To determine whether metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and total lesion glycolysis (TLG) are able to predict recurrence risk in locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) patients.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of LABC patients who undertook neoadjuvant, local and adjuvant treatment and follow up. A 18F-FDG PET/CT study for initial staging was performed analysing in this study different metabolic parameters (MTV, TLG, SUVmax and SUVmed) both in the primary tumor (T) as well as in axillary nodes (N) and whole-body (WB).
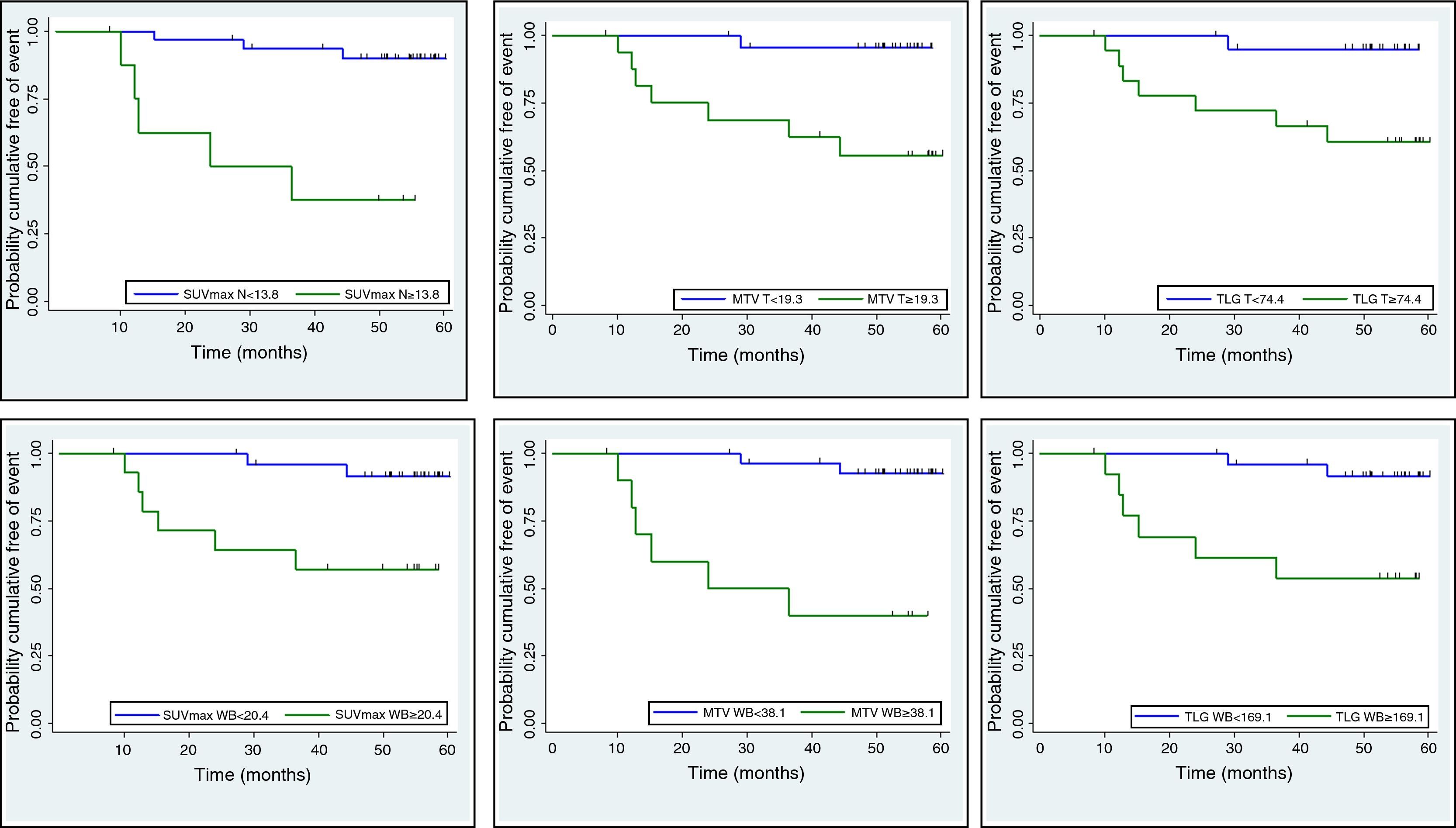
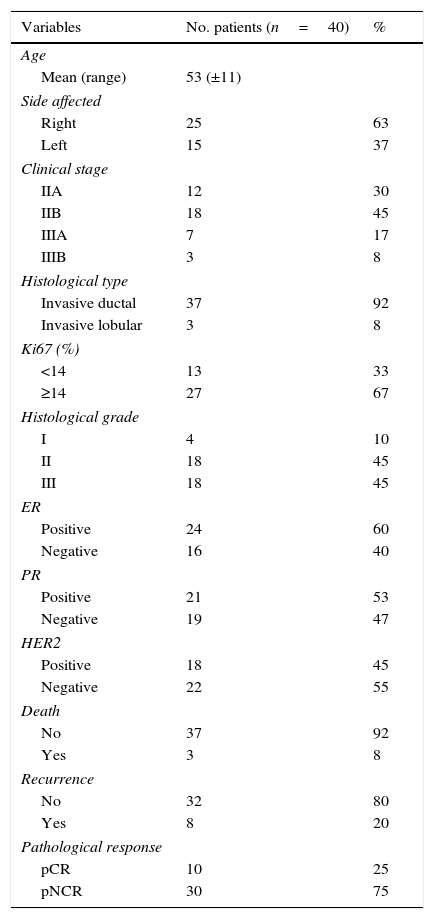
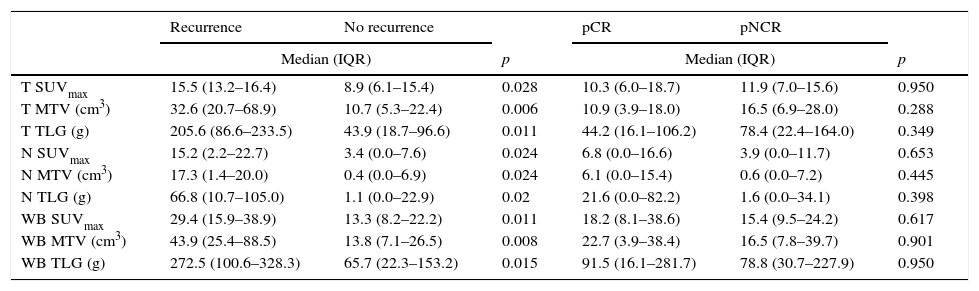
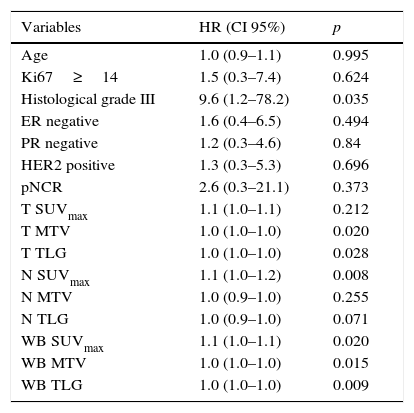
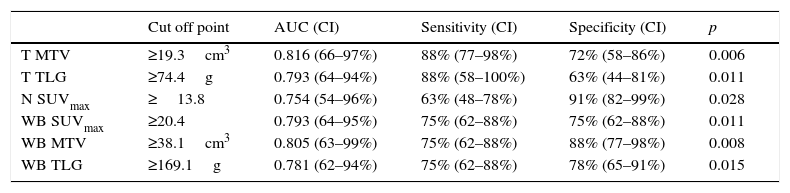
ResultsForty females were included between January 2010 and 2011; follow up until January 2015 was completed. The average follow-up was 46 months. Twenty percent presented recurrence: local disease (n=2) and distant metastasis (n=6); 3 patients died (38% of the patients which recurred and 7.5% from the total). SUVmax, MTV and TLG, in T, N and WB, were higher in those patients with recurrence. The MTV and TLG parameters in the tumor (T) were related to the recurrence rate (p=.020 and p=.028, respectively); whereas SUVmax in the lymph nodes (N) was significantly related (p=.008) to the recurrence rate. The best cut-off points to predict recurrence where: MTV T≥19.3cm3, TLG T≥74.4g and SUVmax N≥13.8, being 10–12 times more likely to recidivate when these thresholds where exceeded. Tumor grade was the only clinical-pathological variable which was related to recurrence probability (p=.035).
ConclusionsIn this study of LABC patients the metabolic parameters which have a better relationship with recurrence rate are: MTV and TLG in the primary tumor, SUVmax in the regional lymph node disease and whole-body PET data.
Conocer si el volumen metabólico tumoral (VMT) y la glucólisis tumoral total (GTT) pueden predecir el riesgo de recurrencia en cáncer localmente avanzado de mama (CLAM).
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de pacientes con CLAM tratados con tratamiento neoadyuvante, local y adyuvante; en seguimiento. Se realizó una 18F-FDG PET/TC para estadificar la enfermedad, midiéndose diferentes parámetros metabólicos (VMT, GTT, SUVmáx y SUVmed), tanto en el tumor primario (T) como en los ganglios metastásicos (N) y en el cuerpo entero (CE).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 40 mujeres entre enero de 2010-2011; seguimiento hasta enero de 2015. Con una mediana de seguimiento de 46 meses el 20% tuvieron recidiva, local (n=2) o a distancia (n=6); fallecieron 3 (38% de aquellas con recidiva y 7,5% del total). EL SUVmáx, VMT y GTT, tanto en T, como N y CE, fue mayor en aquellas que presentaron recidiva. En el T tanto el VMT como la GTT se relacionaron con la recidiva de la enfermedad (p=0,020 y p=0,028, respectivamente), mientras que en la N fue el SUVmáx (p=0,008). Los puntos de corte óptimos para predecir recurrencia fueron: VMT T≥19,3cm3, GTT T≥74,4g y SUVmáx N≥13,8, existiendo 10-12 veces más probabilidad de experimentar progresión tumoral cuando superaban estos umbrales. El grado tumoral fue la única variable clínico-patológica asociada con la recidiva (p=0,035).
ConclusionesEn este estudio de CLAM los parámetros metabólicos que más se asocian con la tasa de recidiva son el VMT y la GTT en el tumor primario, el SUVmáx en la enfermedad ganglionar regional y los 3 índices PET en el cuerpo entero. Estos parámetros podrían utilizarse en la práctica asistencial para identificar a las pacientes con mayor riesgo.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora