The overall objective of the study is to determine the ability of TOF-Cuff device (blood-pressure modified cuff, including stimulation electrodes) to monitor with the same device the non-invasive blood pressure (NIBP) and the depth of a neuromuscular blockade (NMB) induced pharmacologically, by stimulation of the brachial plexus at the humeral level and recording evoked changes in arterial pressure.
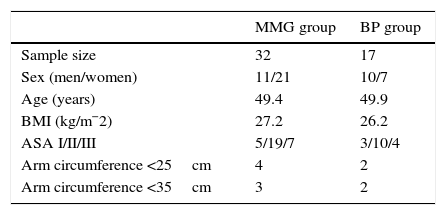
Material and methodClinical, single-centre, open-controlled study with 32 adult patients ASA I-III for scheduled elective surgery under general anaesthesia in supine position, for the validation of neuromuscular monitoring, comparing the values obtained from neuromuscular relaxation TOF-Cuff with those obtained by mechanomyography (MMG) (control method) during the recovery phase of NMB, when a TOF ratio >0.7 and >0.9 (primary endpoint) were reached respectively. And an additional consecutive study of 17 patients for validation of NIBP monitoring with TOF-Cuff device vs invasive blood pressure measured by an intra-arterial catheter. All data were analysed using the Bland–Altman method.
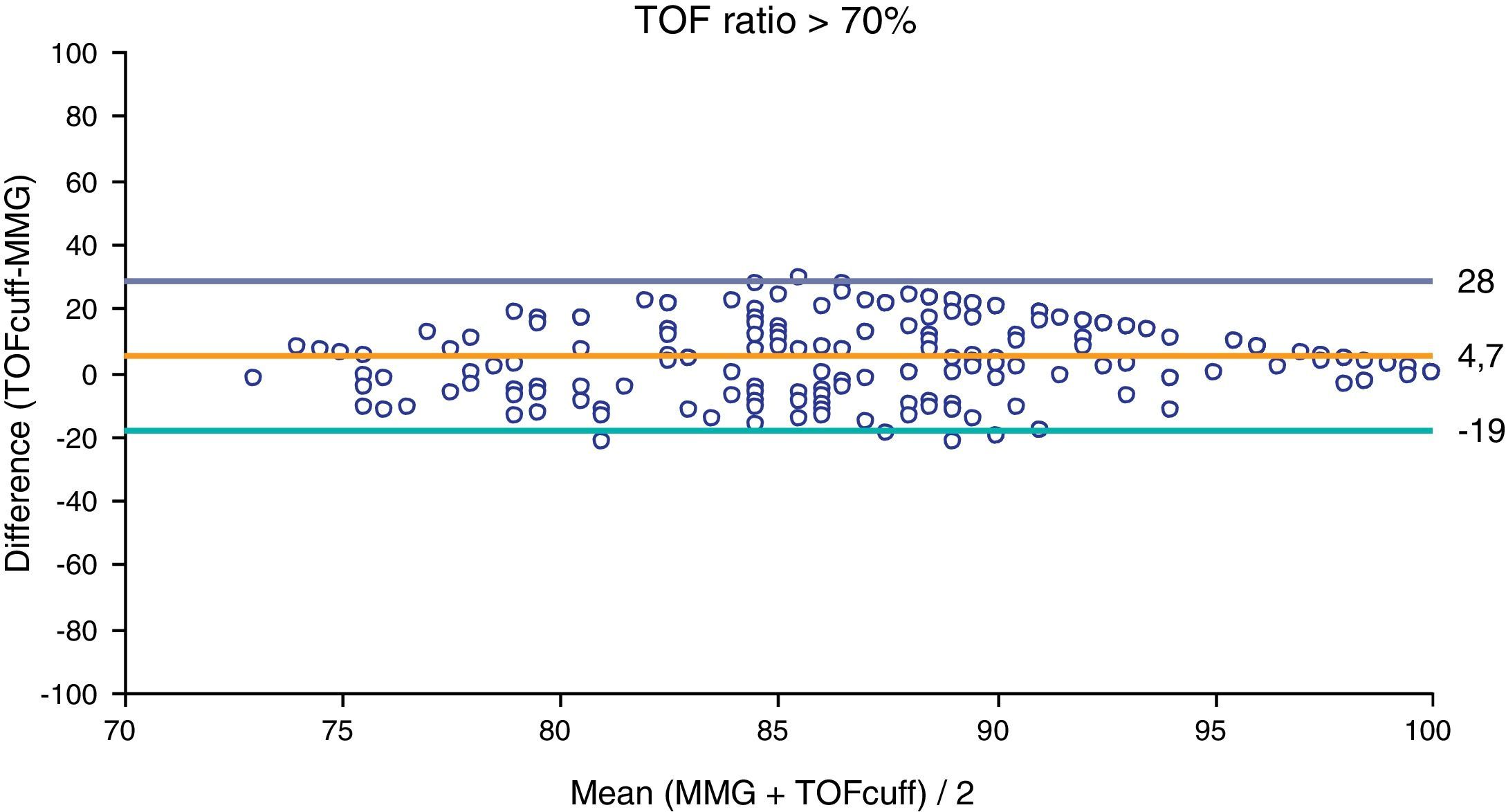
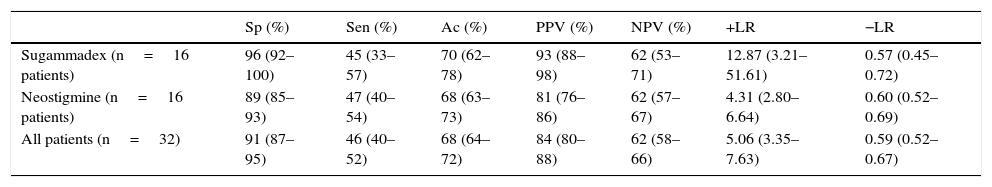
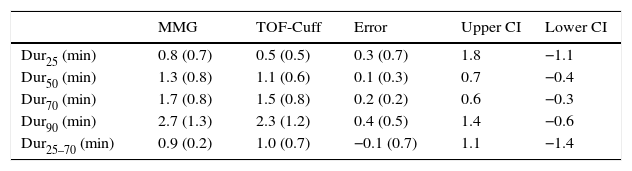
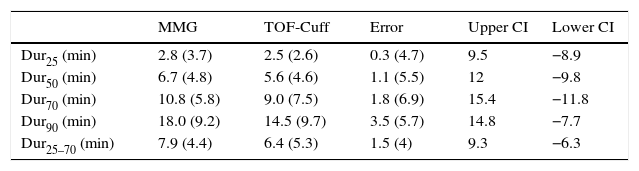
ResultsRecovery from NMB measured with the TOF-Cuff was earlier compared to MMG. Comparing TOF-ratio >0.9 measured with TOF-Cuff vs TOF-ratio >0.7 with MMG, a specificity of 91% and a positive predictive value of 84% were obtained.
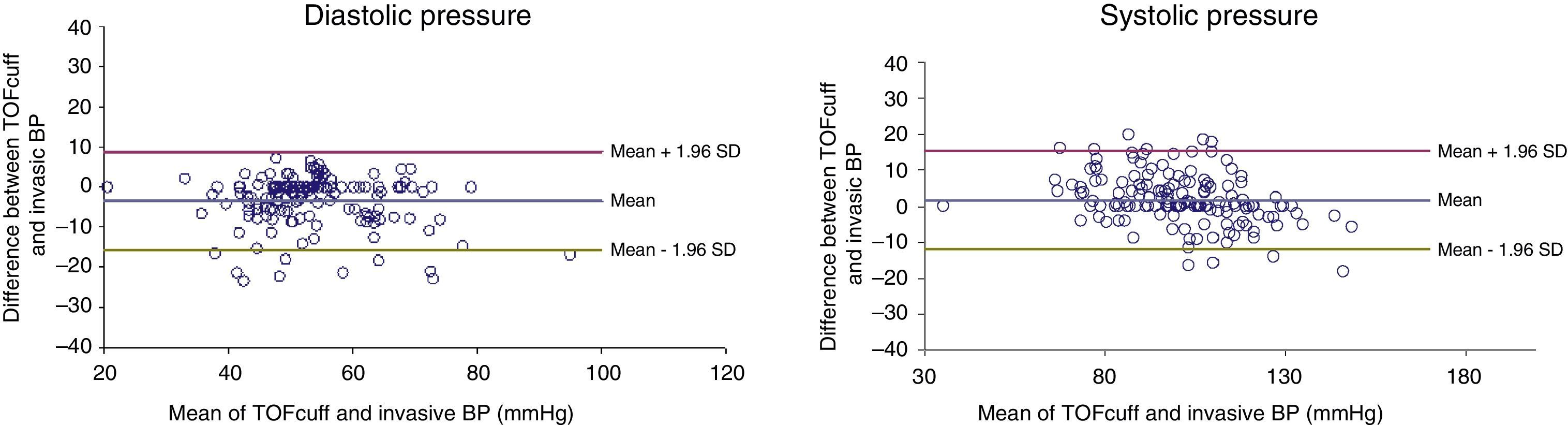
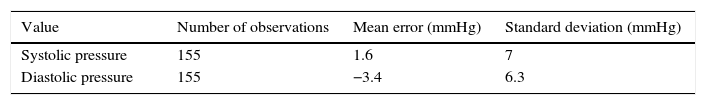
In NIBP measurement, the mean error and standard deviation of both systolic blood pressure (1.6±7mmHg) and diastolic blood pressure (−3.4±6.3) were within the European accuracy requirements for medical devices.
ConclusionsThe TOF-Cuff device has been shown to be valid and safe in the monitoring of NMB and in the measurement of NIBP, with no patient presenting any adverse events, skin-level lesions or residual pain. It is not interchangeable with MMG, having a TOF-ratio >0.9 quantified by the TOF-Cuff device, a good correlation with a TOF-ratio >0.7 on MMG.
Determinar la capacidad del dispositivo TOF-Cuff (manguito de presión modificado que incluye electrodos de estimulación) para monitorizar la presión arterial no invasiva (PANI) y el nivel de bloqueo neuromuscular (BNM) inducido farmacológicamente.
Material y métodoEstudio observacional, prospectivo, de 32 pacientes adultos ASA I-III programados para cirugía bajo anestesia general, para la validación de la monitorización del BNM con el dispositivo TOF-Cuff vs. mecanomiografía (MMG, método control) durante la fase de recuperación del BNM, cuando se alcanzó un TOF-ratio de 0,9 con TOF-Cuff y de 0,7 con la MMG (variable principal). Para completar el estudio principal se realizó un estudio adicional consecutivo al anterior y que incluyó a 17 pacientes para validar el dispositivo TOF-Cuff en la monitorización de la PANI en comparación con la presión arterial invasiva a nivel de la arteria radial (método control). Los datos fueron analizados mediante el método de Bland-Altman.
ResultadosSe produjo un adelanto de la recuperación medida con TOF-Cuff respecto a la mecanomiografía. Al comparar un TOF-ratio>0,9 cuantificado mediante TOF-Cuff con un TOF-ratio>0,7 en la MMG tuvo una especificidad del 91% y un valor predictivo positivo del 84%.
En la medición de la PANI, el error medio y la desviación estándar tanto de la presión arterial sistólica (1,6±7mmHg) como diastólica (−3,4±6,3) estuvieron dentro de los requisitos europeos de precisión para aparatos sanitarios.
ConclusionesEl dispositivo TOF-Cuff ha mostrado ser válido y seguro en la monitorización del BNM y en la medición de la PANI, no presentando ningún paciente acontecimientos adversos, lesiones a nivel de la piel o dolor residual. No es intercambiable con la MMG, teniendo un TOF-ratio>0,9 cuantificado mediante el dispositivo TOF-Cuff, una buena correlación con un TOF-ratio>0,7 en la MMG.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora