Our aim was to analyse the performance of [11C]choline PET/CT in prostate cancer (PCa) surveillance, especially in patients with prostate specific antigen (PSA) < 1 ng/mL.
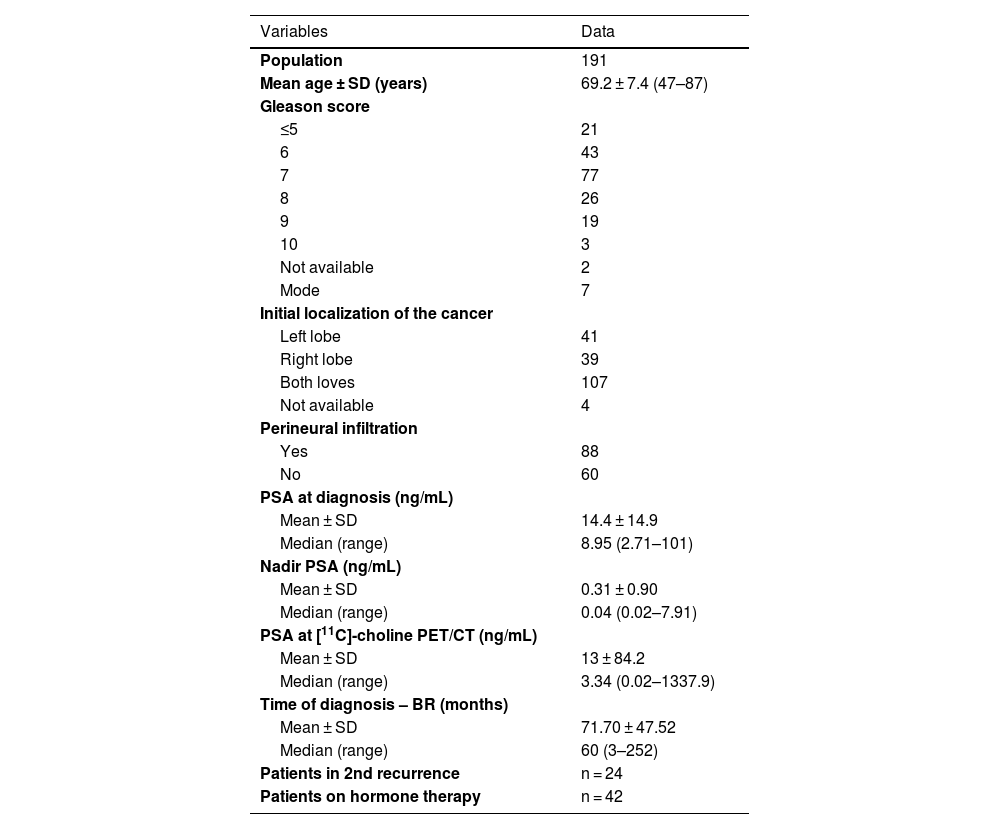
Material and methodsThree hundred and twenty-nine [11C]choline PET/CT examinations from 191 patients (68.2 ± 7.2 years) submitted for PCa surveillance or biochemical recurrence were retrospectively evaluated. PSA at study was 13.0 ± 84.2 ng/mL. Main initial treatment was radical prostatectomy (RP) in 81 patients, and other treatments (radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormonotherapy) in 110. PET/CT was acquired 20’ after injection of 555-740 MBq of [11C]choline. Minimum follow-up was 12 months.
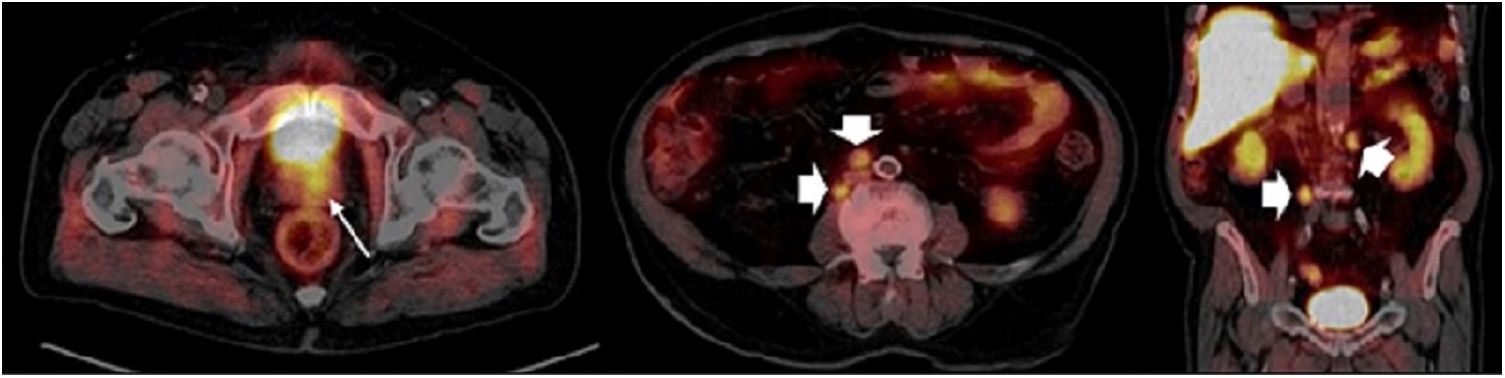
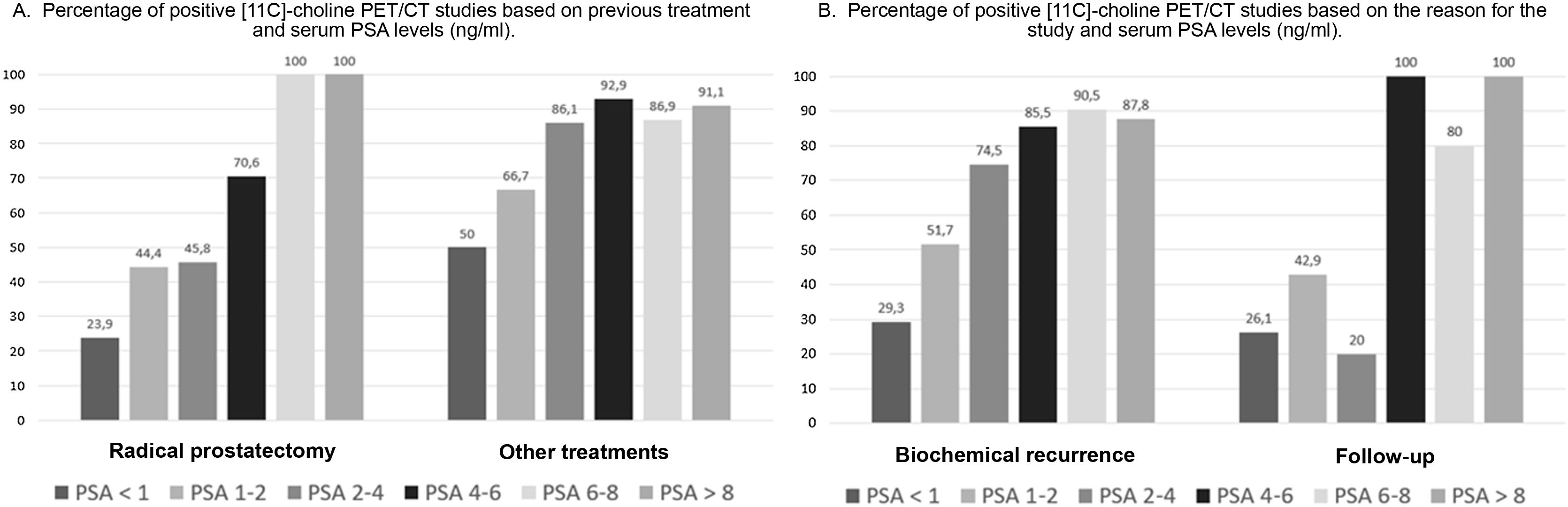
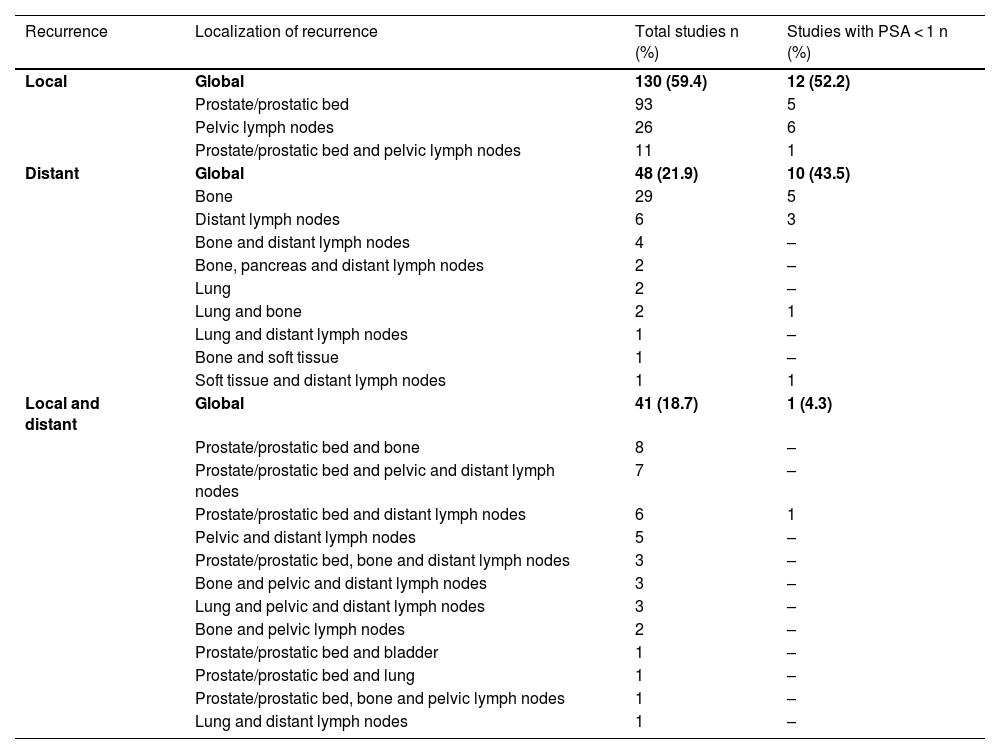
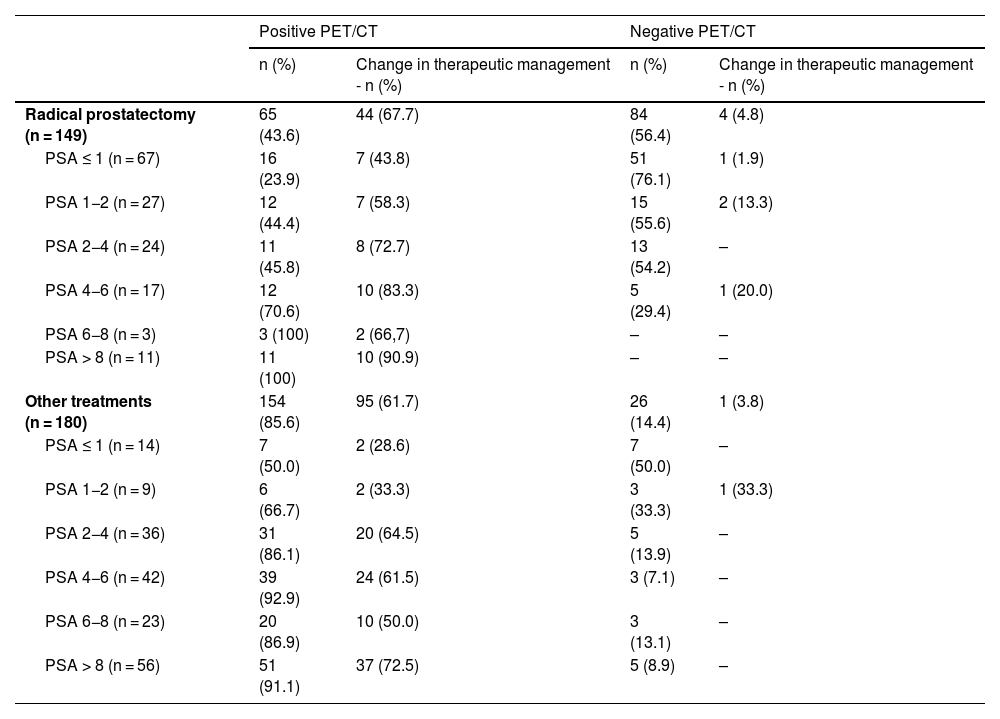
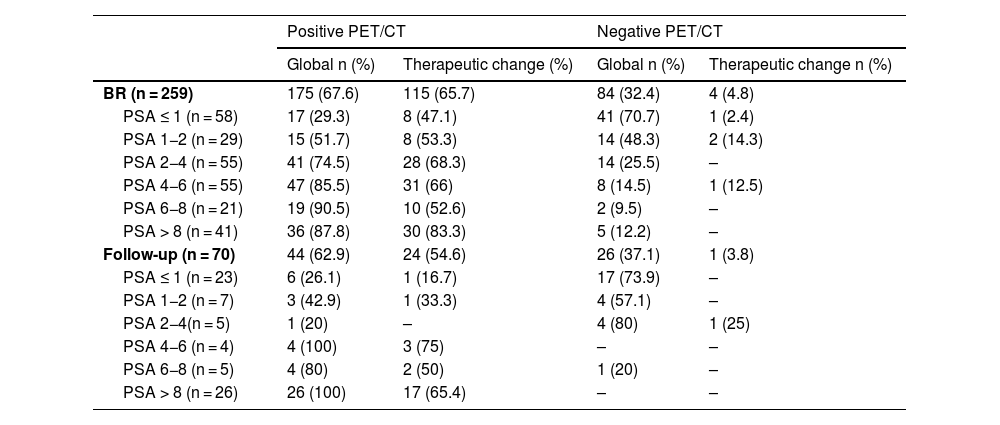
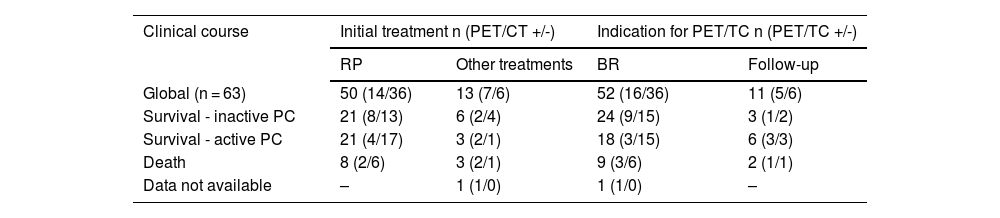
ResultsTwo hundred and nineteen (66.6%) out of the 329 PET/CT examinations were positive. The percentage of positive examinations was significantly higher in patients with other initial treatment than RP compared to patients with RP (85.6% vs. 43.6%, respectively). One hundred and thirty PET/CT (59.4%) showed local recurrence, 48 (21.9%) distant recurrence, and 41 (18.7%) local plus distant recurrence. Initial therapeutic approach was changed in 139 cases (63.5%). In the subgroup of 81 [11C]choline PET/CT scans performed with PSA < 1 ng/mL, 23 (28.4%) showed a positive result. Initial therapeutic approach was changed in 9 (11.1%). Three (4.8%) out of 63 patients died as per PCa.
Conclusion[11C]choline PET/CT demonstrated its effectiveness in PCa surveillance and restaging, even in patients with serum PSA < 1 ng/mL. The diagnostic performance was different depending on the initial treatment, been higher in patients with non-surgical treatment.
Analizar el rendimiento diagnóstico de la PET/TC con [11C]colina en el seguimiento del cáncer de próstata (CaP), especialmente en pacientes con antígeno prostático específico (PSA) < 1 ng/mL.
Material y métodosSe evaluaron retrospectivamente 329 exploraciones PET/TC con [11C]colina de 191 pacientes (68,2 ± 7,2 años) con CaP con recaída bioquímica o en seguimiento (PSA al momento del PET/TC: 13,0 ± 84,2 ng/mL). El tratamiento inicial fue prostatectomía radical (PR) en 81 pacientes y otros tratamientos (radioterapia, quimioterapia, hormonoterapia) en 110. La PET/TC se adquirió 20' después de la inyección de 555-740 MBq de [11C]colina. El seguimiento mínimo fue superior a 12 meses.
ResultadosDoscientos diecinueve (66,6%) de las 329 exploraciones PET/TC fueron positivas. El porcentaje de positivos fue significativamente mayor en los pacientes con otro tratamiento inicial diferente a la PR (85,6% frente a 43,6%, respectivamente). Ciento treinta PET/TC (59,4%) mostraron recidiva local, 48 (21,9%) a distancia y 41 (18,7%) local más a distancia. El abordaje terapéutico inicial se modificó en 139 casos (63,5%). De los 81 PET/TC con [11C]colina realizados con PSA < 1 ng/mL, 23 (28,4%) fueron positivos. El abordaje terapéutico inicial se modificó en 9 (11,1%). Tres de 63 pacientes (4,8%) fallecieron por CaP.
ConclusionesLa PET/TC con [11C]colina demostró su eficacia en el seguimiento y la reestadificación del CaP, incluso en pacientes con PSA sérico < 1 ng/mL. El rendimiento diagnóstico fue diferente según el tratamiento inicial al que fueron sometidos los pacientes, siendo mayor en aquellos tratados inicialmente con otros tratamientos distintos de la PR.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)