Estudiar el valor de la carga viral para predecir la persistencia y/o la progresión en LSIL.
Diseño del estudioEstudio prospectivo. Todos los casos diagnosticados como LSIL en el año 2006, y seguidos a los 6, 12 y 24 meses después del diagnóstico.
MétodoCitología líquida (ThinPrep®, Hologic, Malborough, MA, EE. UU.) para realizar el estudio citológico. Test de captura de híbridos (HCII-HR, Quiagen, Hilden, Alemania), utilizando el test para determinar la presencia de VPH de alto riesgo.
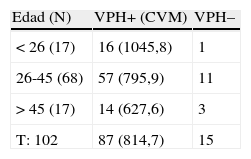
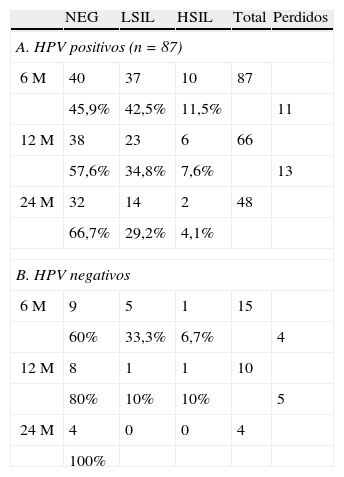
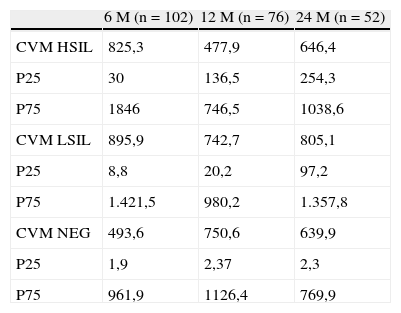
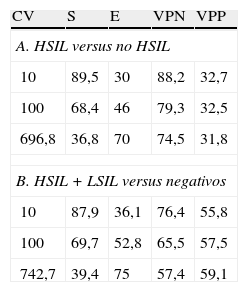
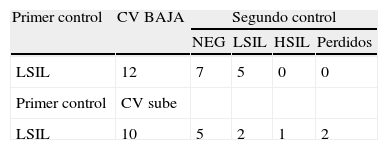
ResultadosDe los 102 casos, 87 fueron HPV positivos (85,3%). La persistencia o progresión se observó en el 54% de los casos en el primer control, en el 42,4% en el segundo control y en el 33,3% en el tercer control. No se demostró lesión en el seguimiento en el 46% de los casos en el primer control, en el 57% de los casos en el segundo control y en el 66,7% de los casos en el tercer control. Diecinueve casos progresaron a HSIL: 11 detectados en el primer control, 6 en el segundo y 2 en el tercero. La sensibilidad para HSIL nunca superó el 89%, con una especificidad siempre menor del 40%.
ConclusionesLa determinación de la carga viral mediante HC2 en LSIL no es útil para predecir su comportamiento.
To study the HPV viral load (VL) in the prediction of the persistence and/or progression in LSIL cases.
Study designProspective study. 102 consecutive cases diagnosed as LSIL in 2006 with follow-ups at 6, 12 and 24 months subsequent to diagnosis.
MethodLiquid based cytology (ThinPrep®, Hologic, Malborough, MA, USA), for the cytological study. Hybrid Captute II Test (HCII-HR, Quiagen, Hilden, Germany), for the determination of the presence or absence of High-Risk HPV.
Results87 of the 102 cases studied were HR-HPV positive (85.3%). The presence or progression was detected in 54%, 42% and 33.35% of the cases in the first, second and third controls respectively. No lesion was demonstrated in 46%, 57% and 66.7% of the cases at first, second and third controls respectively. 19 cases progressed to HSIL; 11 of which were detected on the first control, 6 on the second and 2 on the third. The sensitivity of the VL for detecting HSIL never exceeded 89%, with a specificity always inferior to 40%.
ConclusionThe VL determined by the HC2 method is not a useful indicator of prognosis in the follow-up of LSIL cases.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora