Evaluar la captación metabólica de diferentes signos tomográficos observados en pacientes con hallazgos estructurales incidentales sugestivos de neumonía por COVID-19 mediante PET/TC con 18F-FDG.
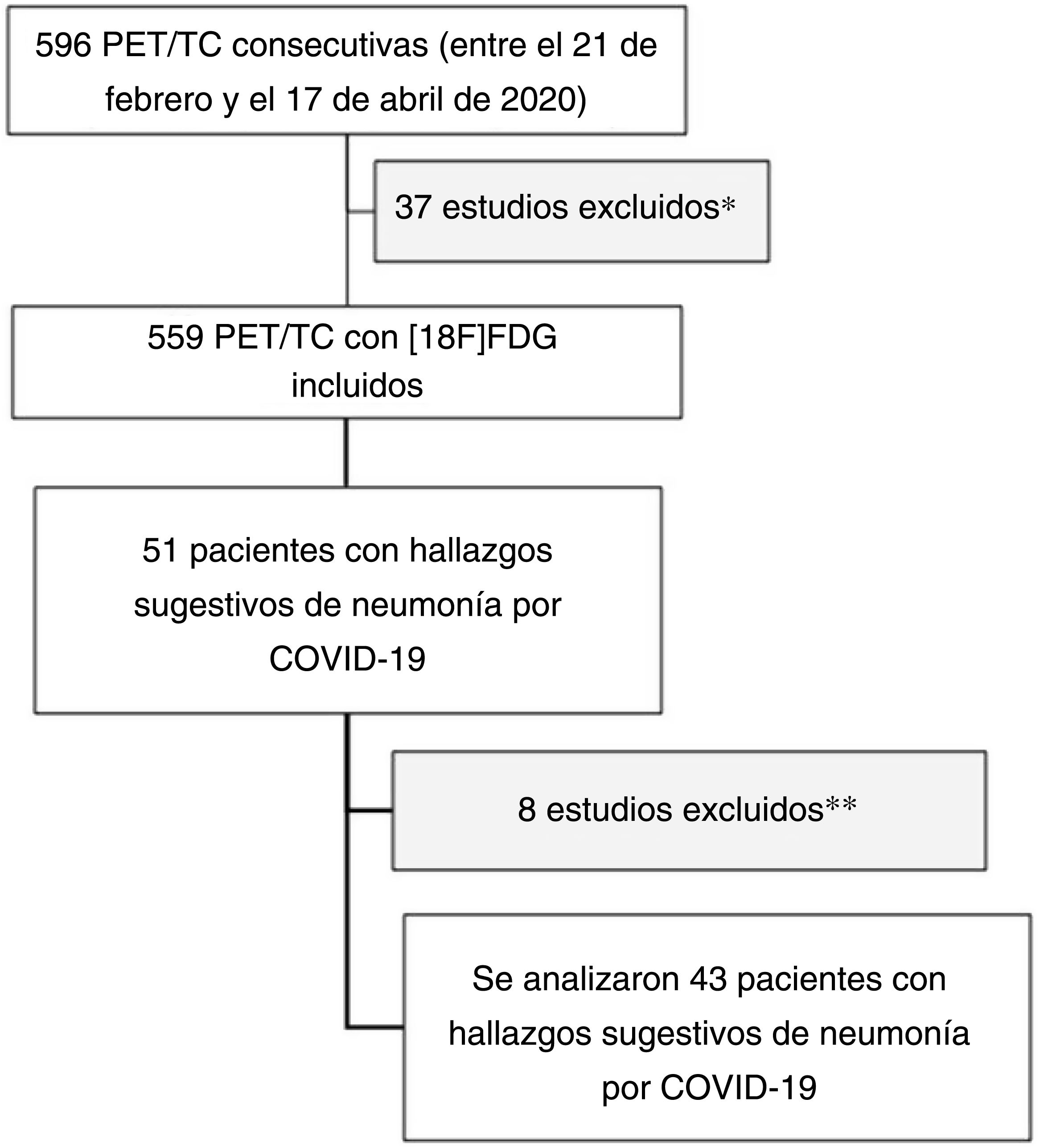
Material y métodosSe analizaron retrospectivamente 596 estudios PET/TC realizados desde el 21 de febrero de 2020 hasta el 17 de abril de 2020. Tras excluir 37 exploraciones (trazadores PET diferentes a la 18F-FDG y estudios cerebrales), se evaluó la actividad metabólica de varios cambios estructurales integrados en la puntuación CO-RADS mediante el SUVmáx de estudios multimodales con 18F-FDG.
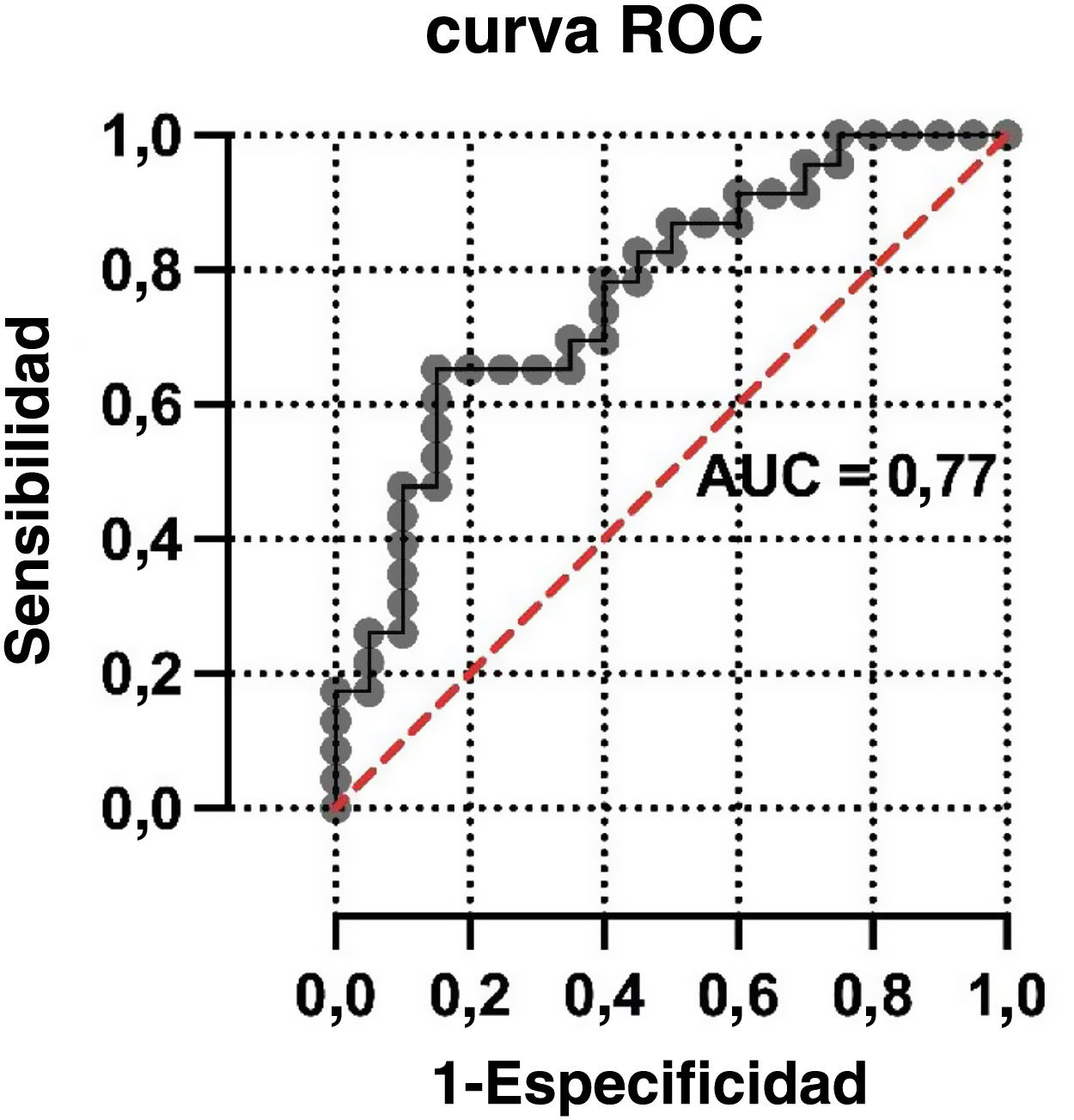
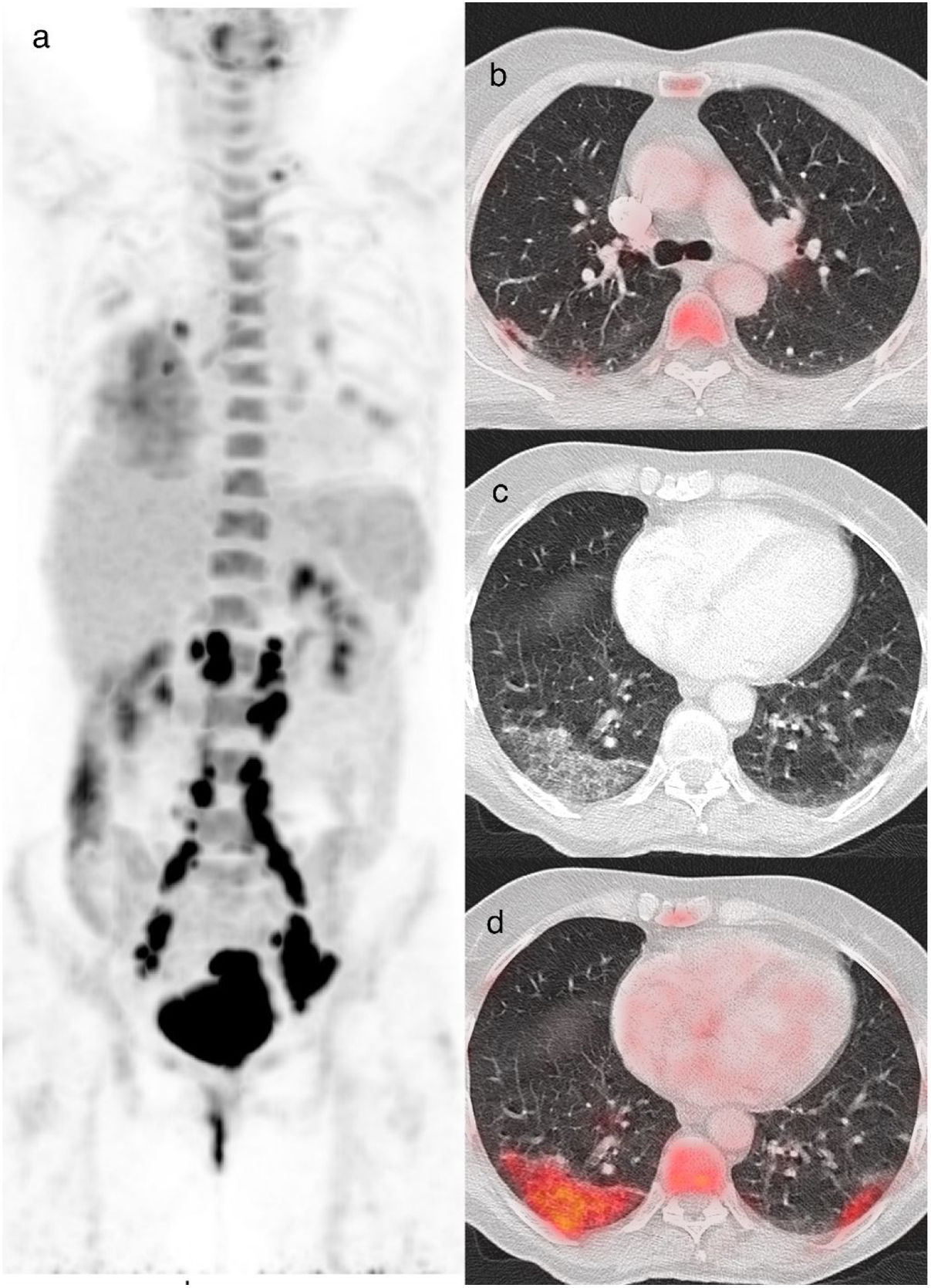
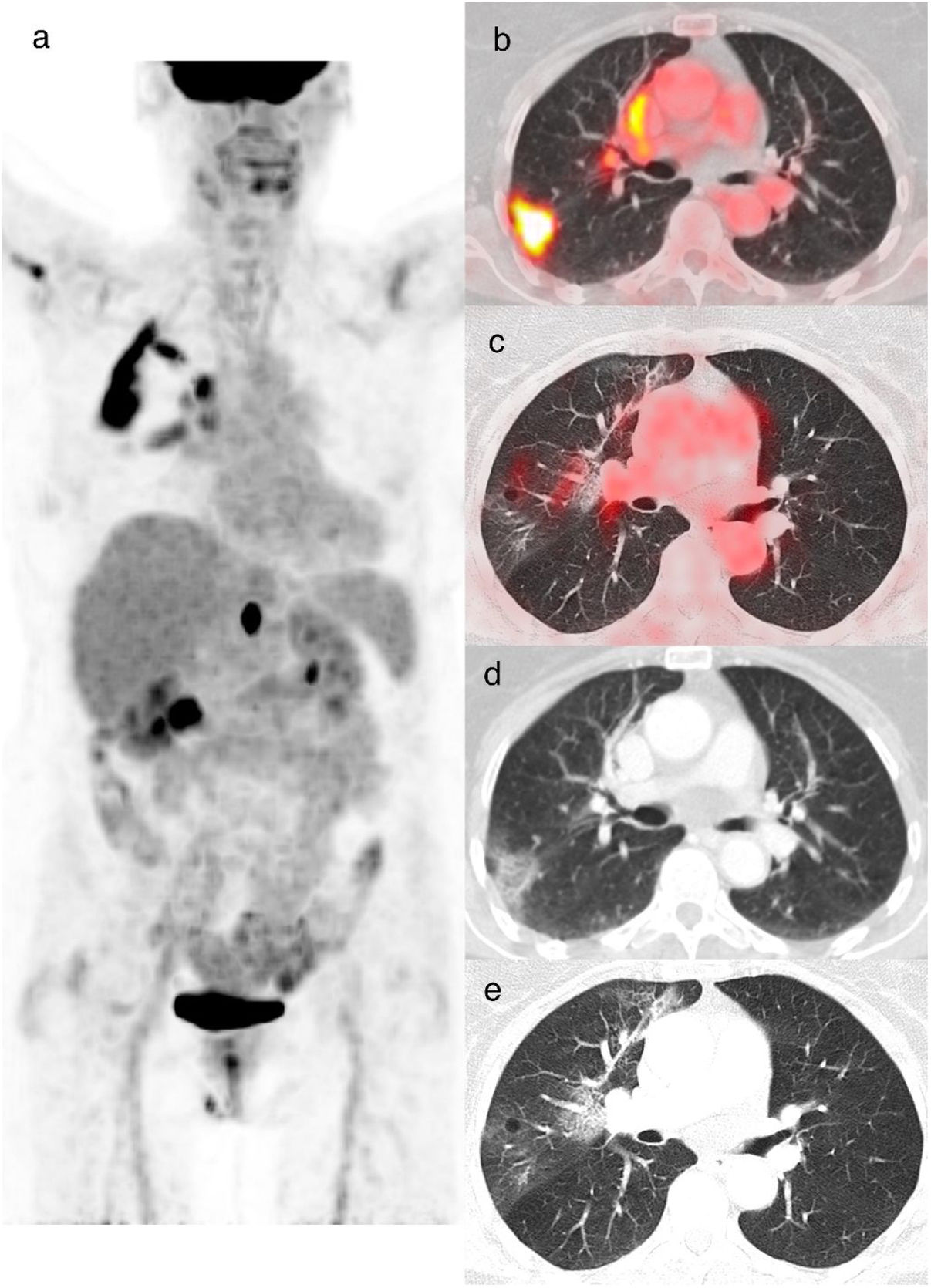
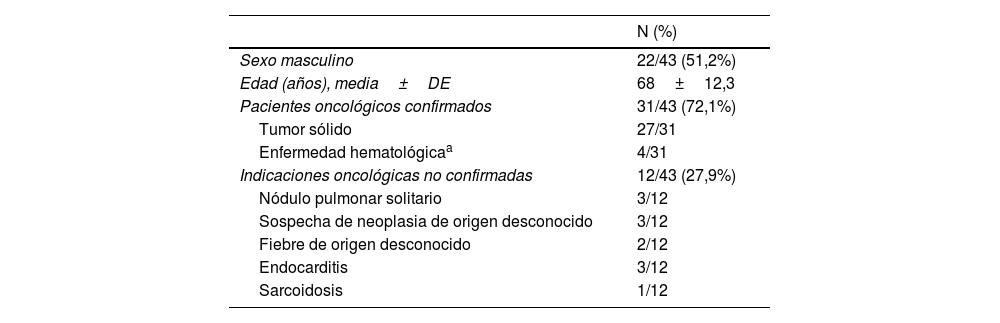
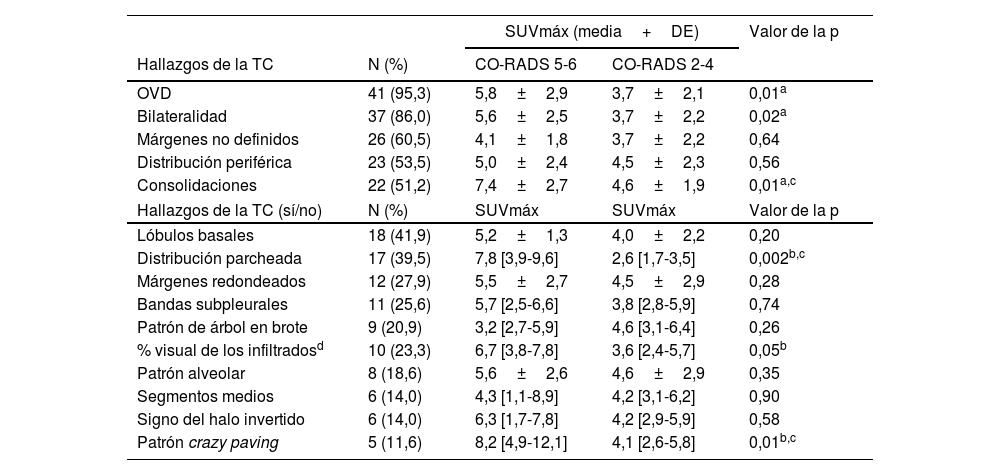
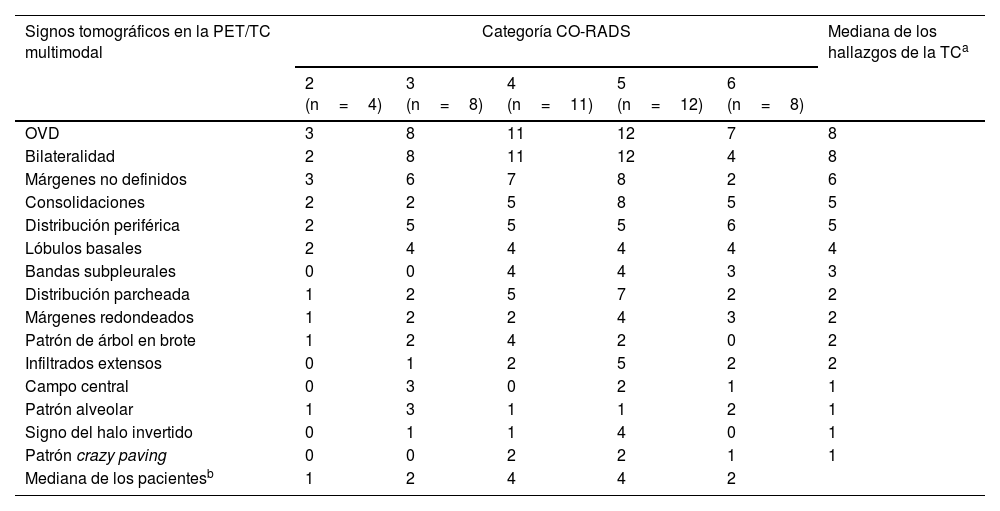
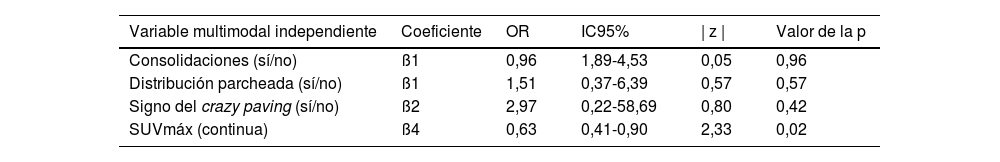
ResultadosSe incluyeron 43 pacientes r COVID-19 en la 18F-FDG PET/TC (edad media: 68±12,3 años, 22 varones). Los valores de SUVmáx fueron mayores en los pacientes con categorías CO-RADS 5-6 respecto a los de categorías CO-RADS inferiores (6,1±3,0 vs. 3,6±2,1, p=0,004). En los pacientes con CO-RADS 5-6, las opacidades en vidrio deslustrado, la bilateralidad y las consolidaciones mostraron valores de SUVmáx más elevados (valores de la p de 0,01, 0,02 y 0,01, respectivamente). La distribución parcheada y el patrón crazy paving también se asociaron a valores de SUVmáx más elevados (valores de p de 0,002 y 0,01). Tras el análisis multivariable, el SUVmáx se asoció significativamente con un diagnóstico estructural positivo de neumonía por COVID-19 (odds ratio=0,63, intervalo de confianza del 95%=0,41-0,90; p=0,02). La curva ROC del modelo de regresión destinado a confirmar o descartar el diagnóstico estructural de neumonía por COVID-19 mostró un AUC de 0,77 (error estándar=0,072; p=0,003).
ConclusionesEn aquellos pacientes remitidos a 18F-FDG PET/TC por indicaciones oncológicas y no oncológicas estándar (43/559; 7,7%) durante la pandemia, la obtención de imágenes multimodales es una herramienta útil durante la detección incidental de neumonía. Diferentes hallazgos en la TC característicos de la neumonía por COVID-19, específicamente los incluidos en las puntuaciones CO-RADS diagnósticas (5-6), se asociaron con valores SUVmáx más elevados.
To evaluate the metabolic uptake of different tomographic signs observed in patients with incidental structural findings suggestive of COVID-19 pneumonia through 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Material and methodsWe retrospectively analyzed 596 PET/CT studies performed from February 21, 2020 to April 17, 2020. After excluding 37 scans (non-18F-FDG PET tracers and brain studies), we analyzed the metabolic activity of several structural changes integrated in the CO-RADS score using the SUVmax of multimodal studies with 18F-FDG.
ResultsForty-three patients with 18F-FDG PET/CT findings suggestive of COVID-19 pneumonia were included (mean age: 68±12.3 years, 22 male). SUVmax values were higher in patients with CO-RADS categories 5–6 than in those with lower CO-RADS categories (6.1±3.0 vs. 3.6±2.1, p=0.004). In patients with CO-RADS 5–6, ground-glass opacities, bilaterality and consolidations exhibited higher SUVmax values (p-values of 0.01, 0.02 and 0.01, respectively). Patchy distribution and crazy paving pattern were also associated with higher SUVmax (p-values of 0.002 and 0.01). After multivariate analysis, SUVmax was significantly associated with a positive structural diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia (odds ratio=0.63, 95% confidence interval=0.41–0.90; p=0.02). The ROC curve of the regression model intended to confirm or rule out the structural diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia showed an AUC of 0.77 (standard error=0.072, p=0.003).
ConclusionsIn those patients referred for standard oncologic and non-oncologic indications (43/559; 7.7%) during pandemic, imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT is a useful tool during incidental detection of COVID-19 pneumonia. Several CT findings characteristic of COVID-19 pneumonia, specifically those included in diagnostic CO-RADS scores (5–6), were associated with higher SUVmax values.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora