Analizar la perfusión cerebral y el metabolismo cerebral de glucosa en el deterioro cognitivo mediante SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO y 18F-FDG PET/TAC.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 22 pacientes con deterioro cognitivo: 4 quejas subjetivas de memoria (QSM), 8 deterioro cognitivo leve (DCL) amnésico, 5 enfermedad de Alzheimer (EA) prodrómica y 5 EA. Se realizó una comparación visual de la SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO y 18F-FDG PET/TAC en cada grupo clínico.
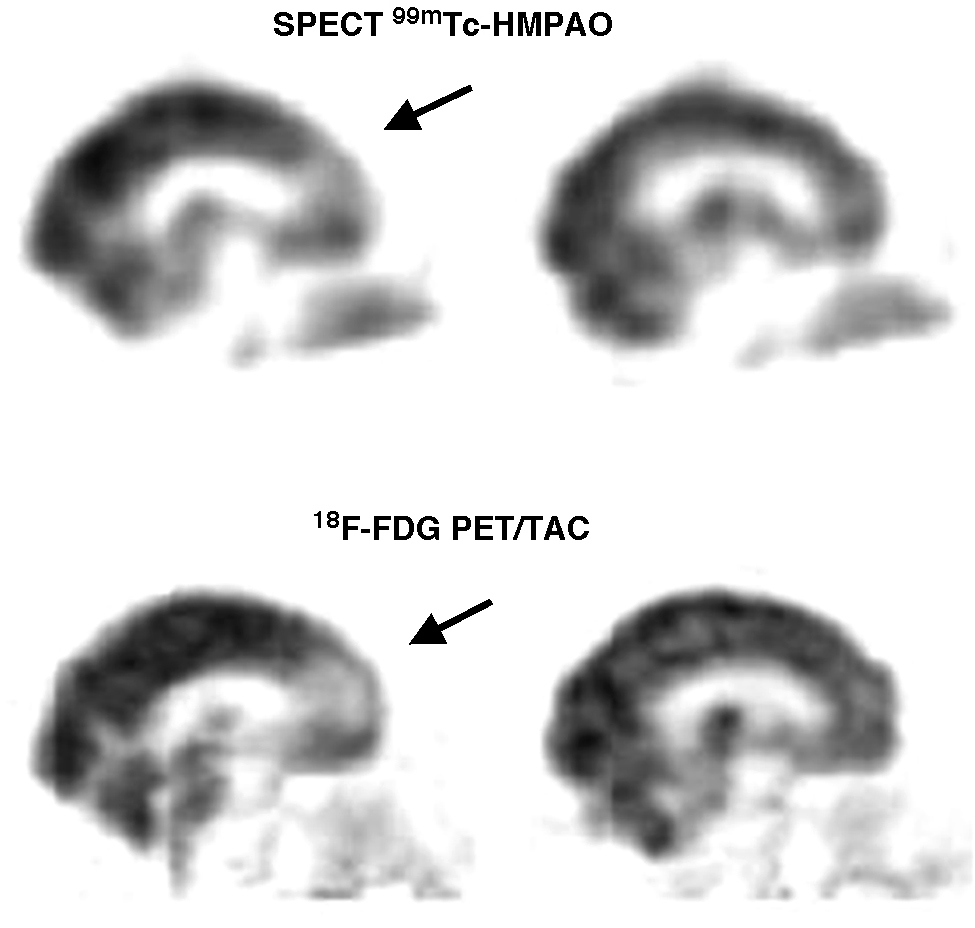
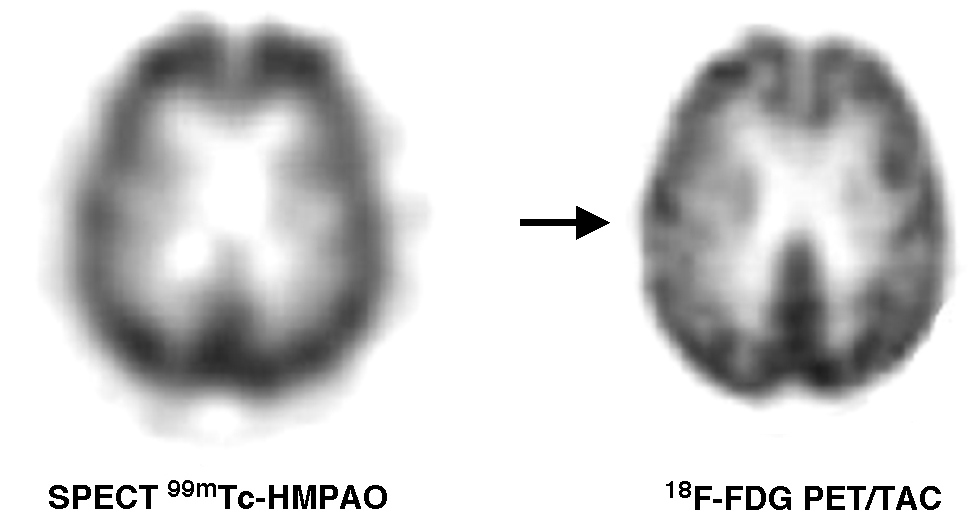
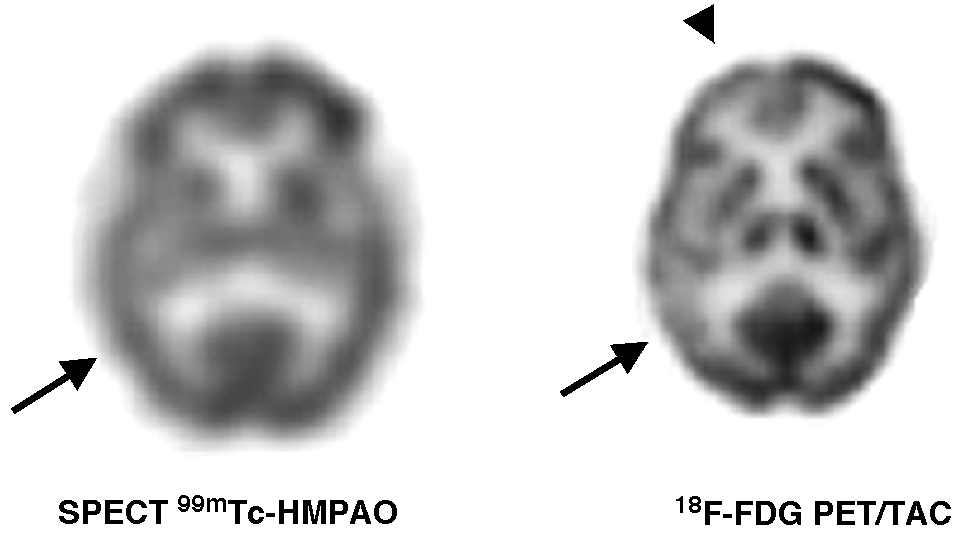
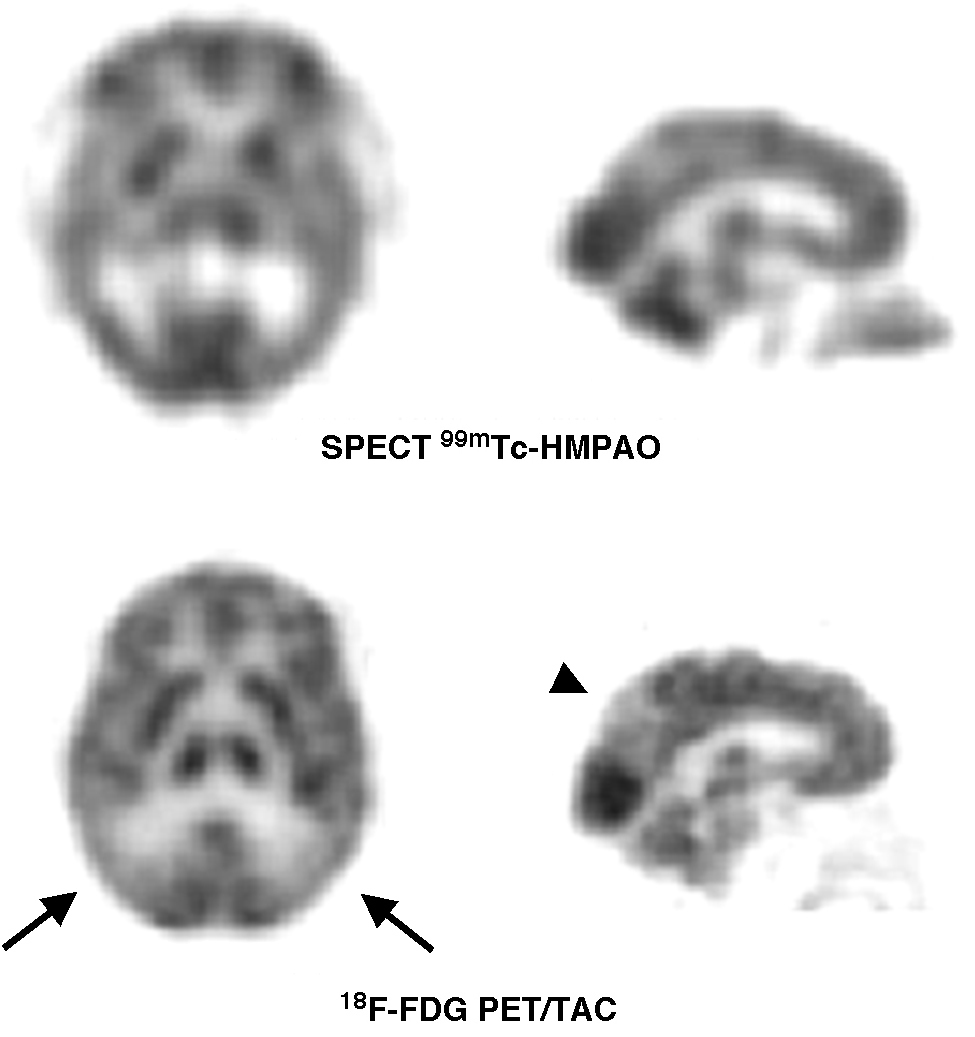
ResultadosLa SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO mostró áreas de hipoperfusión en 15 pacientes y fue normal en 7. La 18F-FDG PET/TAC mostró hipometabolismo regional cerebral en 19 pacientes y fue normal en tres. La distribución de las alteraciones en la SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO y en la 18F-FDG PET/TAC fue similar en 9 pacientes (2 QSM, 2 DCL amnésico, 2 EA prodrómica y 3 EA). En 6 pacientes (1 DCL amnésico, 2 EA prodrómica y 3 EA) el hipometabolismo de FDG fue más extenso que la hipoperfusión cerebral. En 4 pacientes (1 QSM, 3 DCL amnésico) la 18F-FDG PET/TAC fue patológica con SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO normal. Ambos estudios fueron normales en tres pacientes (1 QSM, 2 DCL amnésico).
ConclusiónLa SPECT de perfusión cerebral 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT y la 18F-FDG PET/TAC mostraron alteraciones en la perfusión y en el metabolismo cerebral de pacientes con deterioro cognitivo, incluso en pacientes con QSM. En pacientes con SPECT de perfusión cerebral normal se puede detectar hipometabolismo cerebral de la glucosa. En algunos pacientes la extension del hipometabolismo de la FDG es mayor que la correspondiente área de hipoperfusión.
The aim of this study was to analyze cerebral perfusion and glucose metabolism in patients with cognitive impairment using cerebral blood flow 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans.
Material and methodsTwenty-two patients with cognitive impairment were included: 4 subjective memory complaints (SMC), 8 amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI), 5 prodromic Alzheimer's disease (AD) and 5 AD. In each clinical group, 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans were performed.
Results99mTc-HMPAO SPECT showed regions of cerebral hypoperfusion in 15 patients and was normal in 7 of the 22 patients. 18F-FDG PET/CT scan showed cerebral regional hypometabolism in 19 patients and was normal in the other 3 patients. The distribution of abnormalities on 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans was similar in 9 patients (2 SMC, 2 amnestic MCI, 2 prodromic AD, and 3 AD). In 6 patients (1 amnestic MCI, 2 prodromic AD, and 3 AD), FDG hypometabolism was more extensive than the cerebral hypoperfusion. Four patients (1SMC, 3 amnestic MCI) had an abnormal 18F-FDG PET/CT scan and normal 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT. There were 3 patients (1 SMC 2, amnestic MCI) with normal 99mTc-HMPAO SPECT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans.
Conclusion99mTc-HMPAO SPECT and 18F-FDG PET/CT scans showed cerebral hypoperfusion and hypometabolism in patients with cognitive impairment, even in patients with clinical diagnosis of SMC. In patients with a normal cerebral blood flow SPECT, brain glucose cerebral hypometabolism can be detected. In some patients, the extension of FDG hypometabolism is more pronounced than that corresponding to the hypoperfusion area.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora