This retrospective study was designed to investigate the role of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG-PET/CT) in determination of recurrence and/or intraabdominal metastasis in patients with ovarian cancer having increased tumor markers or suspicious lesion detected by a contrast-enhanced abdominal CT (ceCT).
Materials and methodsA total of 34 female patients who were treated for histopathologically proven ovarian cancer, underwent PET/CT examination for restaging and suspected recurrence. Patients with pathology report, tumor marker levels, ceCT and PET/CT performed within one month were included in the study.
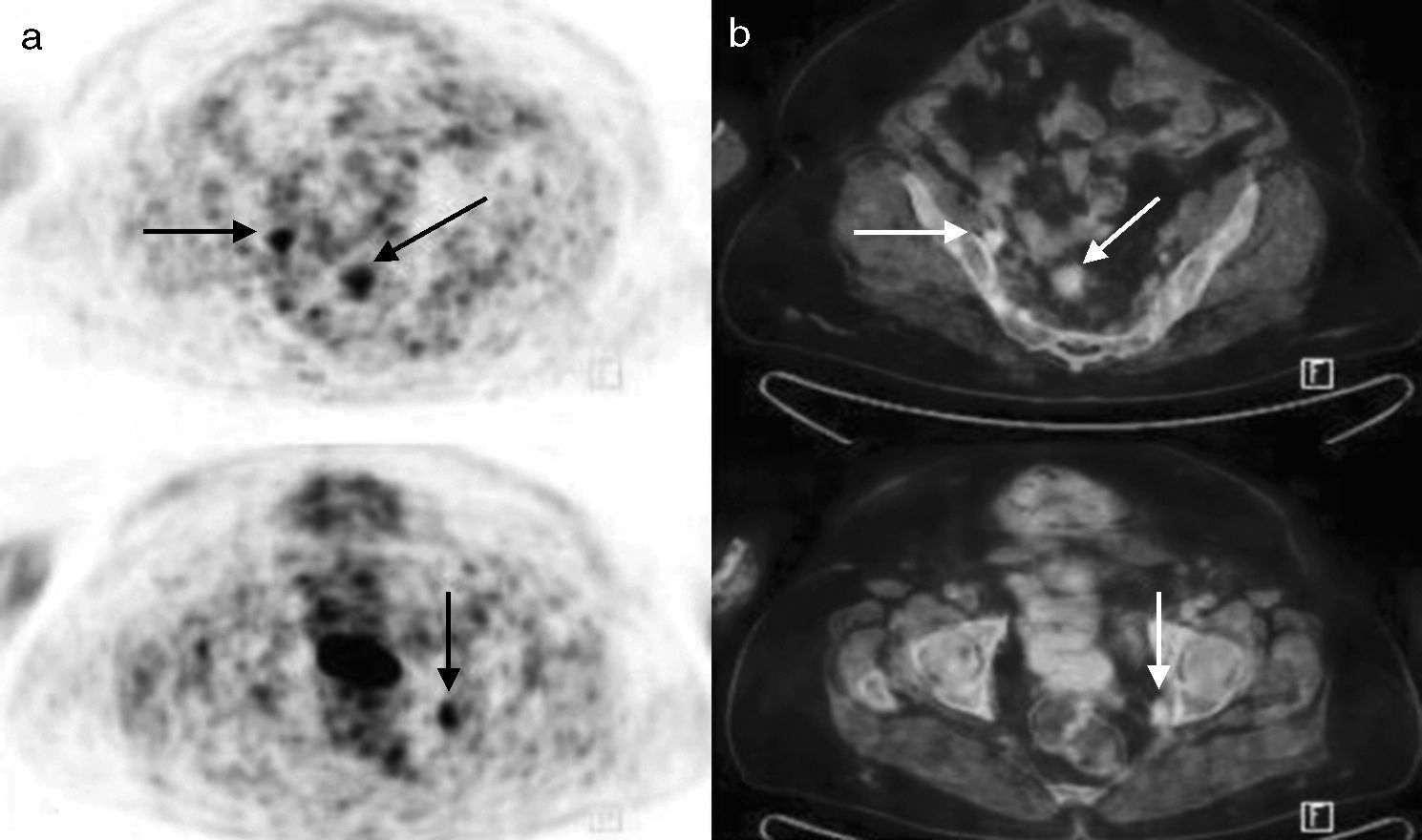
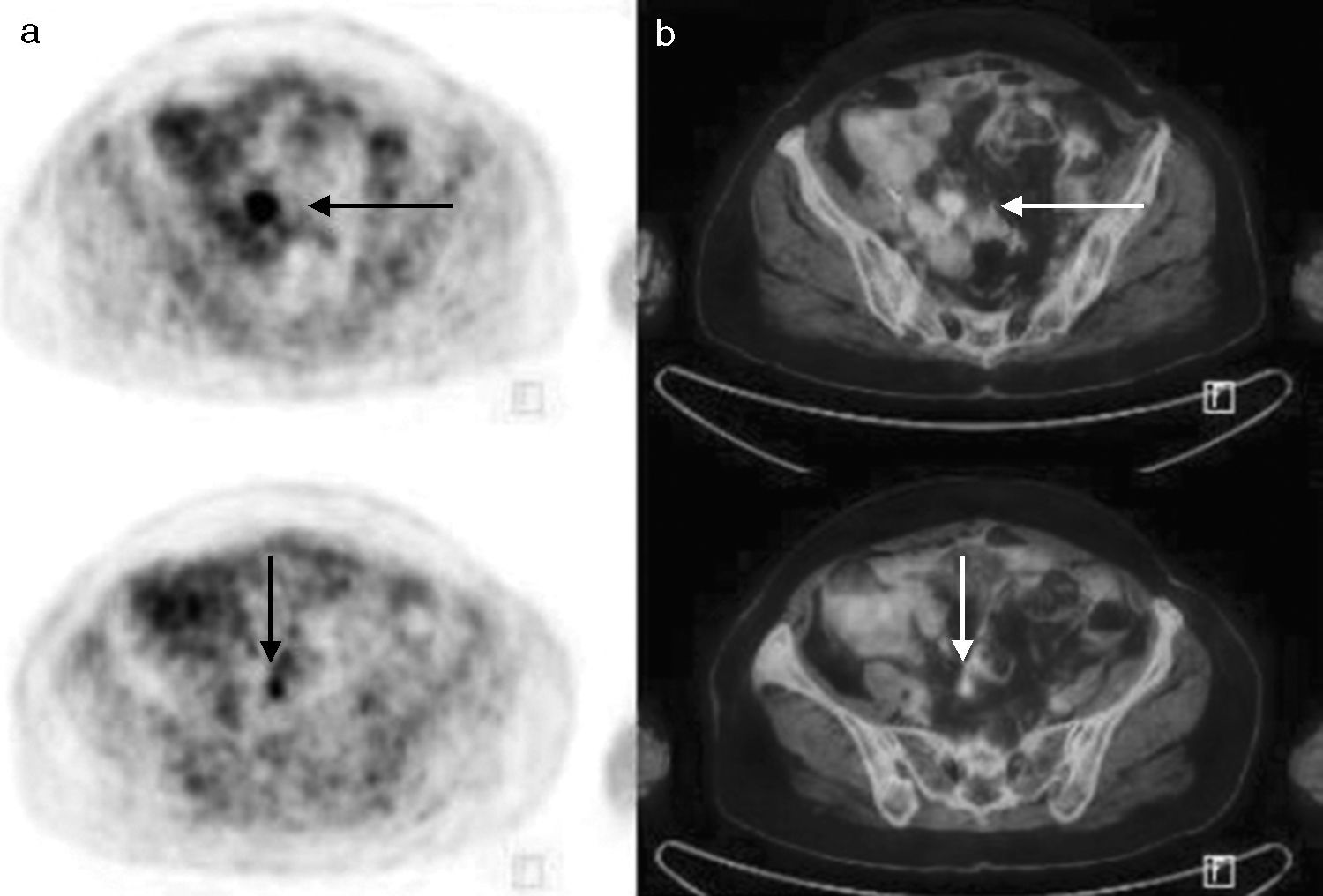
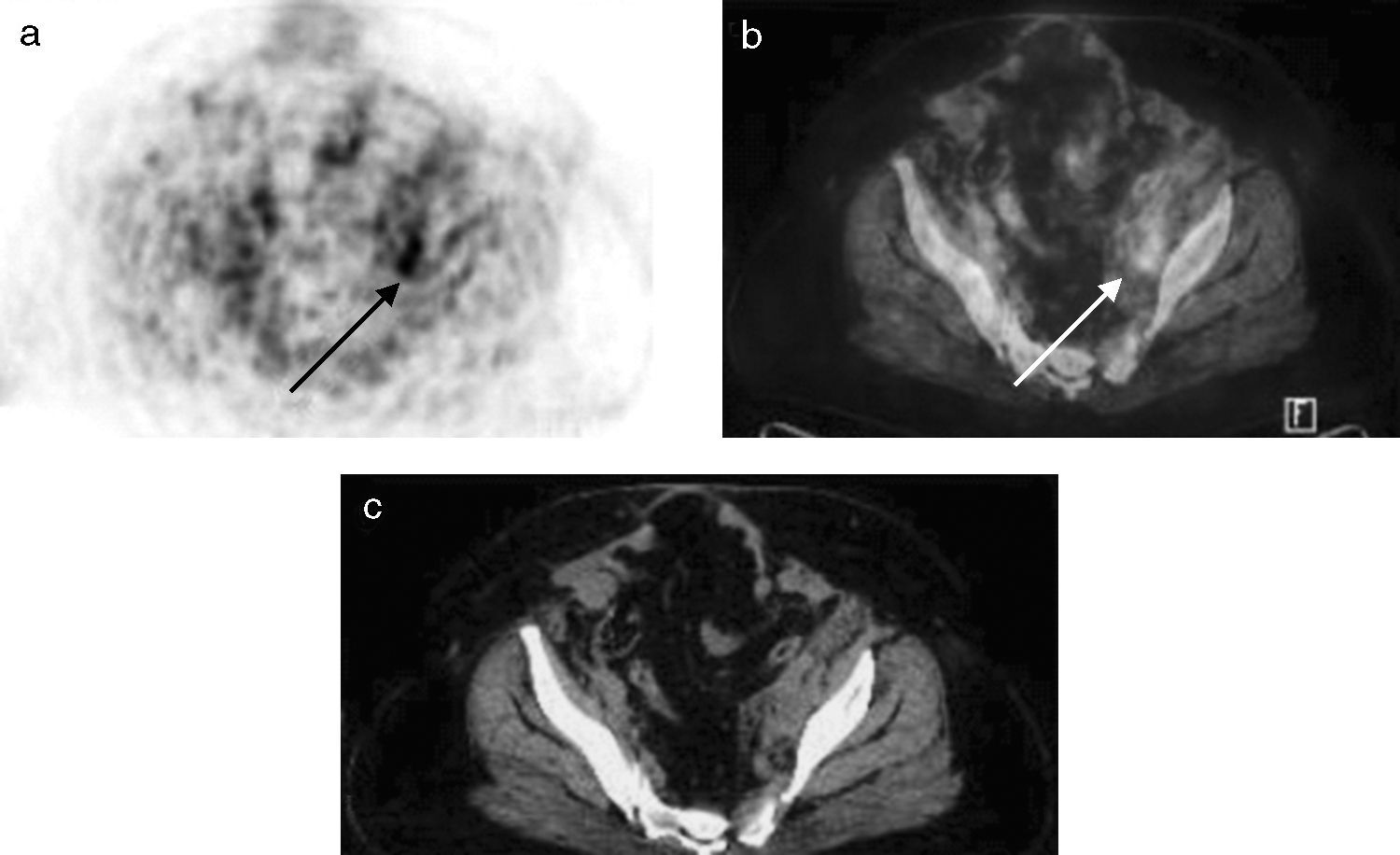
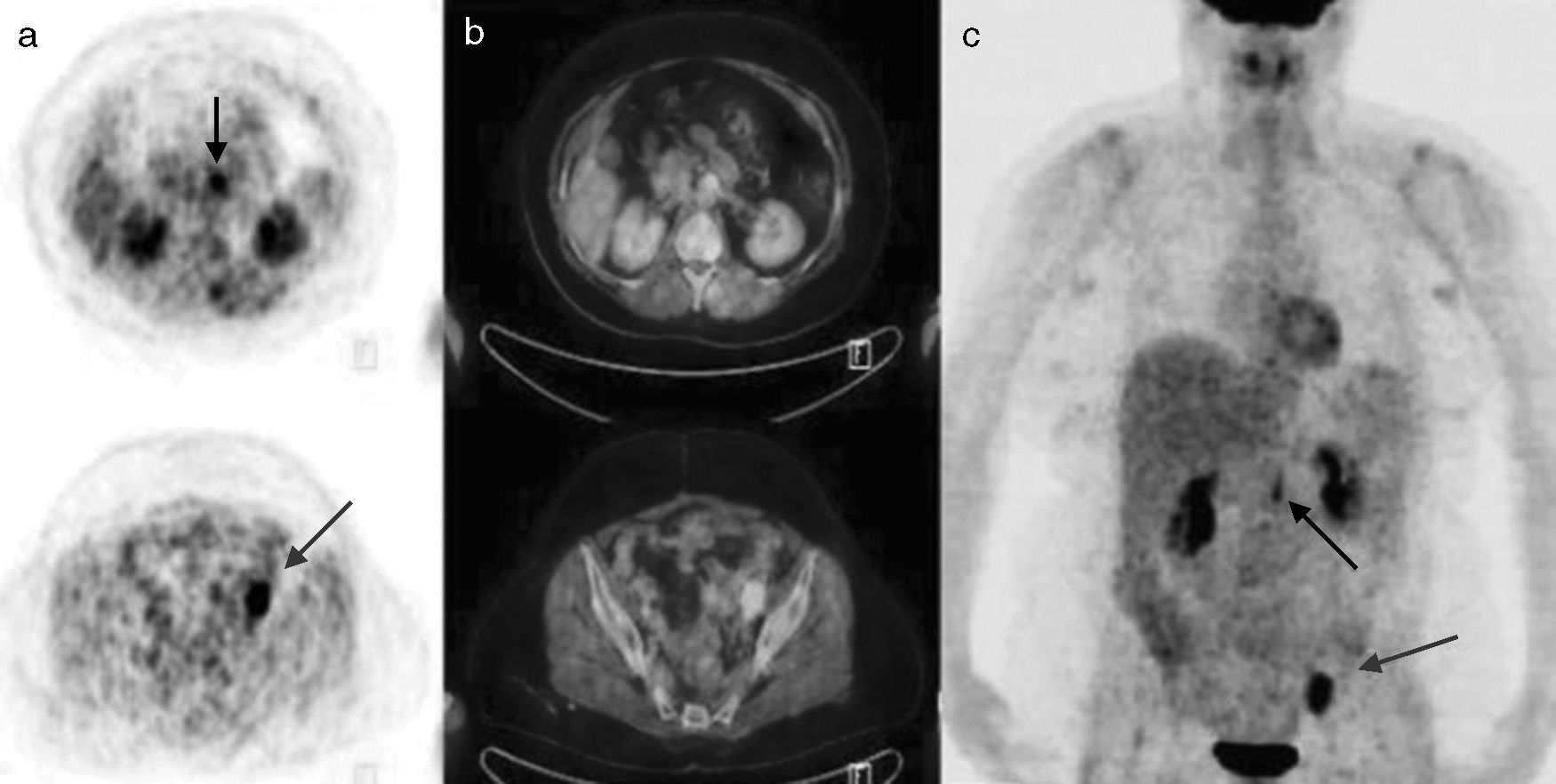
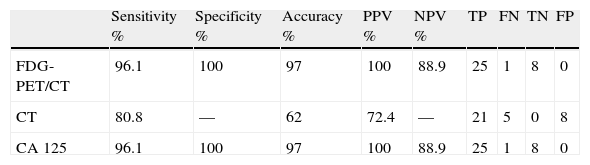
ResultsA total of 34 patients were included in the study. 25 of 34 patients had high tumor marker (CA 125) level. The remaining 9 patients had suspected recurrence on ceCT imaging with normal tumor marker levels. Recurrence was confirmed by re-operation and biopsy (n=4), clinical and imaging follow-up (n=21) in 25 patients with elevated tumor markers. Recurrent disease was not shown in 5 of 25 patients on ceCT imaging and 1 of 25 patients on PET/CT imaging with high CA125 values. Both ceCT and PET/CT revealed recurrent disease in 19 of 25 patients. PET/CT showed more lesions in 11 of 19 patients. Sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of the PET/CT were 96.1%, 100% and 97%, respectively.
ConclusionPET/CT is found as a beneficial method for detection of the recurrence, in patients with increased serum CA 125 level and negative CT findings or with normal CA 125 level and recurrence detected by CT which was performed due to clinical symptoms.
Este estudio retrospectivo fue diseñado para investigar el papel de una tomografía por emisión de positrones con 18F-fluorodeoxiglucosa/tomografía axial computerizada (PET-FDG) (FDG- PET/CT) en la determinación de recurrencia y/o metástasis intraabdominal en pacientes con cáncer de ovario con marcadores tumorales aumentados o lesión de sospecha detectada con TAC abdominal con contraste (TAC-c).
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio PET/TAC en 34 pacientes femeninos tratados por cáncer de ovario verificado histopatológicamente para reestratificación y sospecha de recurrencia. Se incluyeron a pacientes con informe patológico, niveles de marcador tumoral, TAC-c y PET/TAC dentro de un mes del estudio.
ResultadosSe reclutaron a 34 pacientes, 25 de las cuales tenían un nivel alto del marcador tumoral CA 125. Las 9 pacientes restantes tenían sospecha de recurrencia en la imagen del TAC-c con niveles del marcador tumoral normales. Se confirmaron recurrencia con re-operación y biopsia (n=4), seguimiento clínico y de imagen (n=21) en 25 pacientes y marcadores tumorales elevados. No se encontraron enfermedad recurrente en 5 de 25 pacientes en la imagen TAC-c y 1 de 25 pacientes en la imagen PET/TAC con altos niveles de CA125. Tanto TAC-c y el PET/TAC demostraron enfermedad recurrente en 19 de 25 pacientes. La sensibilidad, especificidad y presión del PET/TAC fueron 96,1, 100 y 97%, respectivamente.
ConclusiónPET/TAC es un método beneficioso para la detección de recurrencia en pacientes con un nivel de CA 125 en suero elevado y hallazgos negativos en la TAC, o con un nivel normal de CA 125 y recurrencia detectado por TAC llevado a cabo debido a síntomas clínicos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora