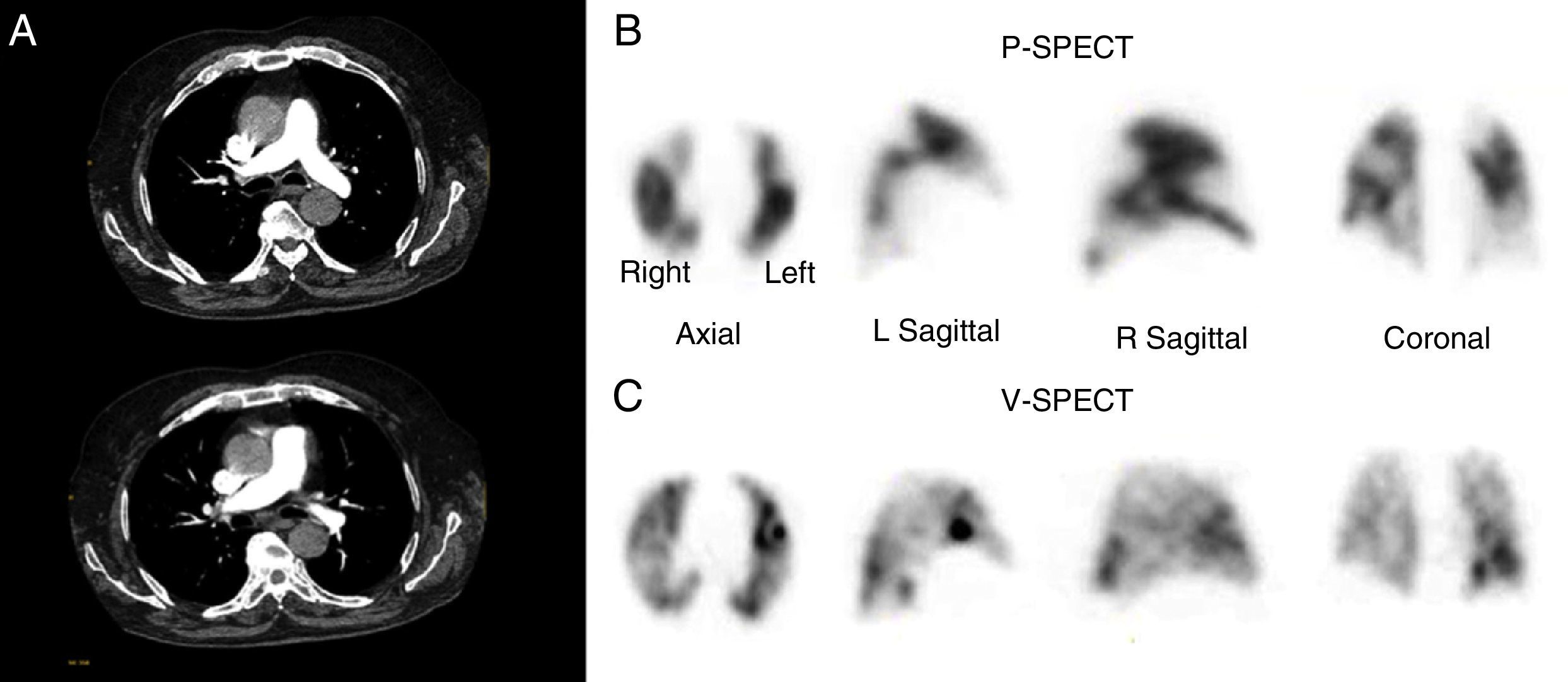
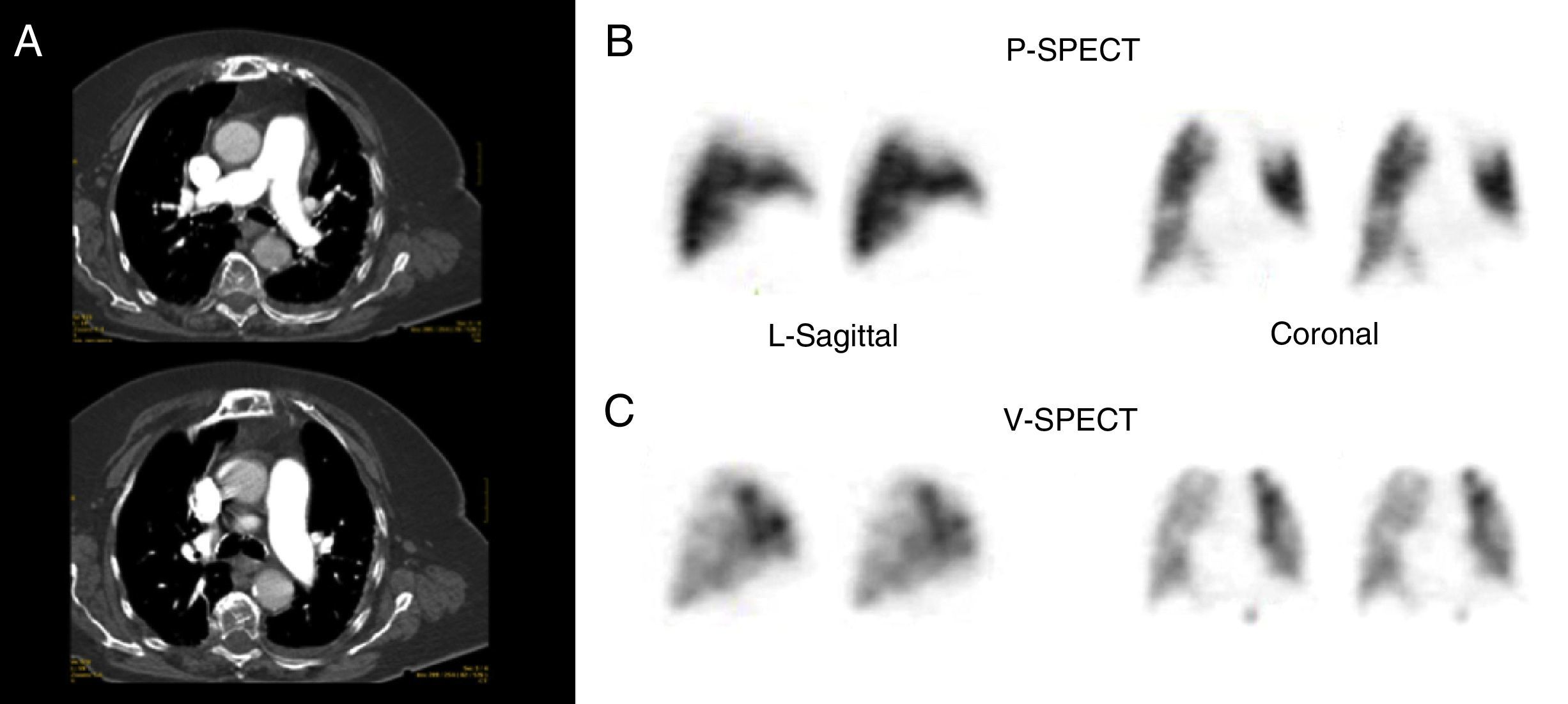
The aim was to compare ventilation/perfusion SPECT lung scintigraphy (V/Q-SPECT) and computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) in patients with suspicion of pulmonary embolism (PE).
Material and methodsThis prospectively designed study included 53 patients with intermediate or high clinical probability of PE. A V/Q-SPECT and CTPA was performed on all patients. The V/Q-SPECT was interpreted according to the European Association of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (EANMMI) guidelines. CTPA was reported as positive, negative, or indeterminate.
ResultsCTPA was positive in 22 cases, negative in 28, and indeterminate in 3. V/Q-SPECT was positive in 27 cases, negative in 24, and non-diagnostic in 2. In the 22 with positive CTPA, V/Q-SPECT was positive in 18, negative in 3, and non-diagnostic in 1. In the 28 with negative CTPA, V/Q-SPECT was positive in 8, negative in 19, and non-diagnostic in 1. In the 3 with indeterminate CTPA, V/Q-SPECT was positive in 1 and negative in 2. In the 2 non-diagnostic cases V/Q-SPECT, CTPA was positive in 1 and negative in one. In the 10 high clinical probabilities, CTPA and V/Q-SPECT were positive in 7, negative in 2, and in 1, CTPA was positive and V/Q-SPECT negative. In the 38 intermediate probability group, CTPA and V/Q-SPECT were positive in 11, negative in 17, with CTPA negative and V/Q-SPECT positive in 8, and in 2 CTPA was positive and V/Q-SPECT negative. The results show that V/Q-SPECT detected PE in 5 patients more than CTPA.
ConclusionOur results show a 77% concordance of both techniques. Overall V/Q-SPECT detected PE in 18% more patients than CTPA in the intermediate group. Both techniques have a complementary role when a diagnosis cannot be made with one of them.
Comparar la gammagrafía pulmonar SPECT de ventilación/perfusión (SPECT-V/Q) y la angiografía pulmonar computarizada (CTPA) en pacientes con sospecha de tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP).
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo en 53 pacientes con probabilidad intermedia y alta de TEP. A todos se les realizó SPECT-V/Q y CTPA. La SPECT-V/Q fue interpretada según la guía publicada por la European Association of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (EANMMI). La CTPA fue reportada como positiva, negativa o indeterminada.
ResultadosLa CTPA fue positiva en 22, negativa en 28 e indeterminada en 3. La SPECT-V/Q fue positiva en 27, negativa en 24 y no diagnóstica en 2. En 22 con CTPA positiva, la SPECT-V/Q fue positiva en 18, negativa en 3 y no diagnóstica en una. En 28 con CTPA negativa, la SPECT-V/Q fue positiva en 8, negativa en 19 y no diagnóstica en uno. En 3 con CTPA indeterminada, la SPECT-V/Q fue positiva en una y negativa en 2. En 2 con SPECT-V/Q no diagnóstica, la CTPA fue positiva en una y negativa en una. En 10 con probabilidad clínica alta la CTPA y la SPECT-V/Q fueron positivas en 7, negativas en 2 y en una la CTPA fue positiva y la SPECT-V/Q negativa. En 38 con probabilidad intermedia la CTPA y la SPECT-V/Q fueron positivas en 11 y negativas en 17. En 8 la CTPA fue negativa y la SPECT-V/Q positiva, en 2 la CTPA fue positiva y la SPECT-V/Q negativa; por lo tanto, la SPECT-V/Q detectó TEP en 5 pacientes más de la CTPA.
ConclusiónNuestros resultados muestran un 77% de concordancia entre ambas técnicas. En general la SPECT-V/Q detectó TEP en 18% más pacientes que la CTPA en el grupo con probabilidad intermedia. Ambas técnicas tienen un papel complementario cuando el diagnóstico no puede ser alcanzado por una de ellas.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora