This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the role of metabolic parameters of 18F-FDG PET/CT in pediatric lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL).
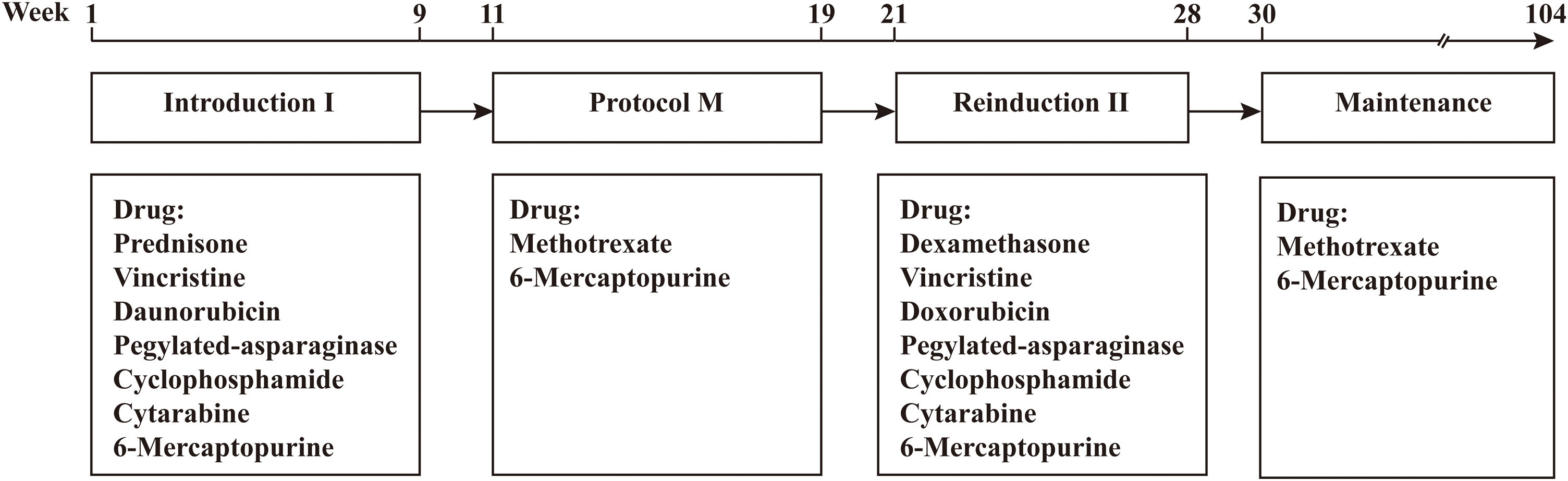
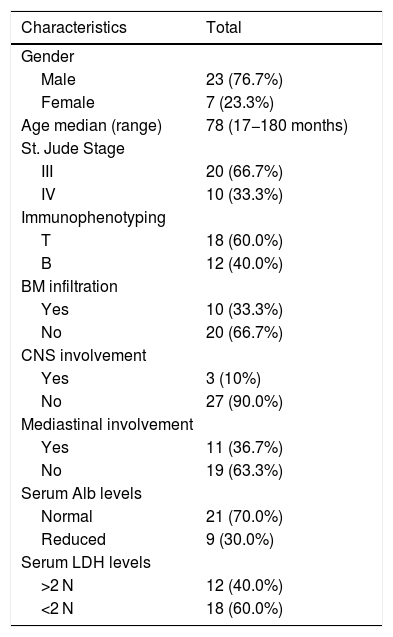
MethodsThirty patients with LBL underwent 42 scans. Metabolic parameters including maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), total metabolic tumor volume (TMTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG) were measured at baseline PET/CT. Univariate and multivariate analysis for survival were performed to assess their prognostic value. Twelve patients underwent PET/CT after reinduction regime, and the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of PET/CT for predicting relapse were calculated.
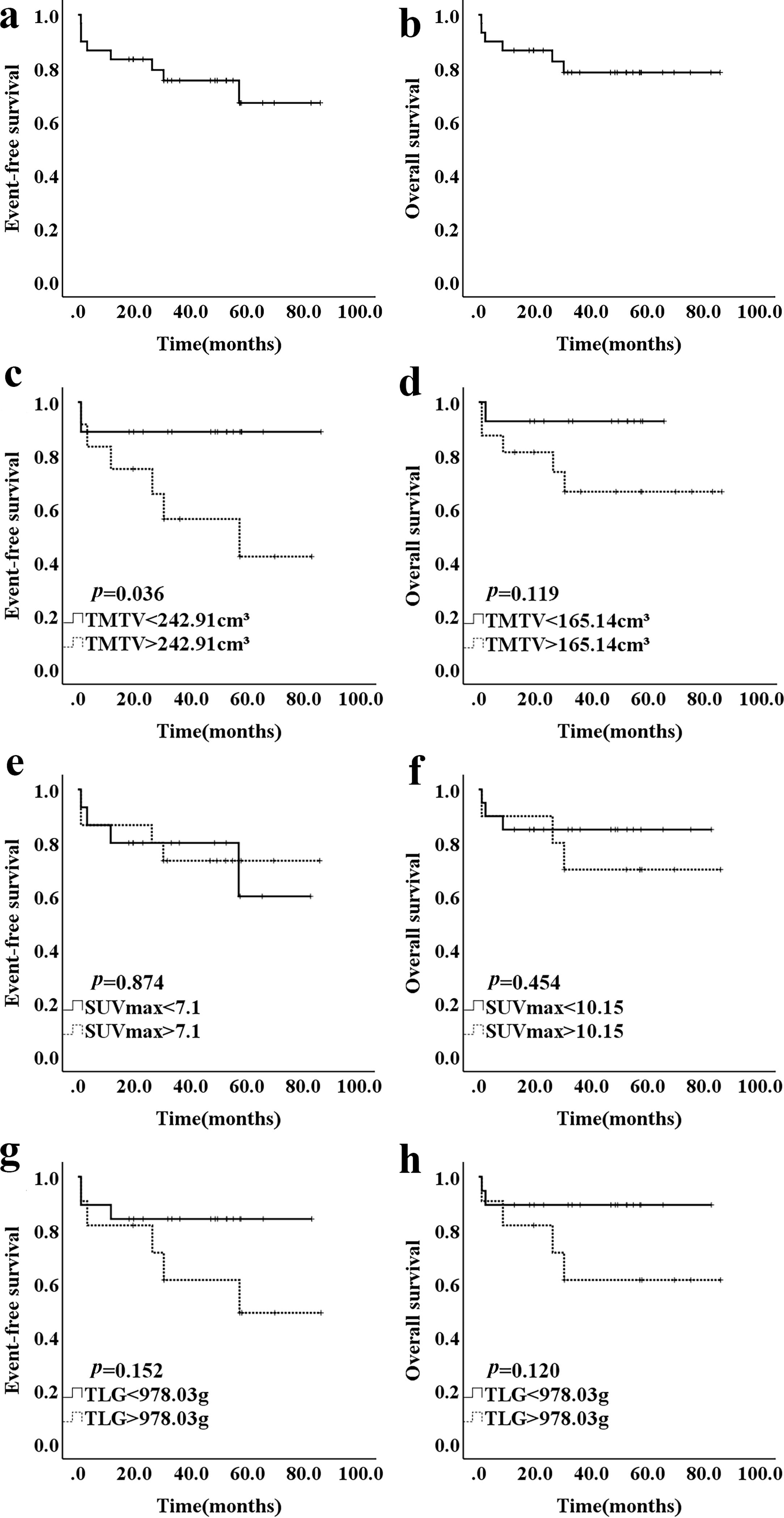
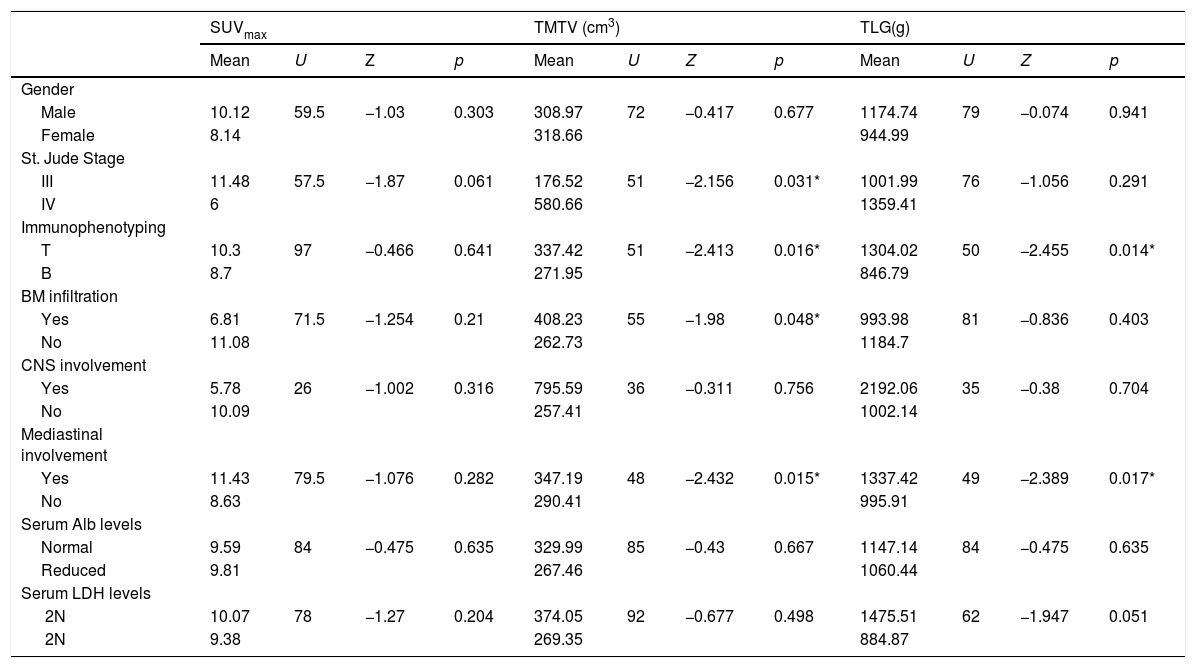
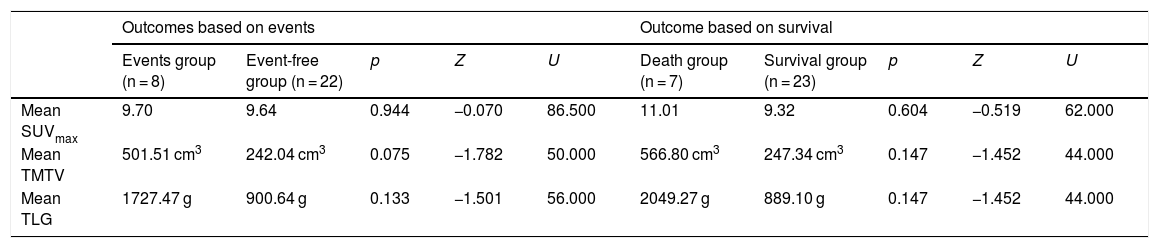
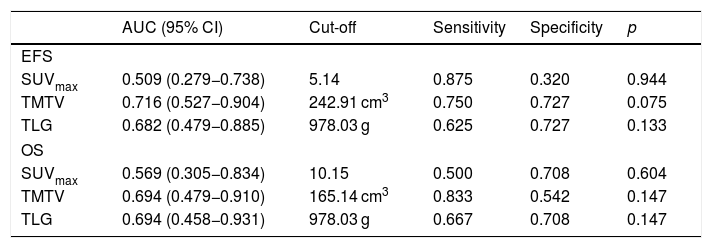
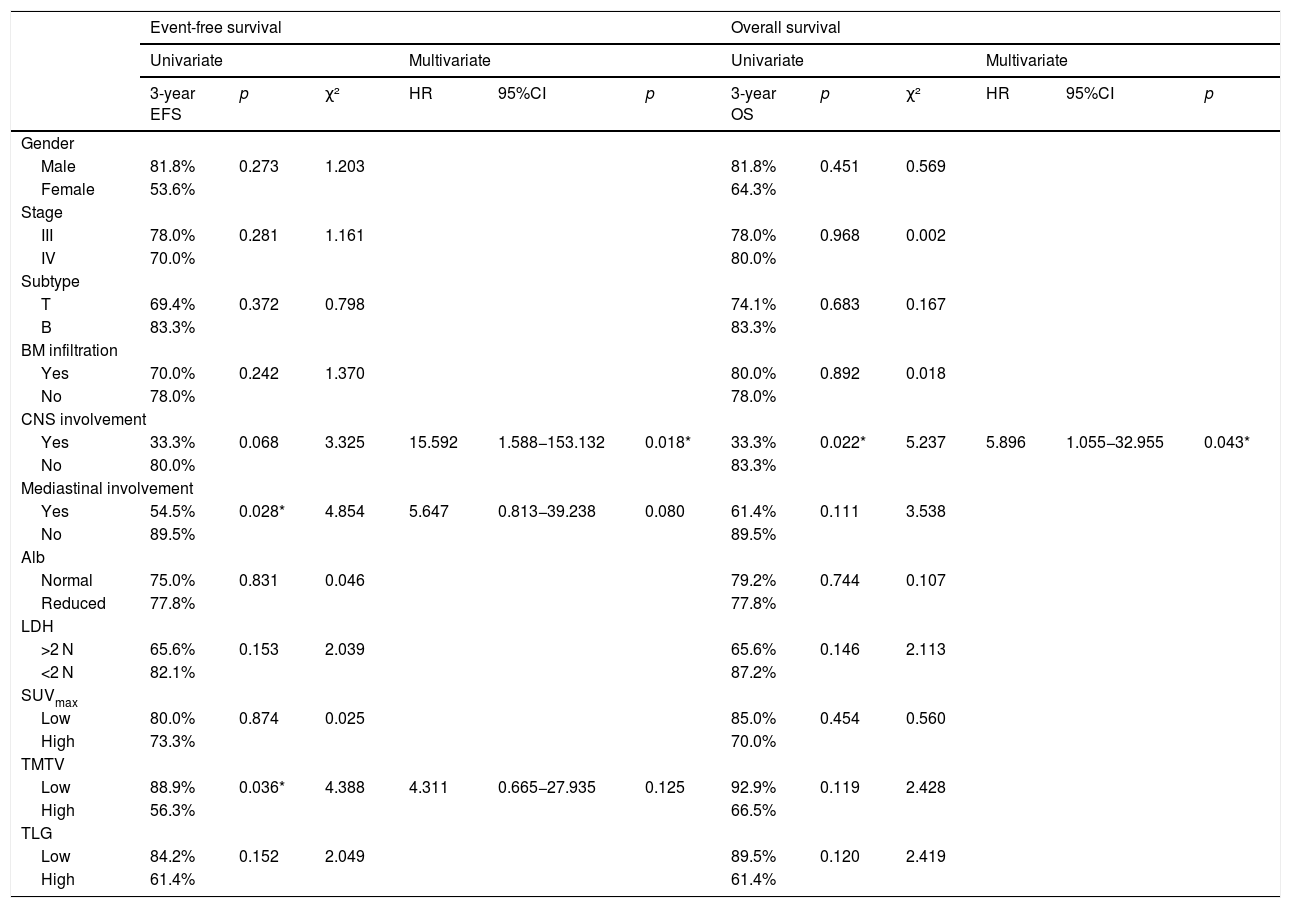
ResultsPatients with stage Ⅳ had a higher TMTV than those with stage III (p = 0.031). Besides, patients with T-LBL or mediastinal involvement had a high TMTV and TLG (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in PET/CT metabolic parameters between patients with different outcomes (p > 0.05). Children with a low TMTV (<242.91 cm³) had a better 3-year EFS compared with those with a high TMTV (88.9% vs. 56.3%; p = 0.036). SUVmax and TLG were not predictive of EFS (p = 0.874; p = 0.152). However, none of the metabolic parameters of baseline PET/CT were independent prognostic factors for outcomes of pediatric LBL. PET/CT underwent after reinduction regime present with higher sensitivity (50% vs. 0%) and NPV (90% vs. 83.3%) for predicting relapse than CT alone.
ConclusionsMetabolic parameters of baseline PET/CT were not predictive of outcomes in children with LBL. PET/CT done after the reinduction regime had better sensitivity and NPV than CT alone, and a negative scan could be a reliable indicator for sustained remission.
Este estudio retrospectivo tuvo como objetivo evaluar el papel de los parámetros metabólicos de la 18F-FDG PET/TC en el linfoma linfoblástico pediátrico (LBL).
MétodosTreinta pacientes con LBL se sometieron a 42 exploraciones. Los parámetros metabólicos, incluyeron el valor máximo de captación estandarizado (SUVmax), el volumen tumoral metabólico total (TMTV) y la glicólisis de lesión total (TLG) se midieron en la PET/TC basal. Se realizaron análisis univariantes y multivariantes de la supervivencia para evaluar su valor pronóstico. Doce pacientes se sometieron a PET/TC después del régimen de reinducción, y se calcularon la sensibilidad, la especificidad, el valor predictivo positivo (VPP), el valor predictivo negativo (VPN) y la precisión de la PET/TC para predecir la recaída.
ResultadosLos pacientes con estadio Ⅳ tuvieron una TMTV más alta que los que tenían un estadio III (p = 0,031). Además, los pacientes con T-LBL o afectación mediastínica tenían una TMTV y TLG altos (p < 0,05). No hubo diferencias significativas en los parámetros metabólicos la PET/TC entre los pacientes con diferente evolución (p > 0,05). Los niños con una TMTV baja (<242.91 cm³) tuvieron una mejor EFS a los 3 años comparados con aquellos con una TMTV elevada (88.9% vs. 56.3%; p = 0.036). El SUVmax y el TLG no fueron predictivos de la EFS (p = 0,874; p = 0,152). Sin embargo, ninguno de los parámetros metabólicos de la PET/TC basales fueron factores pronósticos independientes para los resultados del LBL pediátrico. La PET/TC realizada después del régimen de reinducción presentó una mayor sensibilidad (50% vs. 0%) y VAN (90% vs. 83,3%) para predecir la recaída que la TC sola.
ConclusionesLos parámetros metabólicos de la TEP/TC de referencia no fueron predictivos de los resultados en los niños con LBL. La TEP/TC realizada después del régimen de reinducción tuvo una mejor sensibilidad y VPN que la TC sola, y una exploración negativa podría ser un indicador fiable de remisión sostenida.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora