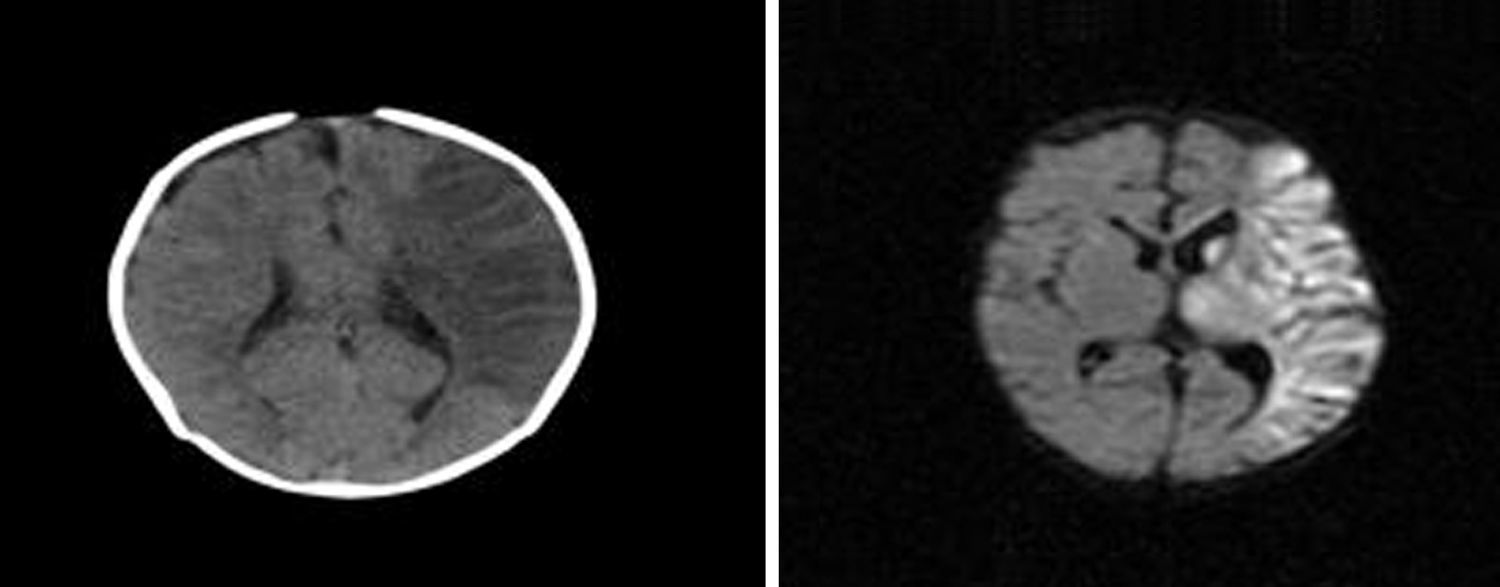
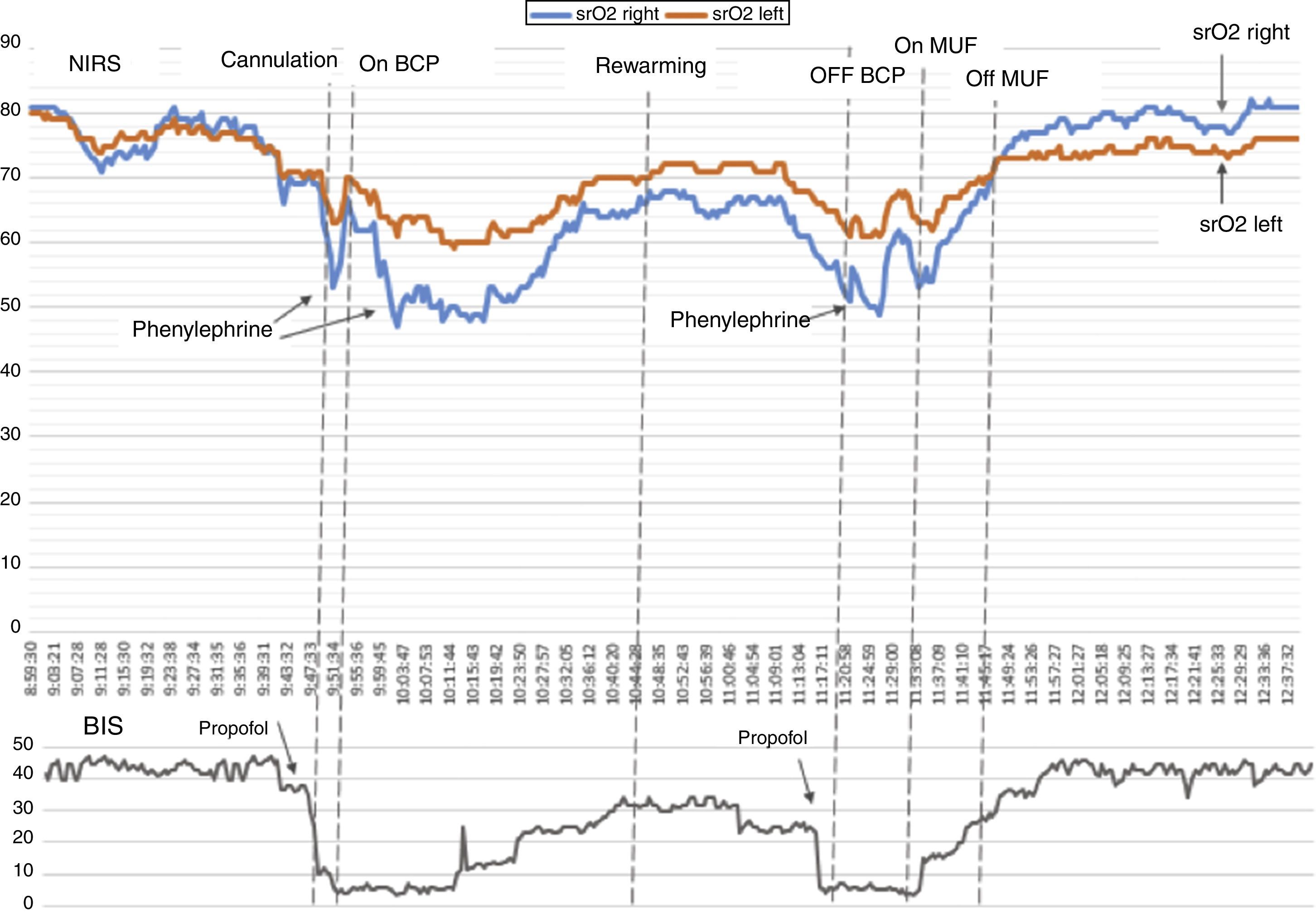
Cerebral oximetry based on near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) technology is used to determine cerebral tissue oxygenation. We hereby present the clinical case of a 12-month old child with right hemiparesis secondary to prior left middle cerebral artery stroke 8 months ago. The child underwent surgical enlargement of the right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) with cardiopulmonary bypass. During cardiopulmonary bypass, asymmetric NIRS results were detected between both hemispheres. The utilization of multimodal neuromonitoring (NIRS-BIS) allowed acting on both perfusion pressure and anesthetic depth to balance out the supply and demand of cerebral oxygen consumption. No new neurological sequelae were observed postoperatively. We consider bilateral NIRS monitoring necessary in order to detect asymmetries between cerebral hemispheres. Although asymmetries were not present at baseline, they can arise intraoperatively and its monitoring thus allows the detection and treatment of cerebral ischemia-hypoxia in the healthy hemisphere, which if undetected and untreated would lead to additional neurological damage.
La oximetría cerebral «near infrared spectroscopy» (NIRS) determina la oxigenación tisular cerebral. Describimos el caso clínico de un niño de 12 meses de edad con hemiparesia derecha secundaria a infarto de arteria cerebral media izquierda hacía 8 meses. El niño fue sometido a una ampliación del tracto de salida del ventrículo derecho por estenosis pulmonar mediante bypass cardiopulmonar. En periodos del bypass cardiopulmonar se detectan asimetrías NIRS entre ambos hemisferios cerebrales con descensos críticos en hemisferio derecho lo que indica estados de perfusión y consumo de oxígeno diferentes entre los 2 hemisferios. La utilización de neuromonitorización multimodal NIRS-BIS permitió actuar sobre la presión de perfusión y profundidad anestésica para equilibrar la balanza entre el aporte y el consumo de oxígeno cerebral. No se detectó daño neurológico sobreañadido en el postoperatorio.
Consideramos necesaria la monitorización NIRS bilateral para detectar asimetrías entre los 2 hemisferios, que aunque no se manifiesten en el registro basal, pueden surgir en el periodo intraoperatorio, permitiendo detectar y tratar la isquemia-hipoxia cerebral en el hemisferio sano, que provocaría un daño neurológico sobreañadido.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora