The erector spinae plane (ESP) block is a novel technique for the treatment of acute and chronic pain. Its mechanism and site of action has not yet been explained properly.
ObjectivesIn order to explain the mechanism of action of the ESP block, injections were performed with methylene blue to simulate the local anaesthetics and to determine its distribution from the anterior side of the thorax. To find an aperture or channel through which the local anaesthetic passes from posterior to anterior through the muscular and bone structures.
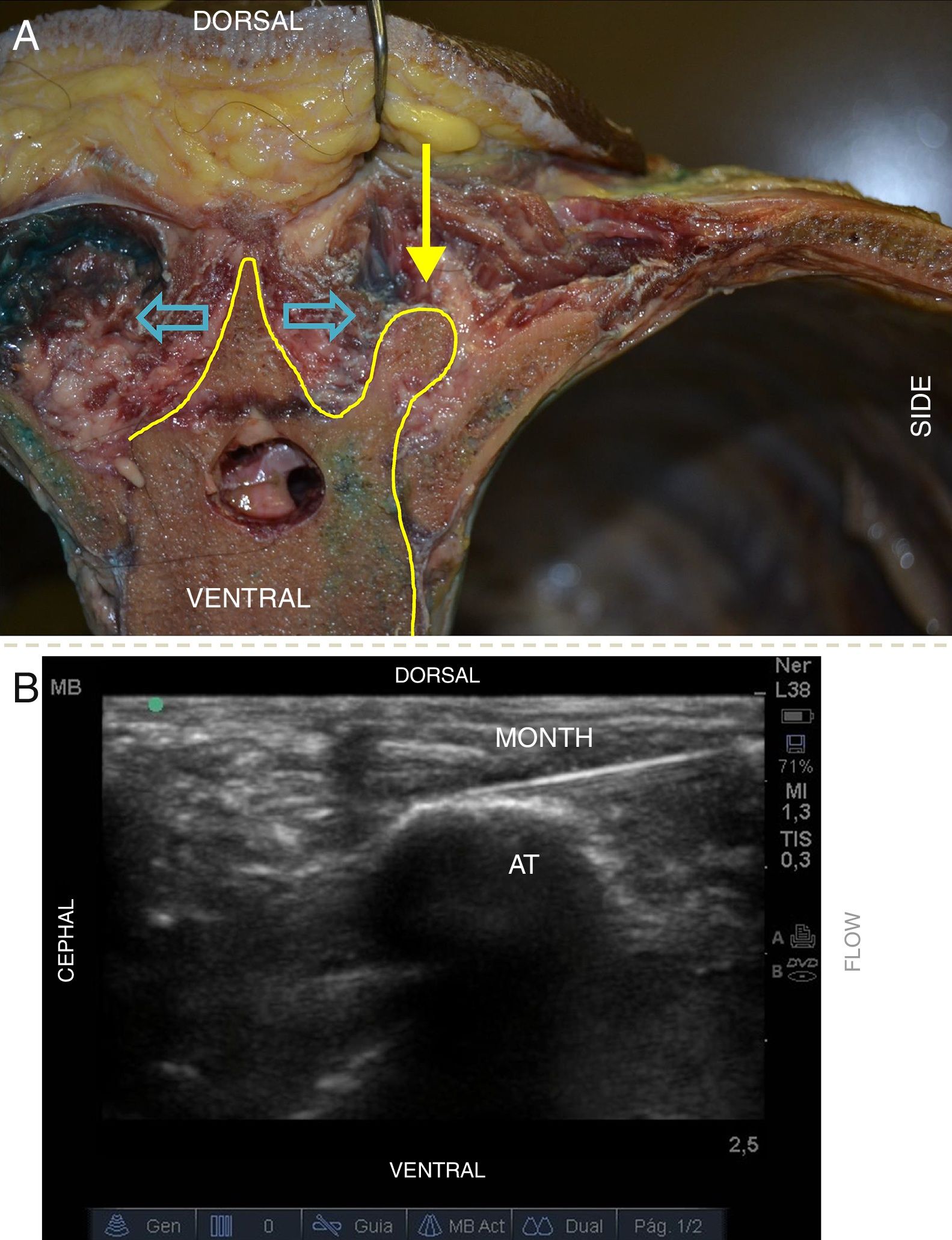
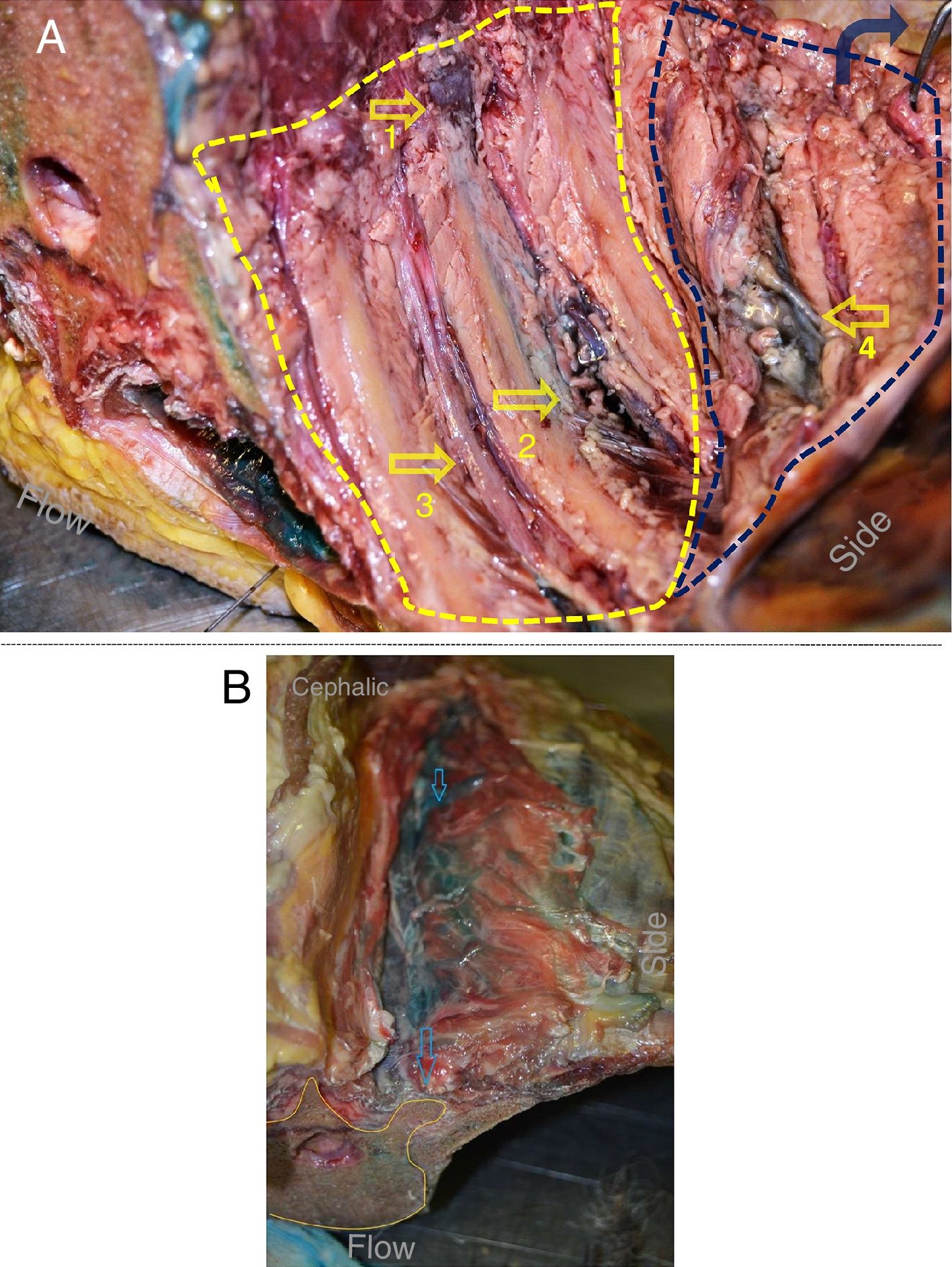
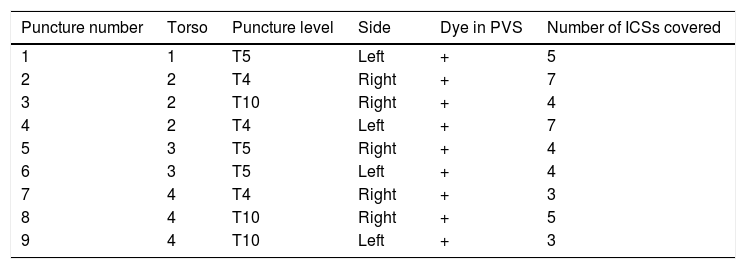
Materials and methodsFour spinal columns of fresh cryopreserved corpses were used. A total of 9 ultrasound-guided ESP blocks were performed in different regions of the specimens using 20ml of 0.01% methylene blue per block. The distribution of the dye was observed from the anterior side of the thorax, measuring the amount of intercostal spaces stained, before and after the removal of the parietal pleura, and the structures in which the stain was found were recorded.
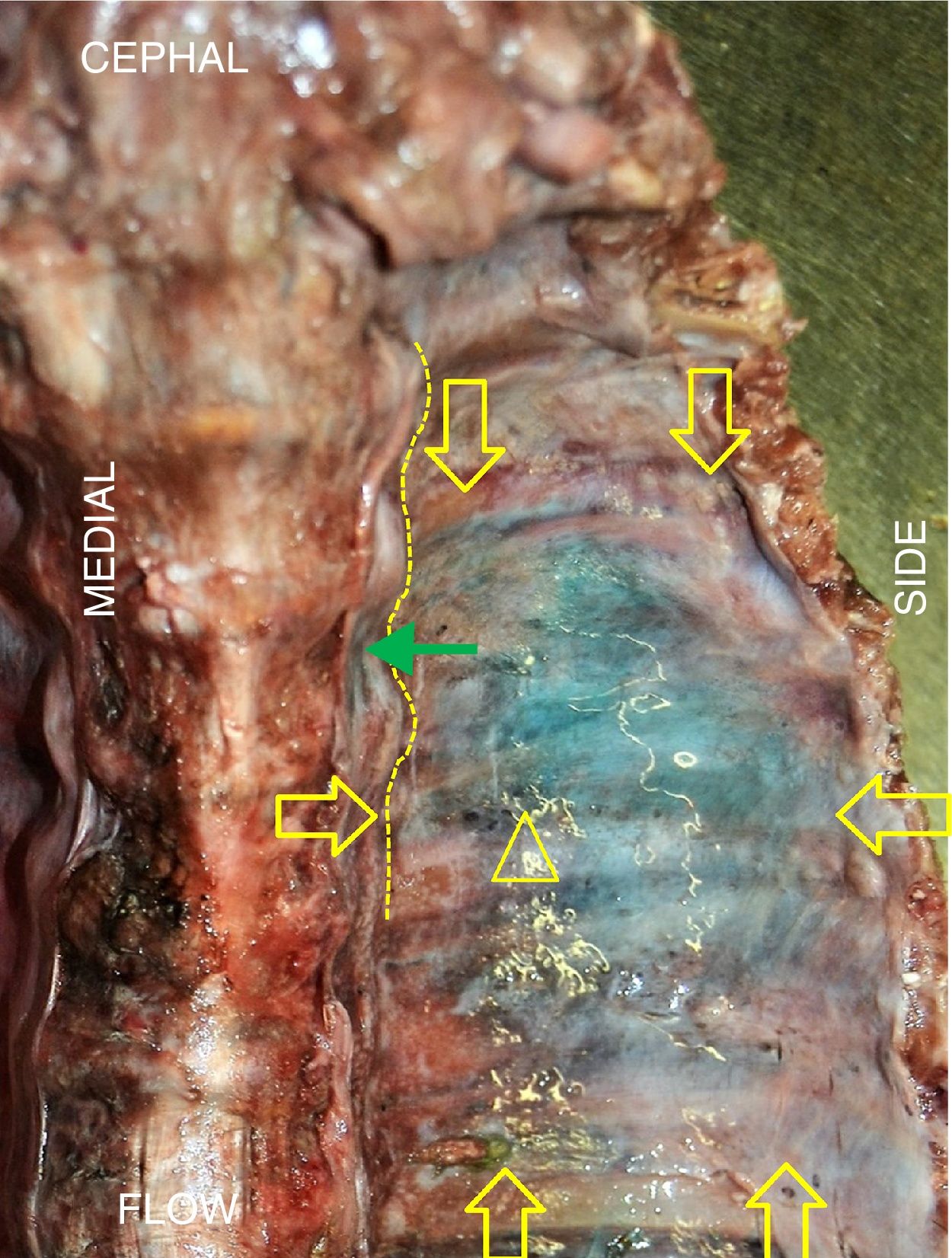
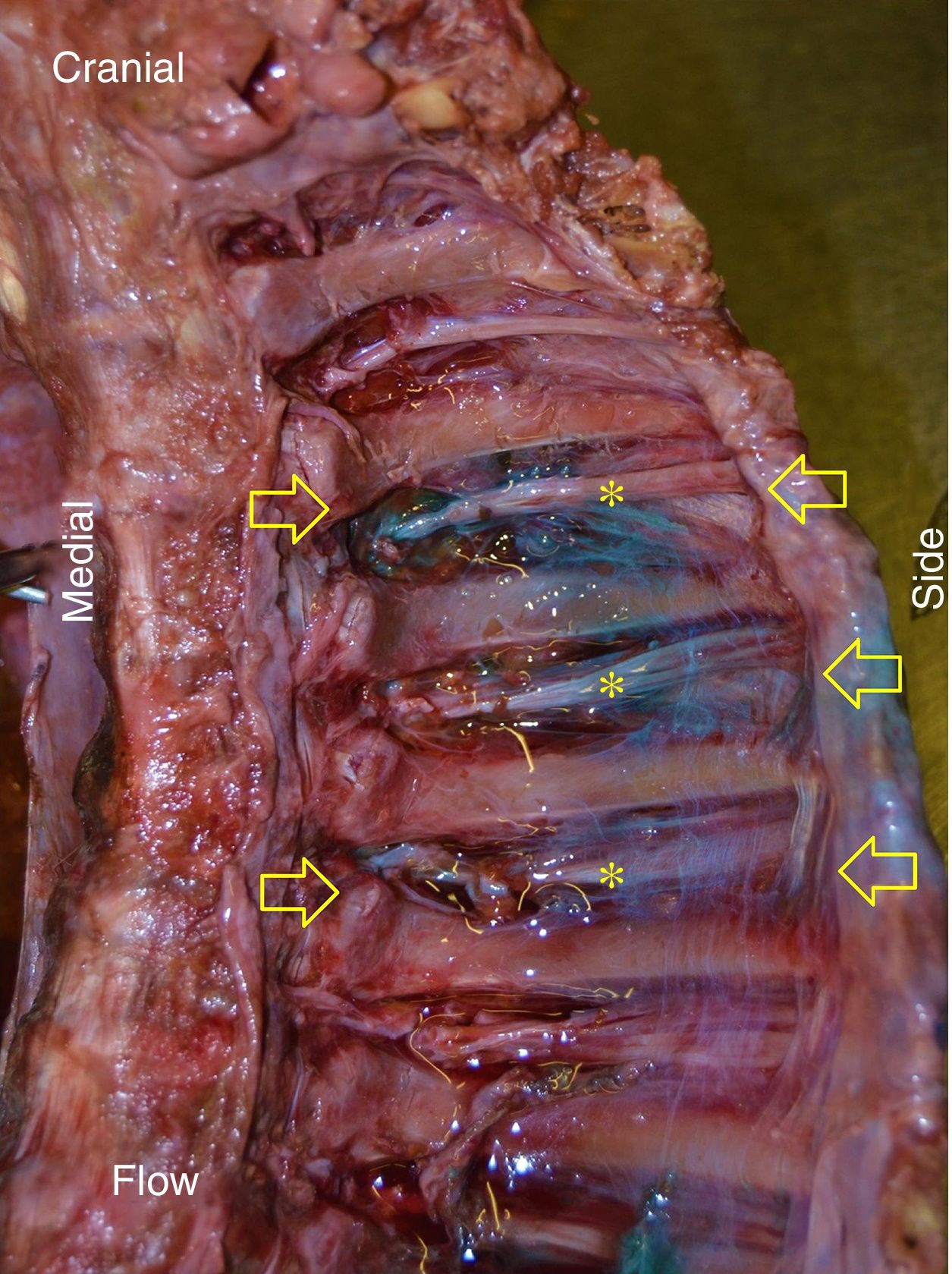
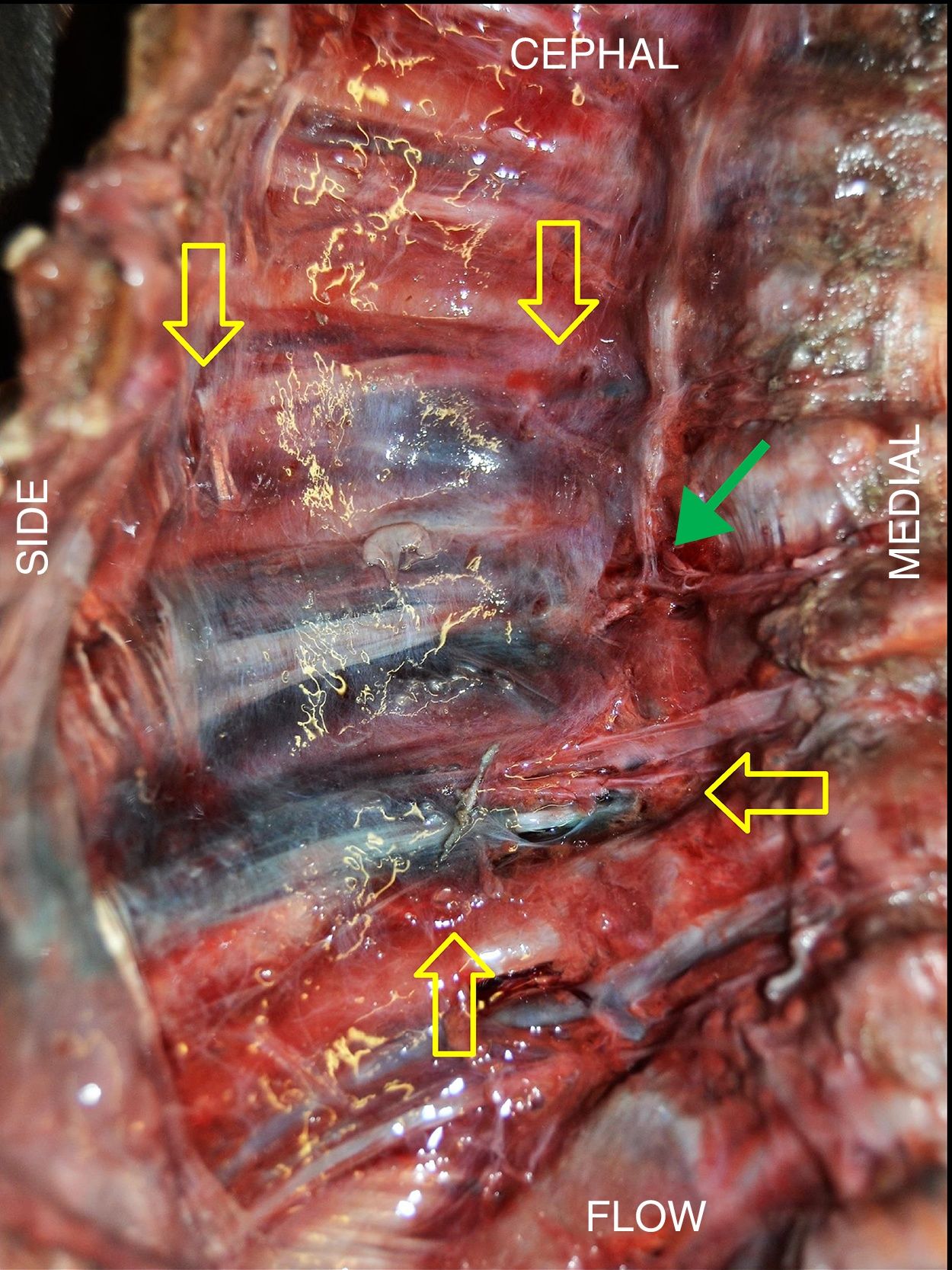
ResultsIn all blocks of the ESP, dye was found in the paravertebral space, intercostal spaces, and in some cases in the prevertebral chain. The blocks had a mean of 4.6 intercostal spaces stained, with a maximum of 7 and a minimum of 3. The intensity of the dye was greater on the side of the injection, dorsal to the column, than that found in the ventral part below of the pleura. It was not possible to verify a clear channel through which the dye diffuses towards the previous zone.
ConclusionsFrom the data collected in this study, it can be deduced that the blockade of the ESP has a mechanism of anaesthetic action similar to paravertebral blocks. The site from which the anaesthetic would cross from the posterior plane of the spine to the anterior region of the thorax was not clear, and should be investigated in future works.
El bloqueo del plano del músculo erector (ESP) es una técnica novedosa para el tratamiento del dolor agudo y crónico. Su lugar y mecanismo de acción todavía no han sido explicados.
ObjetivosDeterminar el mecanismo de acción del anestésico local en el bloqueo ESP a través de la inyección del azul de metileno, describiendo su distribución desde la cara anterior del tórax. Hallar o determinar un paso o canal por el cual el anestésico atraviesa las estructuras musculares y óseas de posterior a anterior.
Materiales y métodosSe utilizaron 4 columnas de cadáveres frescos criopreservados. Se realizaron 9 bloqueos ESP ecoguiados en diferentes regiones de los especímenes con 20ml de azul de metileno al 0,01% por bloqueo. Se observó la distribución del colorante desde la cara anterior de tórax, midiendo la cantidad de espacios intercostales teñidos, antes y después de la extracción de la pleura parietal, y se registraron las estructuras en que se constató tintura.
ResultadosEn todos los bloqueos ESP se encontró colorante en el espacio paravertebral, los espacios intercostales y en algunos casos en la cadena prevertebral. Los bloqueos tuvieron un promedio de 4,6 espacios intercostales teñidos, con un máximo de 7 y un mínimo de 3. La intensidad del colorante fue mayor del lado de la inyección, dorsal a la columna, que el hallado en la parte ventral por debajo de la pleura. No se logró constatar un mecanismo claro por el que el colorante difundiera hacia el la zona anterior.
ConclusionesPor los datos recogidos en este trabajo se puede deducir que el bloqueo ESP tiene un mecanismo de acción anestésico similar a los bloqueos paravertebrales. El sitio por el cual el anestésico atravesaría desde el plano posterior de la columna a la región anterior del tórax no fue aclarado y debería ser investigado en futuros trabajos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora