]) AND (“Scleroderma, Systemic” [Mesh]) AND (“Dermoscopy”[Mesh]) AND (“Autoimmune Diseases” [Mesh]) OR (“Microscopic Angioscopy” [Mesh]) OR (“Scleroderma, Systemic” [Mesh]) OR (“Dermoscopy”[Mesh]) OR (“Autoimmune Diseases” [Mesh]), finding 66 articles.
ResultsHistorical overviewThe history of capillaroscopy dates back to 1663, when Johan Christophorous Kolhaus was the first to use a primitive microscope to observe the small blood vessels surrounding the nails.3 In the mid-19th Century, the Italian physicist Giovanni Rasori (1766–1837) showed the relationship between an inflamed conjunctiva and capillary abnormalities, using a magnifying lens and it was described as “an inextricable knot of capillary loops”.14 In 1862, Maurice Raynaud presented in Paris his thesis about the local ischemic damage in hands, feet, nose and tongue and his name remained linked to this phenomenon which, over time, became crucial as the sentinel event of many autoimmune diseases; and at the beginning of the 20th Century, Hutchinson was able to differentiate between a primary and a secondary Raynaud's phenomenon, based on the microvascular changes found.15
In 1911, Lombard discovered that by placing a drop of immersion oil in the periungual region, an easy visualization of the human capillaries was allowed; this finding influenced Weiss, who in 1916, standardized the capillaroscopy technique and produced the first images using a primitive camera. By 1925, Brown and O’Leary used the capillaroscopy analyses to show the abnormalities of the microvasculature in the RP associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc), allowing to link the nailfold capillaroscopy to rheumatic diseases.3,16
After a hiatus of several decades, the interest was retaken in 1973, when Maricq and LeRoy published the specific patterns in the capillaroscopy of SSc.17 Between 1980 and 1990, different authors continued with the investigative effort including the use of fluorescein,18 the use of other anatomic sites for the realization of capillaroscopy19 and the integration of other diagnostic means such as the Laser Doppler.20 Finally, in 2000, Cutolo et al., redefined the patterns of capillaroscopic progression of SSc, generating a new pattern of classification in this area of knowledge and laid the foundations for the study of microcirculation in AD.16 Despite the role that the NC has gained in the last years, there are several barriers that make that, in great part of the world, it continues being little known and used; the poor standardization of the technique and the high cost of the equipment (which varies between 5000 and 30,000 euros) are the determining factors.16,21 This generates a poor knowledge of the tool and an inadequate use of it, being estimated than less than 10% of the rheumatologists perform the NC in a proper way.1,22
The interest of the scientific community in capillaroscopy has grown in the last years; this is reflected, for example, in a survey conducted in 2011 in 32 cities of countries belonging to the European League Against Rheumatism, where the capillaroscopy, along with ultrasound, were the best evaluated tools.22 In response to this growing interest, in Italy, since 1996, the capillaroscopy has been included in the academic program of Rheumatology and each resident must perform 50 evaluations within his studies, as well as attend to 200 evaluations as an observer.1 In addition, in 2010, it was created a group of study in the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) dedicated to the capillaroscopy in rheumatic diseases22 and every 2 years are held training courses of global reach in this technique14,16 and highly effective short-term educational strategies have been designed and evaluated.23
TechniqueThe NC should be carried out in a room that is between 20–22°C; the patient should be at rest for at least 15min, without being exposed to extreme temperatures to avoid the appearance of vascular areas of vasoconstriction secondary to cold, a fact that may generate false positives. In addition, the realization of manicure should be avoided between 15 days and one month prior to the procedure, as the cuticular trauma can generate hemorrhages and, when the cuticle is pushed back, the architecture is distorted.24,25
The proper position for the NC is with the patient sitting and the examined hand at the level of the heart. The exam should be done in all fingers, except in the thumb and in those fingers with active infections or recent traumas of the nail bed, since the normal pattern can be altered.14,24,25 Although this evaluation can be performed in any order, it must be standardized to avoid confusions when comparing the studies, being accepted, from the international point of view, to start with the fifth finger of the right hand, ending on the fifth finger of the left hand. A drop of immersion oil, of cedar or almonds (the two latter provide better visibility), should be applied prior to the procedure to increase the transparency of the epidermis. From the technical viewpoint, the fourth and fifth fingers offer and advantage, because their skin has greater transparency. The correct observation of all these steps will avoid technical mistakes that can alter the interpretation of the exam.14,21
The acquisition of the images should be carried out, ideally, with a tool that provides at least a 60× magnification to adequately characterize the patterns of vascular alteration and ideally that allows to capture the images for further analysis. With regard to the differences found with the different magnifications, the magnifications that are lower than 100× allow a more panoramic view, observing the entire capillary pattern of the nail bed, while higher magnifications allow to evaluate the morphological characteristics of each capillary. Currently, the most frequently used magnification is 200×; higher magnifications (up to 1000×) even allow the observation of the individual passage of the erythrocytes through the capillary loop; however, these lenses are mainly used in research and are not common in daily practice.16,24
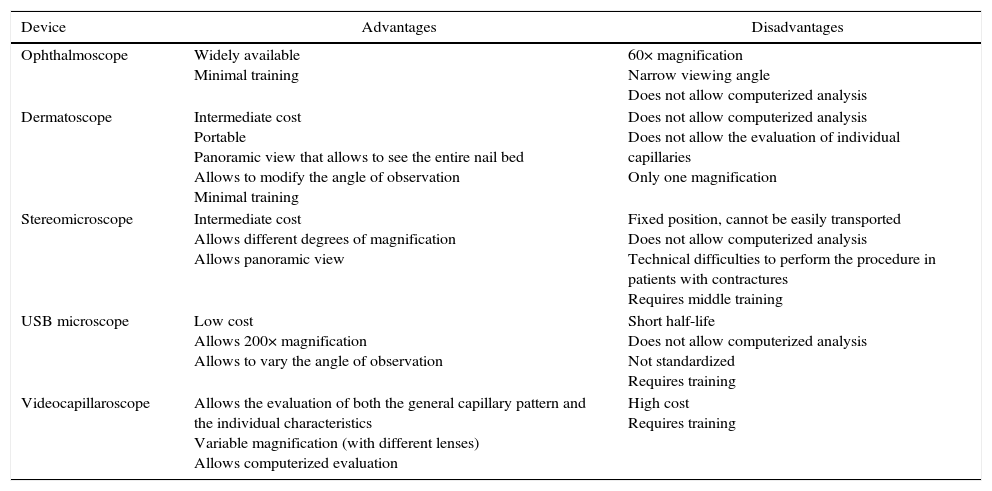
When defining the tool to be used it is important to consider the intrinsic characteristics of the observation instrument (Table 1). Studies performed with the dermatoscope, for example, have found comparable results between it and the videocapillaroscope, with high correlation coefficients for the detection of the different capillary patterns; nevertheless, it is important to emphasize that the dermatoscope, having low magnification, does not allow to evaluate the capillary morphology nor their individual measurements, being then particularly useful for a rapid assessment in the medical consultation that allows to define in a dichotomous manner if the patient would benefit from more complete studies with NC.14,15,26–28
Characteristics of the different elements for the realization of nailfold capillaroscopy.
| Device | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Ophthalmoscope | Widely available Minimal training | 60× magnification Narrow viewing angle Does not allow computerized analysis |
| Dermatoscope | Intermediate cost Portable Panoramic view that allows to see the entire nail bed Allows to modify the angle of observation Minimal training | Does not allow computerized analysis Does not allow the evaluation of individual capillaries Only one magnification |
| Stereomicroscope | Intermediate cost Allows different degrees of magnification Allows panoramic view | Fixed position, cannot be easily transported Does not allow computerized analysis Technical difficulties to perform the procedure in patients with contractures Requires middle training |
| USB microscope | Low cost Allows 200× magnification Allows to vary the angle of observation | Short half-life Does not allow computerized analysis Not standardized Requires training |
| Videocapillaroscope | Allows the evaluation of both the general capillary pattern and the individual characteristics Variable magnification (with different lenses) Allows computerized evaluation | High cost Requires training |
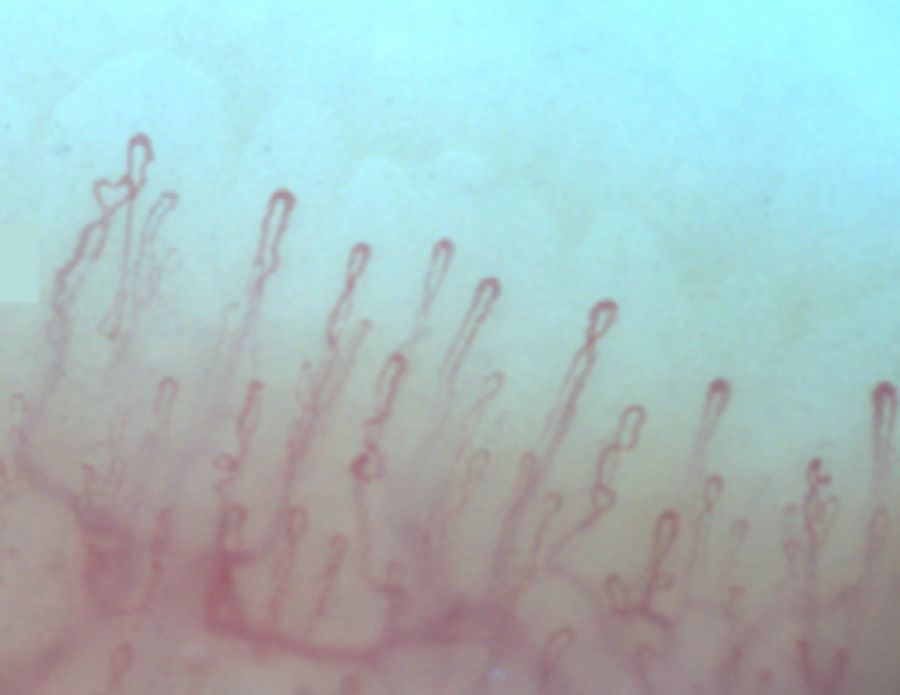
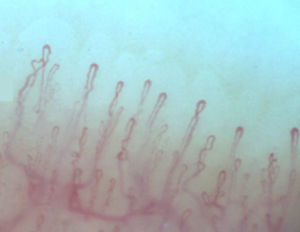
Normally, in the nail bed, are seen 6 to 14 capillary loops per millimeter (mm); they are arranged in a comb-like shape and both their number and morphology tend to remain stable over time.3 When these capillaries are observed individually, they have the shape of hairpin or of “inverted-U”, appearing from 1 to 4 per dermal papilla. Each hairpin is made up by a branch of an afferent arteriole of 6–19μm, whose tunica media has up to 2 layers of muscle and one efferent venous of 8–20μm, which does not contain muscle cells, that bind together distally maintaining a vein: artery relationship not greater than 2:1. These branches are symmetrical, with homogeneous morphology and can measure between 200 and 250μm in length (Fig. 1).21,24,25,29 Below several rows of capillaries, some vessels of greater size can be seen, that represent the subcapillary venous plexus, visible in up to 60% of normal population,3,21,25 which can be viewed thanks to the increased transparency of the skin, and is seen most often in Caucasians.16
Regarding the age-related changes, the normal comb-like capillaroscopic pattern can be detected from two years of age; the capillary architecture of an adult is acquired, usually at the end of childhood.21 The main differences between the pediatric and the adult capillaroscopic patterns are: a lower capillary density, greater heterogeneity, especially with capillaries with unusual shapes (36%) and greater visibility of the subcapillary venous plexus,30–32 being rare in healthy population the presence of megacapillaries, which are seen in only 6% of healthy patients. In older adults, it is difficult to define a normal capillaroscopic pattern, in part because of the difficulty to find a healthy control population; nevertheless, it is clear that in this age group, it can be observed a lengthening and increased tortuosity of the capillaries, as well as secondary apical dilation, possibly, due to a longer history of microtrauma, as well as a decreased cardiac output with increased peripheral vascular resistance. Finally, the subcapillary venous plexus can also be observed more easily, in part due to the thinning of the skin and the congestion of venules and capillaries related with the increased opening of the arteriovenous anastomoses secondary to senile microangiopathic changes.1,14
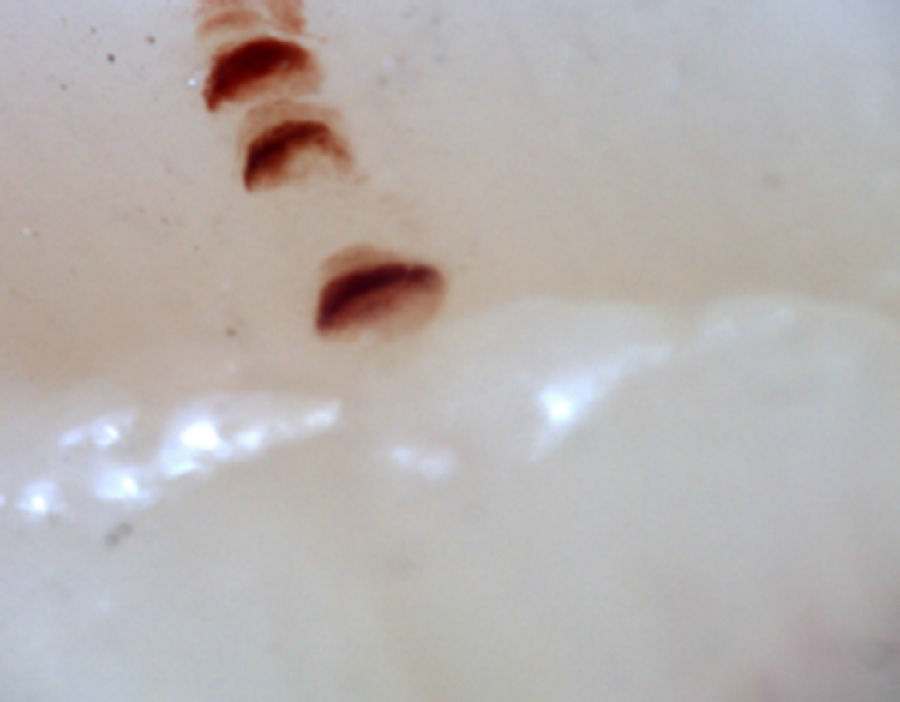
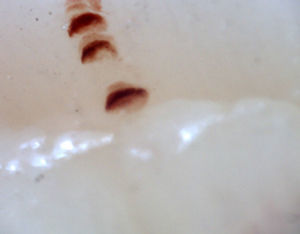
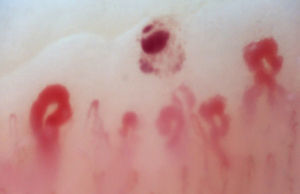
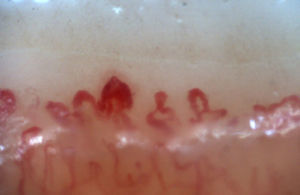
There are many unusual capillary shapes that are not by themselves indicative of disease: intercrossed capillaries, those with an irregular trajectory (tortuous), capillaries with greater than usual length (elongated) and the presence of unusual shapes so-called capillary disorganization (which can be found in normal subjects in a mild form), as well as the presence of capillary edema reflecting the presence of plasma in the interstitial space, giving the image of “fog” between the capillaries. Other alterations are suggestive of a secondary cause of RP as, for example, the presence of blood out of the capillaries called capillary microhemorrhage that, due to the recurrent bleeding episodes, form a characteristic “fumarole-like” image. This alteration can be found occasionally in healthy patients, in an isolated manner. While it is not pathognomonic, the presence of microhemorrhages is characteristic of the AD (Fig. 2).33
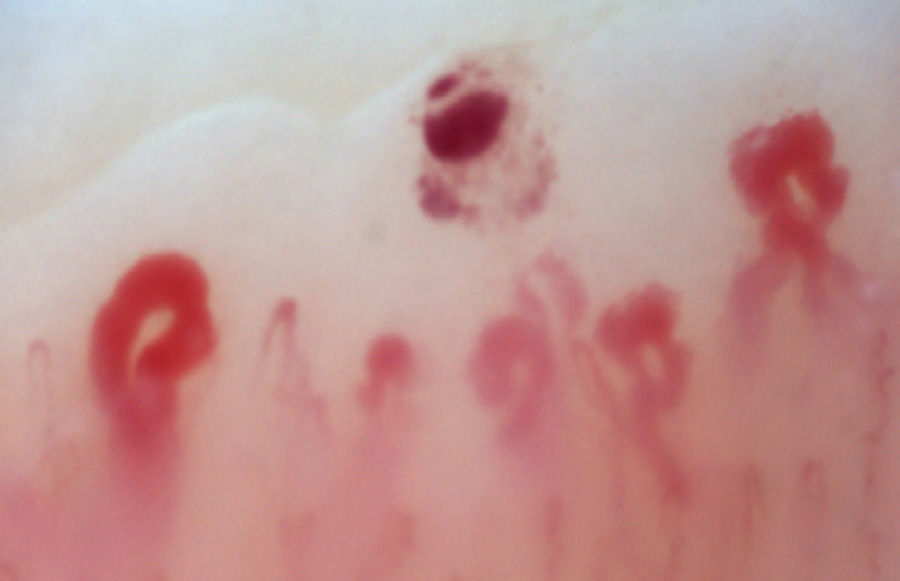
There is another group of alterations that should never be considered normal, such as the avascular areas, secondary to the capillary loss that give an image of a “deserted area” in the middle of the “capillary forest”, either by the absence of 2 capillaries in each dermal papillae or by the presence of an area of 500μm devoid of them. This alteration should be distinguished from the generalized loss of capillaries, where a homogeneous decrease in their number is observed by applying excessive pressure on the nail bed when performing the capillaroscopy, and it can be observed an abrupt transition from a vascularized area into a completely avascular area which is dynamic as the position of the videocapillaroscope varies. Another finding that must always be considered abnormal is the neovascularization, which is chronologically a posterior event, reflecting an attempt to recover the tissue perfusion and the normal architecture which, nevertheless, fails, giving rise to a great heterogeneity of shapes and, sometimes, to a such an intense revascularization that gives the shape of a tree or arborescent capillary. Finally, the alteration most important for the evaluator are the dilated capillaries with a loop diameter greater than 50μm, which are called “megacapillaries” and are the quintessential markers of the microvascular damage in SSc (Fig. 3)16,21,24; they should not be confused with the capillary segmental dilation or with the dilation of only one loop, findings commonly observed in arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus.34
This great variety of capillary shapes generates difficulties when defining normality. It is estimated that only 40% of the healthy population has completely normal capillaries, 50% has minor abnormalities and only 5% has any abnormality with significant clinical relevance.16,29 Studies in healthy population have found, at least, 3 patterns of normality: the “perfectly normal” pattern, where all capillaries have an adequate shape and configuration; the “normal” pattern in which up to 2 tortuous capillary loops are tolerated, and the “unusual normal” pattern, in which can be found, at least, one arborescent capillary, one microhemorrhage, or more than 4 tortuous capillaries.33 Under this order of ideas, is essential to have centers with extensive experience in videocapillaroscopy that know how to interpret, for example, when a microhemorrhage or an arborescent capillary are part of an unusual normality pattern or when they are part of an incipient rheumatologic process.
Raynaud's phenomenon: the importance of capillaroscopyRP affects between 2 and 9% of the general population; it can be primary or derived from vascular alterations or systemic diseases, in which case is considered secondary.35 Between 15–20% of patients who have continued RP with videocapillaroscopic alterations and positive antinuclear antibodies (ANA) for a period of 2 years, can develop an AD, being the SSC the main disease toward they progress.36–38 Early diagnosis of the secondary RP is important, because it allows to predict both the appearance of local complications (ulcers, necrosis and digital superinfection)39,40 and severe organ commitment (pulmonary arterial hypertension)10,41,42 and even mortality.43 Initially, in order to differentiate these subtypes of RP, LeRoy and Medsger, in 1992, proposed a number of clinical criteria by which the presence of asymmetry, digital ulceration, alteration in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, positivity of ANA or alteration in the capillaroscopic pattern can predict the presence of a secondary RP.44
Taking into account that the main disease to which the secondary RP progresses is SSc, Ingegnoli et al., suggested a stratification model for the risk of transformation of an isolated RP into a SSc, classifying it as follows: high risk (greater than 50%) in patients who have capillaroscopic alterations such as decrease in the total number of capillaries and giant capillaries associated with positive ANA; moderate risk (10–50%) in those who have a decrease in the number of capillaries, without giant capillaries and with positive ANA; and slight risk (<10%) in those subjects with normal or decreased number of capillaries and negative ANA.45 Koenig et al. found, in patients with RP and without other signs of connective tissue disease, that those who had alterations in the capillaroscopy had a probability of 47% to progress to SSc in 5 years and of 79% in 15 years and, when this finding was associated with positive ANA, the risk of disease increases up to 15–20% at 2 years26 and to 65.9% at 5 years.38
En 2001, Lonzetti et al., reported that the limited capacity of the ACR criteria to identify patients with SSc improved from 34% to 89% by adding the capillaroscopic alterations in the nail bed. More recently, in a study conducted by Hudson et al., in 101 patients with SSc it was found that 67% met the ACR criteria and that, when adding the nailfold capillaroscopy performed with dermatoscope, this sensitivity increased to 99%.46,47
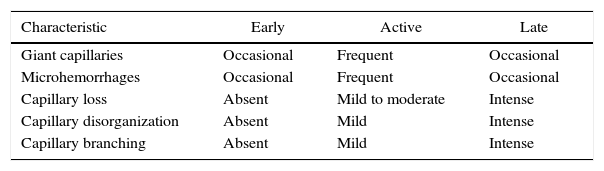
Capillaroscopic changes observed in systemic sclerosisMicrovascular damage is one of the pathophysiological pillars of SSc; in fact, the nailfold capillaroscopy shows findings characteristic of the disease in 80–95% of cases.39,48–50 These findings have been grouped into patterns that allow to get an idea of the degree of affection generated by the disease. Initially, Maricq et al., classified the patterns of SSc into 2 groups: one slow, which shows, at least, 2 megacapillaries with minimal decrease in their number in, at least, 2 out of 10 evaluated fingers; and other active group, which exhibits a moderate or severe loss of the capillaries.51 These capillaroscopic patterns were correlated with the subtypes of SSc described in 1988 by LeRoy et al.52; consequently, the slow pattern correlated with the limited form and the active pattern with the generalized form.51,53,54 Later, Cutolo et al., described 3 patterns associated with SSc, which reflected the progression of the microvascular damage in this disease. This system has as conditio sine qua non the presence of, at least, one giant capillary (measuring 50μm), which represents, as previously mentioned, the first clear alteration of the microvascular damage associated with SSc.16
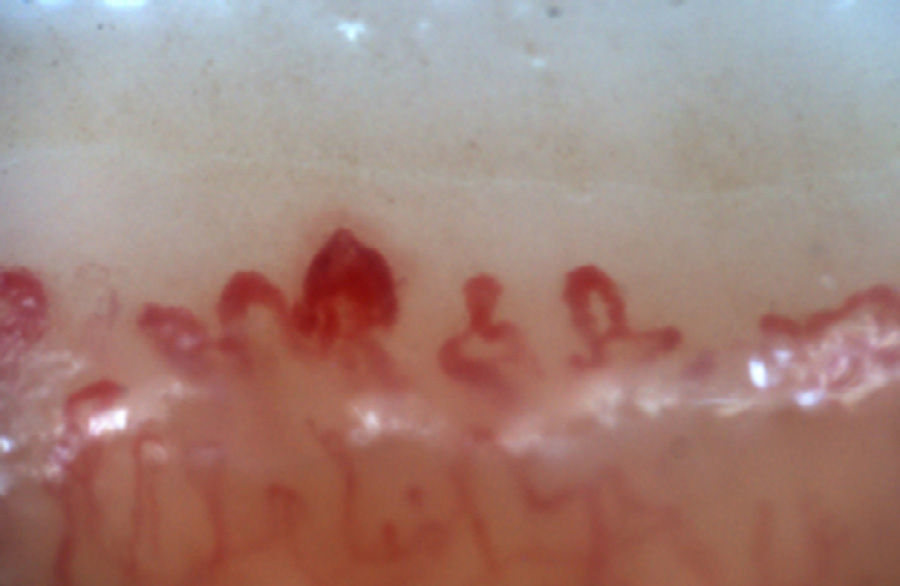
The patterns described by Cutolo et al. (Table 2) reflect the pathophysiological process characteristic of this disease: the hypoxia sustained over time leads to a modification of the capillaries and neoangiogenesis directed by several growth factors (VEGF, PDGF, among others) in the context of a profibrotic environment secondary to the activation of fibroblasts propitiated, among others, by the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ).55 This process is dynamic and starts with the dilatation of the capillaries, configuring megacapillaries; these, due to the previously mentioned process, are labile and prone to rupture, generating microhemorrhages; these first changes constitute the early pattern. As this process advances, the capillary abnormalities will generalize throughout the nail bed, configuring and active pattern; later, the affected capillaries disappear, generating avascular areas, which progress to the emergence of “deserted areas” giving raise to the late pattern. Finally, reactive neovascularization occurs with a loss of the normal microvascular architecture (late pattern) (Fig. 4).56,57
Capillaroscopic patterns in systemic sclerosis.
| Characteristic | Early | Active | Late |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giant capillaries | Occasional | Frequent | Occasional |
| Microhemorrhages | Occasional | Frequent | Occasional |
| Capillary loss | Absent | Mild to moderate | Intense |
| Capillary disorganization | Absent | Mild | Intense |
| Capillary branching | Absent | Mild | Intense |
Several cells and growth factors have been involved in the pathophysiology of the capillaroscopic changes in SSc: it has been described a reduction in the number of progenitor endothelial cells derived from the bone marrow which correlates with the early pattern58; on the contrary, high levels of VEGF have been found in individuals with late pattern.59 High levels of pentraxin 3 and low levels of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF-2) have been found in subjects with the active capillaroscopic pattern of SSc.60 All these alterations lead to vasculopathy and clinically correlate with organic involvements (increased sclerosis cutis determined by the modified Rodnan score, higher incidence of digital ulcers and increased frequency of pulmonary arterial hypertension).
Although patients may progress over time, this is not a universal condition; in some patients, especially in those with the limited variety of SSc, changes in the capillaroscopic pattern do not occur over time. In patients who do have this progression, the time to progression from an early to an active stage and from an early to a late stage is 28±20 months vs. 36±29 months, respectively; likewise, the clinical symptoms progress along with the capillary changes in 60%.22 It is important to take into account that the evidence shows that the patients who have a rapid progression (less than one year) from an early to an active stage, are in risk of progressing quickly to a late stage of microangiopathy and are more frequently associated with the diffuse subtype of SSc.53
Rating or scoring systemThe alterations in the capillaroscopy can be evaluated in a qualitative, quantitative and semiquantitative manner; in the qualitative, the different changes exhibited in the architecture, morphology, density and dimensions of the capillaries are observed and the findings are described24,25,61; in the quantitative, the measures of each capillary evaluated per linear mm are taking into account; and in the semiquantitative, a score of 0–3 is assigned and an average is calculated according to the revised fields; usually, the loss of capillaries, the megacapillaries, the microhemorrhages and the branched capillaries are taken into account.24
To evaluate the loss of capillaries by the semiquantitative method, the scores are obtained by calculating the percentage of loss versus the normally expected number of capillaries per mm, being: 0=no changes (more than 9/mm); 1=less than 33% of capillary alteration/reduction (7–9 capillaries/mm); 2=33–66% of capillary alteration or reduction (4–6 capillaries/mm); 3=more than 66% of capillary alteration/reduction (1–3 capillaries/mm); for example, if the patient has only 6 capillaries, the capillary loss corresponds to 33%, which results in a score of 2.
In the evaluation are taken, usually, 2 to 4 fields per finger and the average of the evaluated fields is calculated by adding their results and dividing the total by the number of fields (usually a total of 16–32 fields per patient). For the rest of the evaluated parameters, the actual, not the ideal, number of capillaries that are found at the moment in the distal row is taken into account.24,25
Attempts has been made to simplify the number of fields to be evaluated, searching to obtain results comparable to the gold standard, in which 32 fields that correspond to 8 fingers (from the 2nd to the 5th) are evaluated, taking 4 fields per finger and intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.90 are achieved when comparing 8/32 fields (95% CI: 0.84–0.93) and of 0.76 when comparing 4/32 fields (95% CI: 0.63–0.85), with which the fewest number of fields to be evaluated to achieve a reliable simplified index would be 8 (evaluating the 8 fingers and one field per finger).62,63
The inter and intra-observer correlation for the qualitative method is useful to distinguish the presence of the SSc pattern, finding a correlation of 90% and 96%, being lower to distinguish between specific patterns, with a correlation of 62% and 81%, respectively.62 As for the semiquantitative method, the intraobserver correlation is excellent in all parameters (0.95) and the interobserver correlation is excellent for the loss of capillaries (0.96), giant capillaries (0.84) and microhemorrhages (0.90), but it is poor for the branched or arboriform capillaries (0.64).48,62
Capillaroscopy and involvement of other organsCapillaroscopy can also be used as a predictor of the appearance of cutaneous ulcers in patients with SSc. Sebastiani et al., developed the skin ulceration risk index in SSc (CSURI).39 This index is determined as follows: carrying out capillaroscopy of the 2, 3, 4 and 5 fingers of both hands and taking the image that contains the smallest number of capillaries found per field (N) and the largest number of megacapillaries (M). The formula for calculating it is: D×M/N2 where (D) is the maximum diameter of the megacapillaries found. If the obtained value is greater than 2.96, the patient is at risk of developing a digital ulcer in the next 3 months, with an area under the curve of 0.884 (95% CI: 0.835–0.922), a specificity of 81.4% and a sensitivity of 92.9%.39,40,64
The NC is considered, currently, a putative biomarker, since it allows to detect which patients might develop a serious organ commitment in the future.10,53,65
Bredemeier et al., in a study conducted in 91 patients with SSc, found that the avascular areas in the capillaroscopy were related with more serious cutaneous alterations, long-lasting disease, peripheral signs of ischemia, esophageal dysfunction, anti-Scl70 antibodies and ground glass opacity in lungs.66 Indeed, in the patients with interstitial lung disease, the NC allows to differentiate between the idiopathic form and the associated with AD.67 In pulmonary arterial hypertension, the main capillaroscopic change is the decrease in the number of capillaries, which is related to the severity of this condition, both in patients with SSc and in subjects with undifferentiated connective tissue disease68 although not all authors have found a correlation between the capillaroscopic alterations and the severity of the pulmonary arterial hypertension.69
ConclusionNailfold videocapillaroscopy, given the current evidence, constitutes a biomarker in rheumatology; it is a tool that allows the adequate evaluation of the primary and secondary RP, facilitates the detection of systemic autoimmune diseases, and provides the opportunity to evaluate the therapeutic response of various pharmacological interventions, thus preventing the development of irreversible vasculopathy and the subsequent cumulative organ damage.
FundingThe work was not supported by any grant or pharmaceutical funds.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Colmenares Roldán LM, Velásquez Franco CJ, Mesa Navas MA. Capilaroscopia en esclerosis sistémica: una revisión narrativa de la literatura. Rev Colomb Reumatol. 2016;23:250–258.