The method for intraoperative sentinel lymph node (SLN) evaluation has still not been established in breast cancer staging. This study has evaluated the diagnostic validity and impact of intraoperative analysis using the frozen section (FS) of SLN.
Material and methodsWe performed a descriptive study of the diagnostic validity of the FS of the SLN in patients with breast cancer and selective sentinel node biopsy (SSNB) from October 2006 to October 2012. The diagnostic validity indexes were evaluated using sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and global value. The final histopathological results of the biopsies was considered as the gold standard.
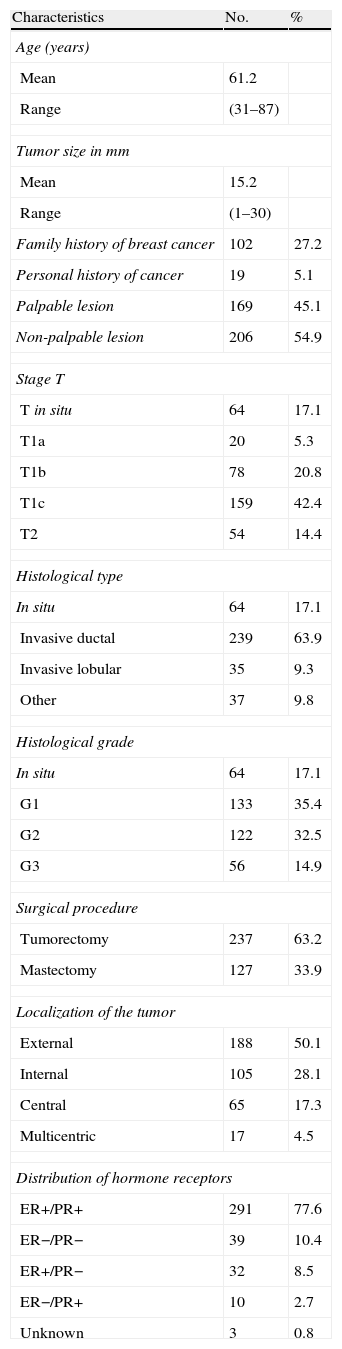
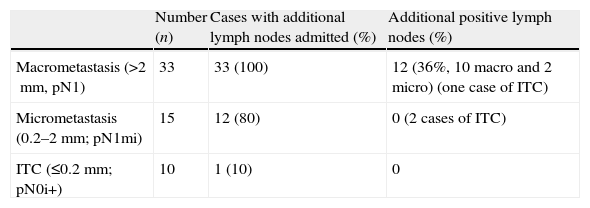
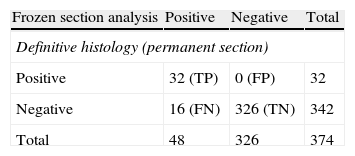
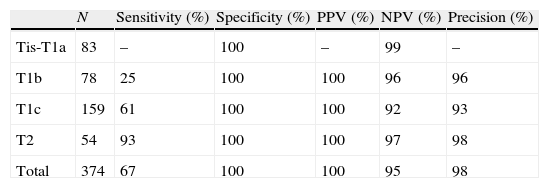
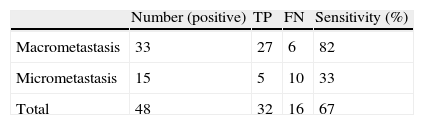
ResultsA total of 370 patients were studied. Sensitivity and specificity for detection of metastasis using FS of the SLN were 67% and 100%, respectively. Global diagnostic validity was 95%. There was a correlation between detection of metastasis and tumor size (p<0.05). Twelve of the 15 patients with SLN micro-metastases underwent axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). Metastatic lymph nodes were not found in any of them.
ConclusionsIntraoperative FS examination of the SLN is a useful and reliable predictor of axillary lymph node staging in patients with initial stages of breast cancer. FS reduces the number of second interventions, at least for most patients who have breast cancer and unequivocal evidence of positive lymph node disease.
En la estadificación del cáncer de mama, el método del análisis intraoperatorio del ganglio centinela (GC) no ha sido todavía adecuadamente establecido. Hemos evaluado la validez diagnóstica y el impacto del análisis intraoperatorio mediante sección en congelación (SC) del GC.
Material y métodosSe ha realizado un estudio descriptivo de validez diagnóstica de la SC del GC en las pacientes con cáncer de mama a las que se realizó biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BSGC) desde octubre de 2006 hasta octubre de 2012. Se evaluaron los índices de validez diagnóstica sensibilidad, especificidad, valores predictivos positivo y negativo y valor global. Se consideró patrón oro el estudio anatomopatológico definitivo de las biopsias.
ResultadosSe estudiaron 370 pacientes. La sensibilidad y especificidad para la detección de metástasis mediante la SC en el GC ha sido del 67% y del 100%, y la validez diagnóstica global del 95%. Se encontró relación entre tamaño del tumor y detección de metástasis (p<0,05). Doce de las 15 pacientes con micrometástasis se sometieron a linfadenectomía y no se hallaron ganglios metastáticos en ninguna de ellas.
ConclusionesEl análisis intraoperatorio mediante SC del GC es un método útil y fiable para la estadificación de los ganglios linfáticos axilares en pacientes con cáncer de mama en estadios iniciales. La SC reduce la necesidad de realizar una segunda cirugía, al menos en la mayoría de los pacientes con cáncer de mama y evidencia inequívoca de GC positivo.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora