Valorar la utilidad de la procalcitonina (PCT) y de otros parámetros analíticos (leucocitos en sangre, proteína C reactiva [PCR]) como indicadores de daño renal agudo en niños tras su primer episodio de infección del tracto urinario febril o afebril (ITU).
Material y métodosSe ha realizado un estudio retrospectivo, con obtención de medidas séricas de PCT, PCR y leucocitos en pacientes pediátricos admitidos entre enero de 2009 y diciembre de 2011, con un primer episodio de ITU, objetivando el daño renal agudo mediante gammagrafía renal con 99mTc-DMSA (DMSA) en las primeras 72h después de la admisión. Se ha llevado a cabo un estudio descriptivo de la muestra y un trazado de curvas ROC con cálculo de puntos de corte óptimos para cada parámetro.
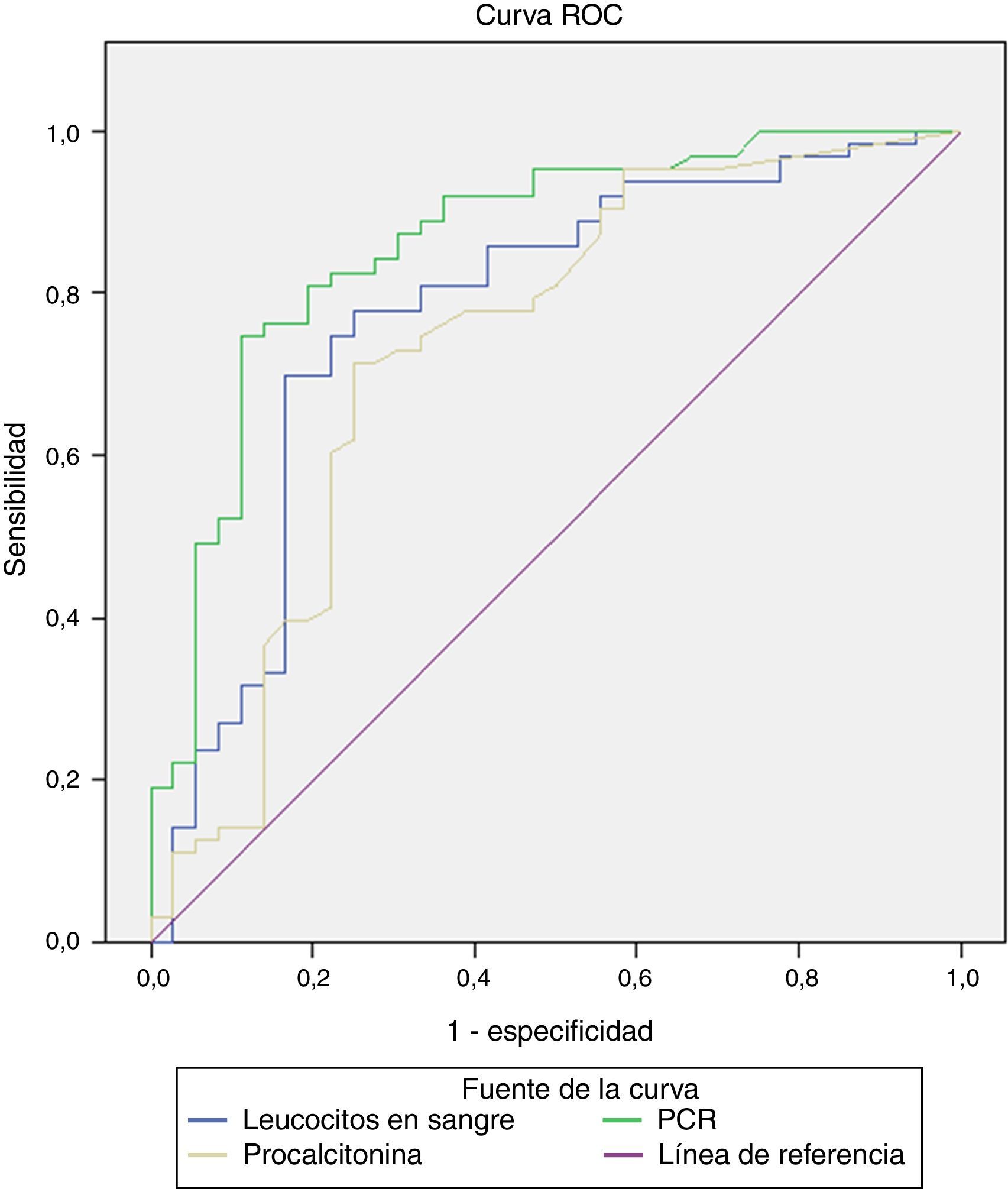
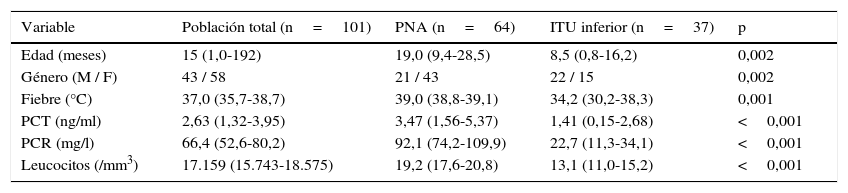
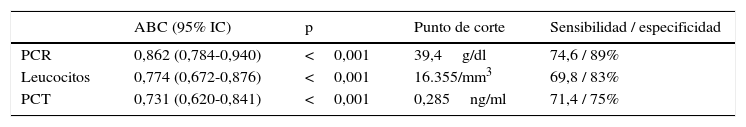
ResultadosSe han incluido 101 pacientes divididos en 2 grupos en función del resultado del DMSA, 64 fueron diagnosticados de pielonefritis aguda (PNA) y 37 de ITU. Las medias de leucocitos en sangre, PCR y PCT fueron significativamente mayores en pacientes con PNA respecto a aquellos con DMSA normal. El área bajo la curva ROC fue de 0,862 para la PCR, 0,774 para leucocitos en sangre y 0,731 para la PCT. El punto de corte óptimo para la PCT fue 0,285ng/ml (sensibilidad 71,4% y especificidad 75%).
ConclusiónSi bien los niveles medios de fiebre, leucocitos, PCR y PCT estuvieron significativamente más elevados en pacientes con PNA que en los que tenían ITU, la sensibilidad y especificidad de estos parámetros analíticos no permiten predecir la existencia de afectación renal aguda, haciendo imprescindible la realización de una gammagrafía renal con DMSA.
To investigate the usefulness of procalcitonin (PCT) and other analytical parameters (white blood cell count [WBC], C-reactive protein [CRP]) as markers of acute renal damage in children after a first febrile or afebrile urinary tract infection (UTI).
MethodsA retrospective study was conducted on children with a first episode of UTI admitted between January 2009 to December 2011, and in whom serum PCT, CRP and white blood cell count were measured, as well as assessing the acute renal damage with renal scintigraphy with 99mTc-DMSA (DMSA) within the first 72h after referral. A descriptive study was performed and ROC curves were plotted, with optimal cut-off points calculated for each parameter.
ResultsThe 101 enrolled patients were divided into two groups according to DMSA scintigraphy results, with 64 patients being classified with acute pyelonephritis (APN), and 37 with UTI. The mean WBC, CRP and PCT values were significantly higher in patients with APN with respect to normal acute DMSA. The area under the ROC curve was 0.862 for PCR, 0.774 for WBC, and 0.731 for PCT. The optimum statistical cut-off value for PCT was 0.285ng/ml (sensitivity 71.4% and specificity 75%).
ConclusionAlthough the mean levels of fever, WBC, CRP, and PCT were significantly increased in patients with APN than in those who had UTI, the sensitivity and specificity of these analytical parameters are unable to predict the existence of acute renal damage, making the contribution by renal DMSA scintigraphy essential.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora