To evaluate SUV changes in the liver in relation to body mass index (BMI) of patients who undergo whole body PET-CT scans.
Material and methodsA retrospective study was performed. The variables studied were injected dose of 18FFDG (mCi), age (years), blood glucose level (mg/dL), height (cm) and weight (kg). BMI was calculated and the SUV mean value was expressed according to gender and BMI. A linear regression analysis was applied to identify the independent variables that best predict the SUV value.
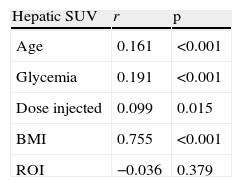
ResultsSix hundred and three patients were studied (305 women, 298 men; mean age: 54.9±15.2 years old). Mean SUV measurement was significantly higher in males than females and increased significantly both in male and female patients who were overweight and even more in obese patients. The independent variables that best predicted the SUV value were gender, age, and BMI. In those patients having similar characteristics related to the analyzed variables, the SUV value increased by 0.002 for each increase in one year, and by 0.066 per unit increase in the BMI value.
ConclusionsHepatic uptake of 18FFDG increases according to the patient's BMI. The independent variables that best predict the hepatic SUV value are age and sex of patients. Our findings show that the practice of using the physiological hepatic metabolic activity level as a reference regarding questionable deposits elsewhere in the abdomen and pelvis is not useful, at least in male patients with overweightness and obesity.
Evaluar variaciones del SUV hepático respecto al índice de masa corporal (IMC) de los pacientes estudiados con PET/TC de cuerpo entero.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo. Variables estudiadas: dosis inyectada de 18F-FDG (mCi), edad (años), glucemia (mg/dl), talla (cm) y peso (kg). Se calculó el IMC y se expresó el valor medio de SUV según sexo e IMC. Se aplicó un análisis de regresión lineal para determinar las variables independientes que mejor predicen el valor de SUV.
ResultadosEl análisis incluyó 603 pacientes: 305 mujeres y 298 hombres, cuyas edades medias fueron 54,9±15,2 años. El SUV hepático promedio fue significativamente mayor en los varones y aumentó de manera significativa tanto en mujeres como en hombres con sobrepeso y aún más en aquellos con obesidad. Las variables independientes que mejor predijeron el valor de SUV fueron sexo, edad e IMC. En pacientes con similares características, el valor de SUV se incrementó en 0,002 por cada aumento en un año de edad y en 0,066 por cada aumento de una unidad en el valor del IMC.
ConclusionesLa captación hepática de 18F-FDG aumenta a medida que lo hace el IMC del paciente. Las variables independientes que mejor predicen el valor de SUV hepático son edad y sexo de los pacientes. Nuestros hallazgos restan utilidad al empleo del valor de actividad metabólica hepática fisiológica como referencial respecto a captaciones dudosas en otros sitios del abdomen y pelvis, al menos en pacientes varones con sobrepeso y obesidad.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora