Our objective was to analyze the accuracy of the sentinel node biopsy, taking into consideration the scintigraphy detection rate after the intratumoural administration of the radiopharmaceutical in patients with breast cancer who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
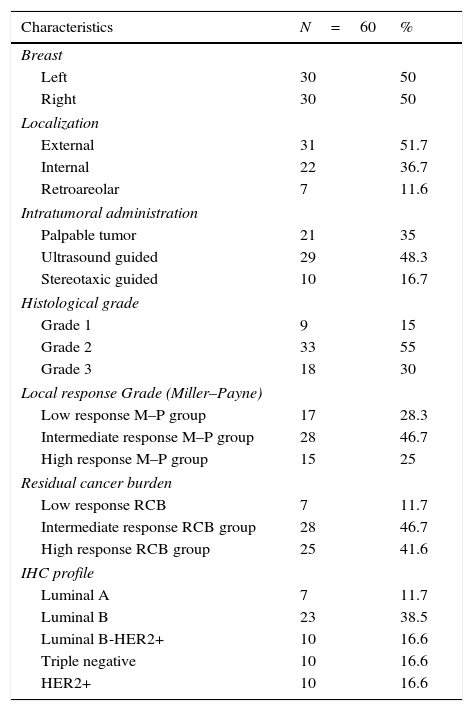
Materials and methodsThe study included 60 patients with a diagnosis of invasive breast carcinoma, stage T1–T3, who received treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and were subsequently subjected to breast surgery and sentinel node biopsy after intra-tumor administration of the radiopharmaceutical.
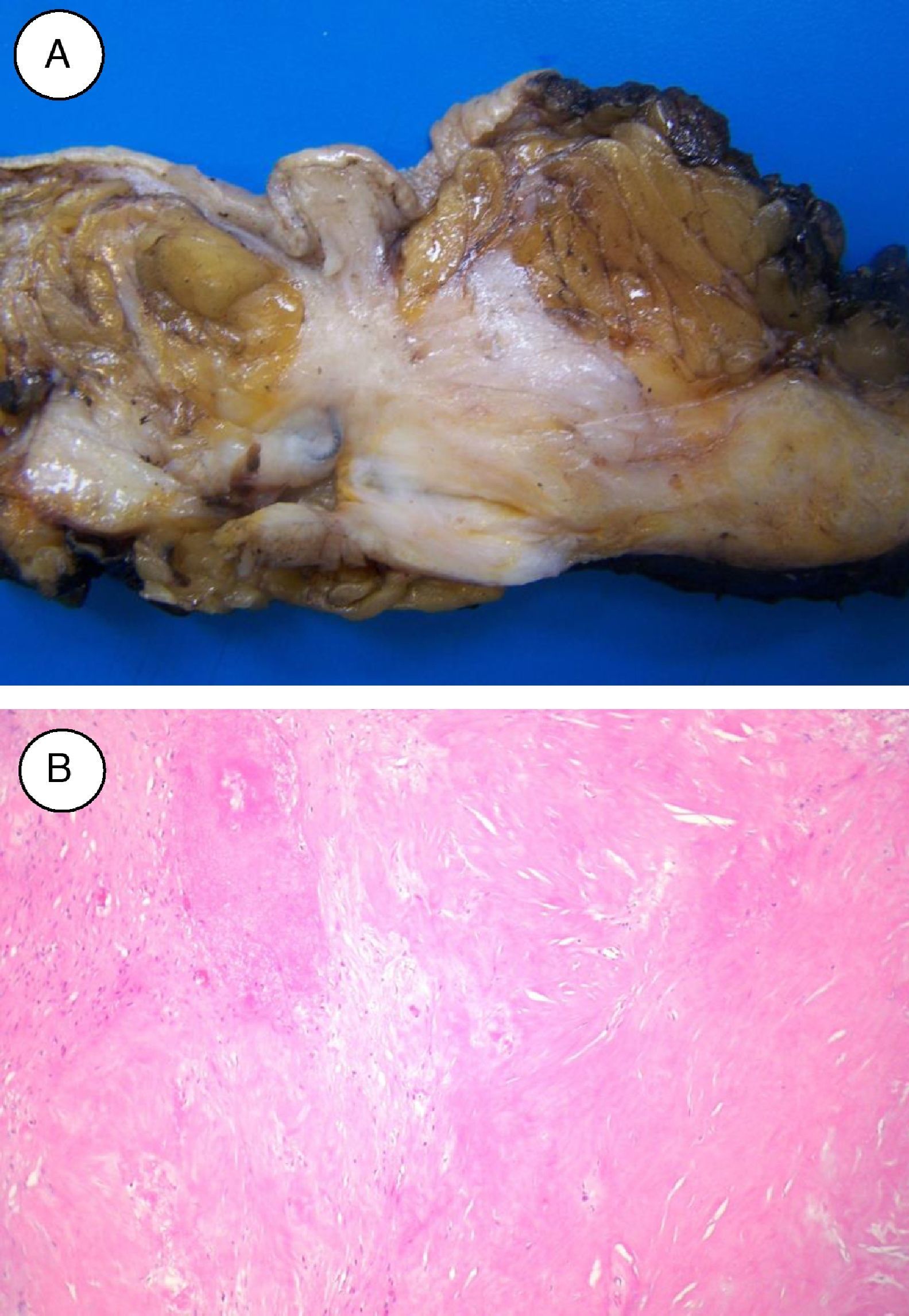
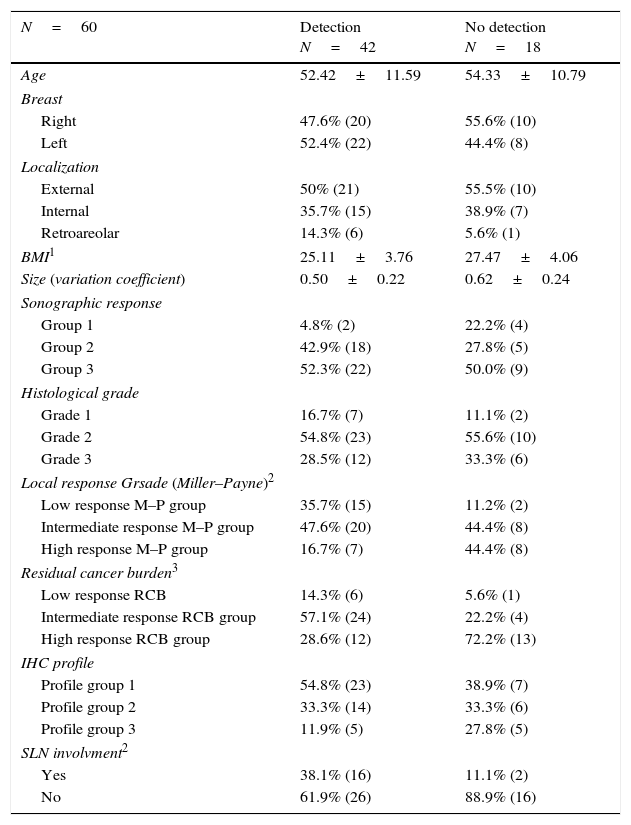
ResultsScintigraphic detection of some sentinel node was achieved in 55/60 patients (91.6%). When those cases that received a second injection of the radiopharmaceutical, performed peri-areolarly due to a lack of tracer migration, were excluded, the detection rate dropped to 70% (42/60). When the detection of sentinel node, or its absence, was compared in those 42 patients, no differences were found with age, laterality-location of the lesion, size pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy, histological grade, or immunohistochemical profile. There were significant differences when comparing the groups according to the degree of pathological tumor response, both with the Miller–Payne system (non-detection 44.4%-detection 16.7%, p=0.003) as well as the residual cancer burden (72.2–28.6%, p<0.01).
ConclusionsThe scintigraphic detection of the sentinel node after intratumoural administration of the radiopharmaceutical in patients with breast cancer who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy was below the optimal value, and sometimes a further, peri-areolar, injection was necessary, probably in relation to an alteration in the lymphatic drainage pathways. There was a significant inverse relationship between the detection of the sentinel node and level of pathological tumor response.
Nuestro objetivo fue analizar el rendimiento de la biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela valorando la detección gammagráfica tras la administración intratumoral del radiofármaco en pacientes con cáncer de mama que recibieron quimioterapia neoadyuvante.
Material y métodosSesenta pacientes con diagnóstico de carcinoma infiltrante de mama, estadios T1-T3, que recibieron tratamiento con quimioterapia neoadyuvante fueron sometidas posteriormente a cirugía mamaria y biopsia del ganglio centinela mediante administración intratumoral del radiofármaco.
ResultadosSe consiguió la detección gammagráfica de algún ganglio centinela en 55/60 pacientes (91,6%). Cuando se excluyeron los casos con reinyección periareolar del radiofármaco por falta de migración, la detección fue del 70% (42/60). Cuando se comparó la detección o no del ganglio centinela en estas 42 pacientes, no se encontraron diferencias en función de la edad, lateralidad-localización de la lesión, tamaño pre y posquimioterapia, grado histológico del tumor o perfil inmunohistoquímico. Sí existieron diferencias significativas al comparar los grupos según el grado de respuesta patológica del tumor, valorado tanto con el sistema de Miller-Payne (no detección 44,4%-detección 16,7%, p=0,003) como con el sistema residual cancer burden (72,2%-28,6%, p<0,01).
ConclusionesLa detección gammagráfica del ganglio centinela tras administración intratumoral del radiofármaco en pacientes con cáncer de mama que recibieron quimioterapia neoadyuvante estuvo por debajo del valor óptimo, siendo necesaria en ocasiones la reinyección periareolar, lo que podría estar en relación con una alteración de las vías de drenaje linfático. Existió una significativa relación inversa entre detección del ganglio centinela y el grado de respuesta patológica tumoral.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora