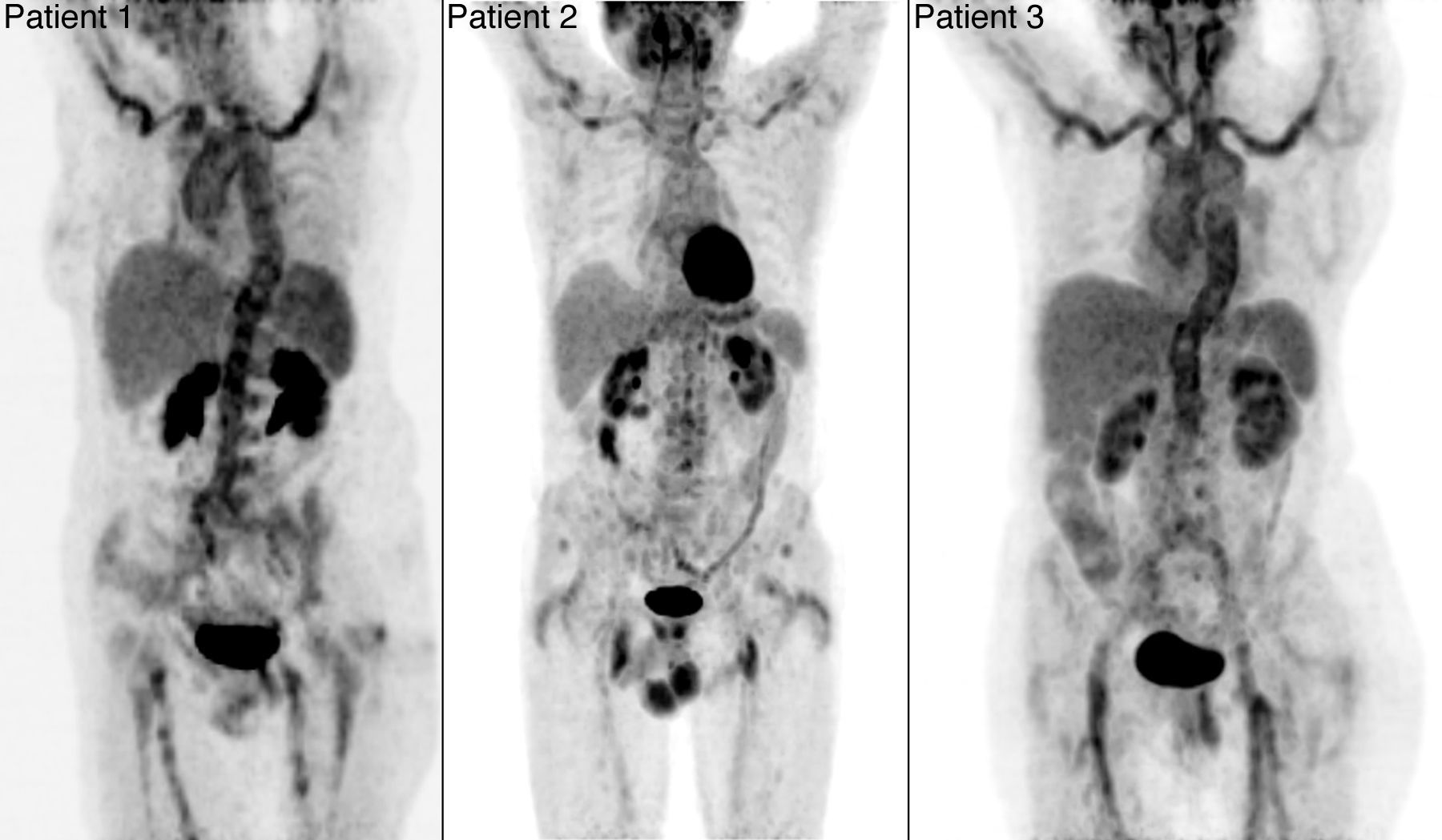
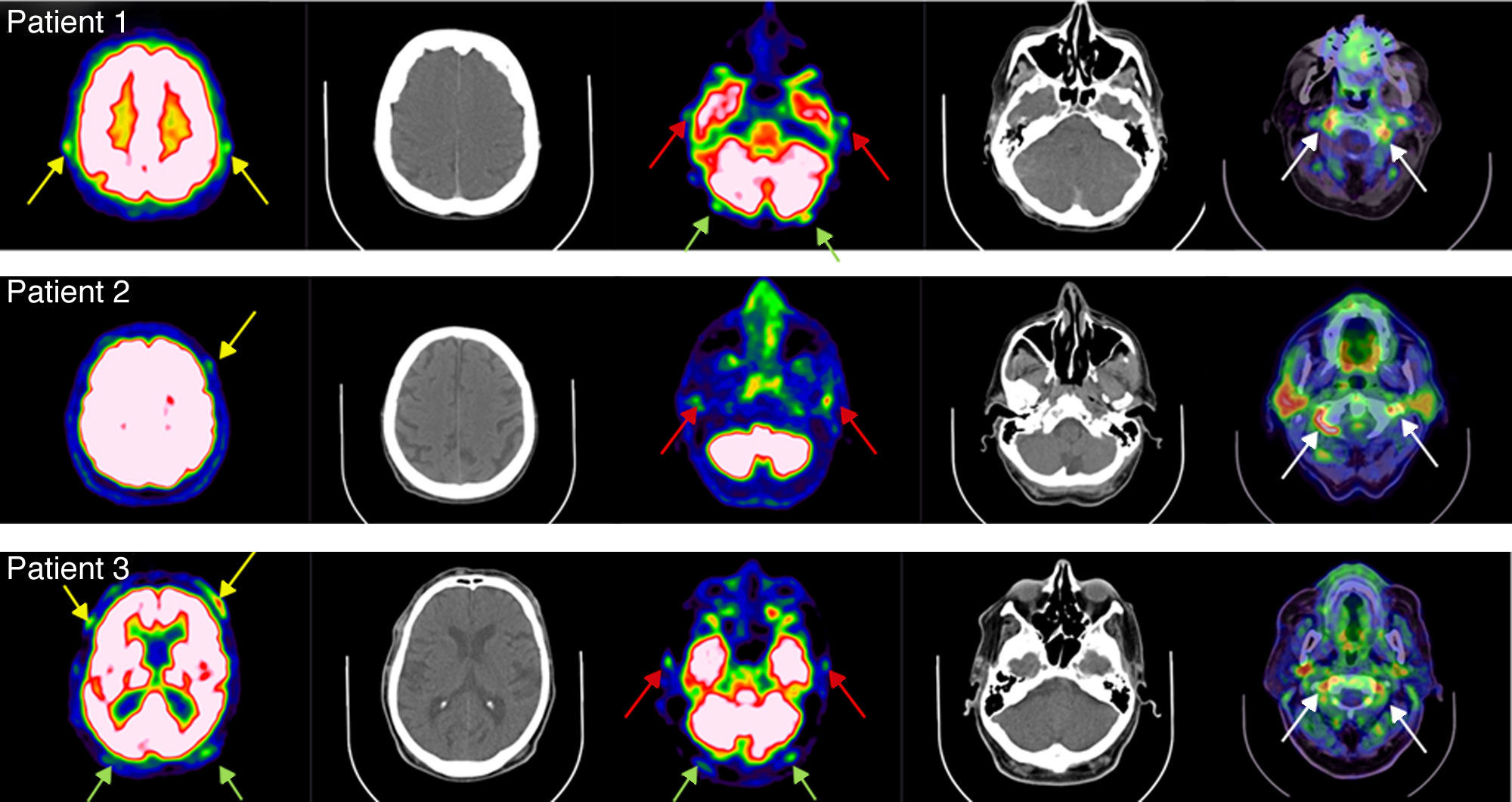
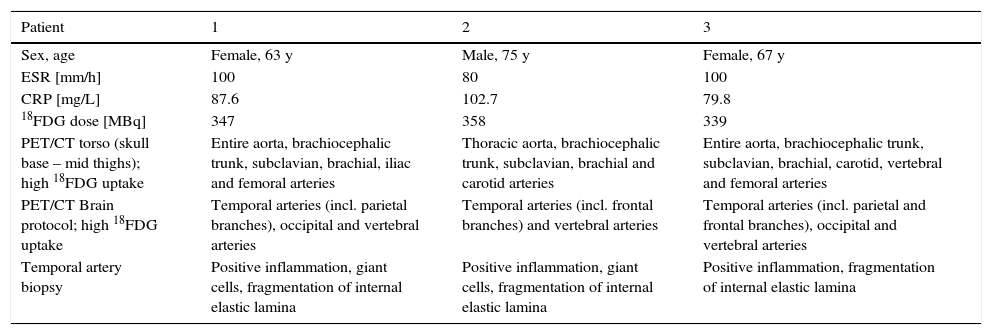
18F-FDG PET/CT imaging is useful in patients with fever of unknown origin and can detect giant cell arteritis in extracranial large arteries. However, it is usually assumed that temporal arteries cannot be visualized with a PET/CT scanner due to their small diameter. Three patients with clinical symptoms of temporal arteritis were examined using a standard whole body PET/CT protocol (skull base – mid thighs) followed by a head PET/CT scan using the brain protocol. High 18F-FDG uptake in the aorta and some arterial branches were detected in all 3 patients with the whole body protocol. Using the brain protocol, head imaging led to detection of high 18F-FDG uptake in temporal arteries as well as in their branches (3 patients), in occipital arteries (2 patients) and also in vertebral arteries (3 patients).
El estudio con 18F-FDG PET/TC es útil en los pacientes con fiebre de origen desconocido y puede detectar la arteritis de células gigantes en las grandes arterias extracraneales. Sin embargo, por lo general se supone que las arterias temporales no pueden ser visualizadas por medio de PET/TC porque su diámetro es pequeño. Se examinó a tres pacientes con arteritis temporal mediante el protocolo PET/TC estándar de cuerpo completo (base del cráneo – mitad del muslo) seguido del protocolo PET/TC de cabeza para cerebro. En los tres pacientes se observó la alta acumulación de 18F-FDG en la aorta y en algunas arterias. Mediante el protocolo para cerebro se observó la intensa acumulación de 18F-FDG en las arterias temporales y sus ramas (3 pacientes), en las arterias occipitales (2 pacientes) y también en las arterias vertebrales (3 pacientes).
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora