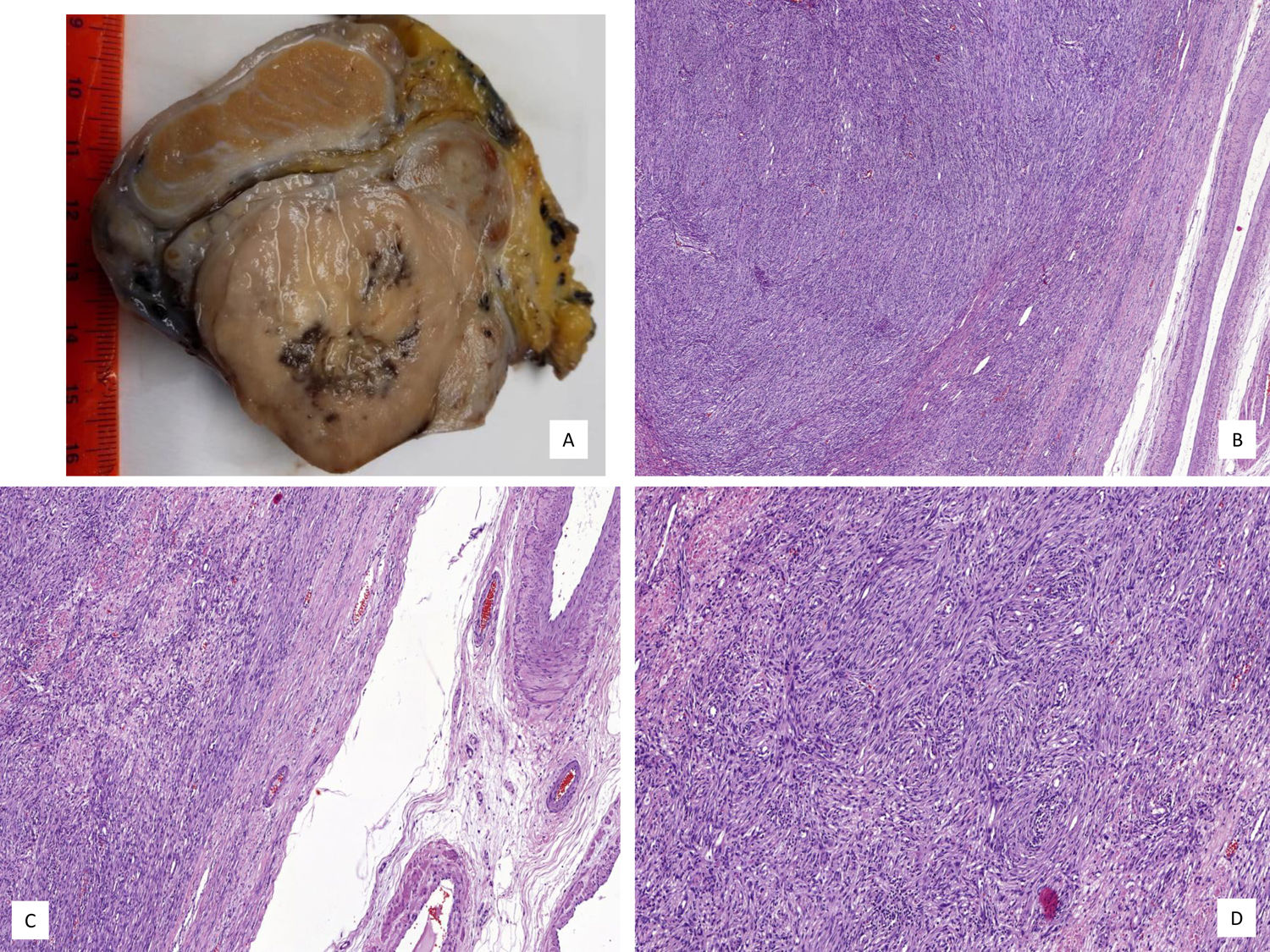
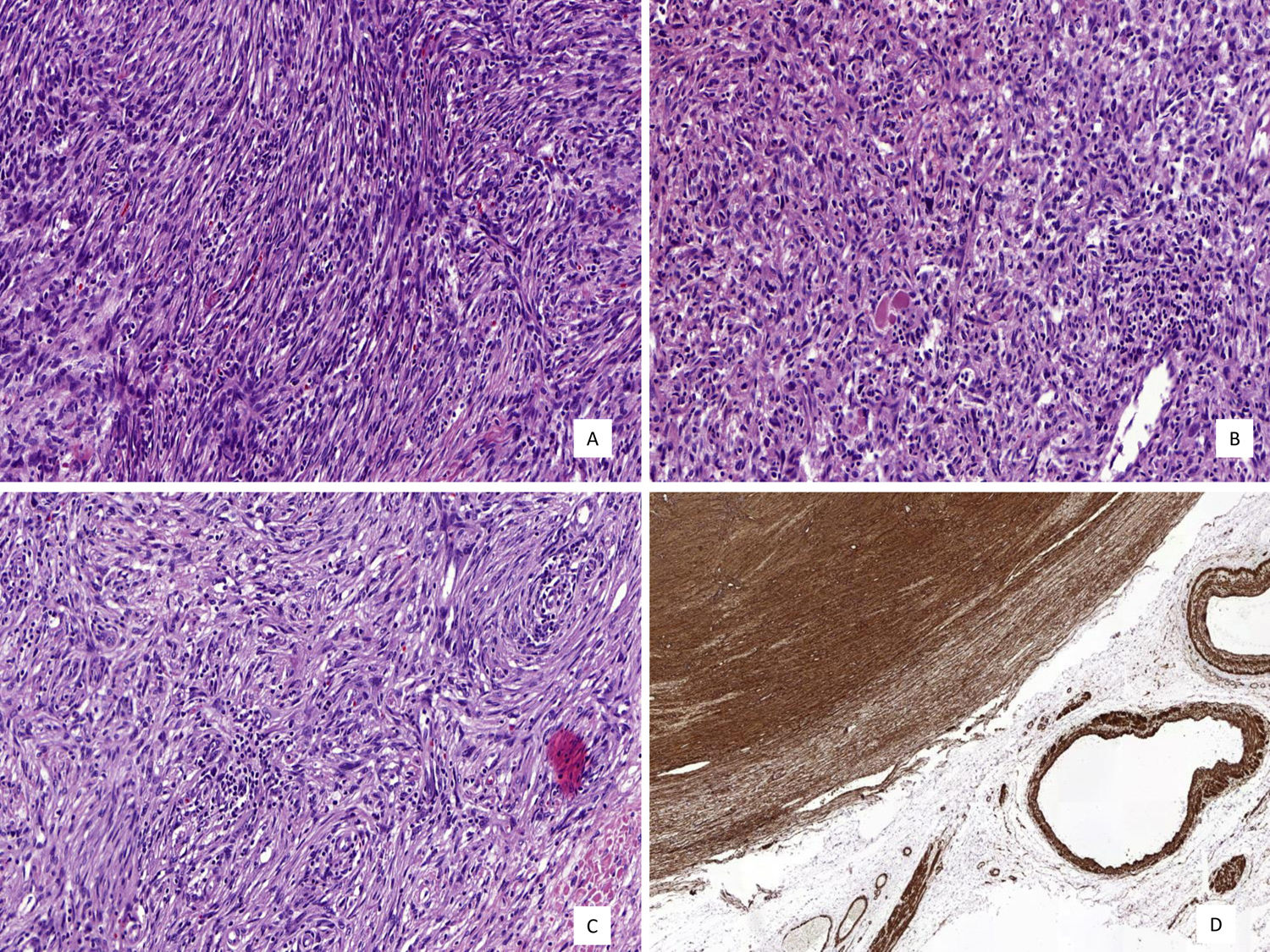
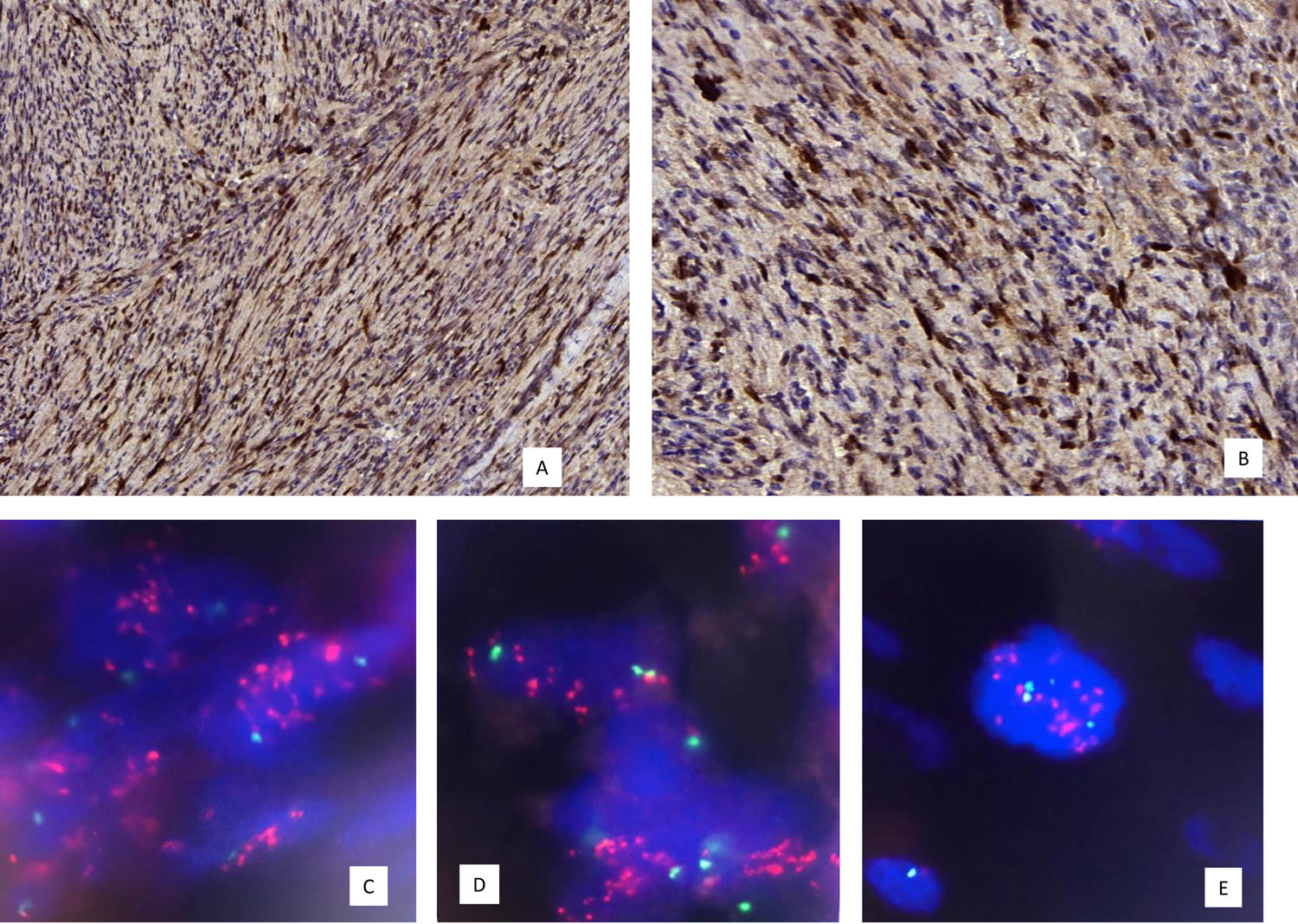
Se presenta un estudio histológico, inmunohistoquímico (IHQ) y molecular de un liposarcoma desdiferenciado paratesticular remitido a nuestro centro, con hallazgos histológicos similares a un tumor miofibroblástico inflamatorio. Las células tumorales fueron positivas para actina músculo liso (AML) y focalmente positivas para CD56, CD99, Bcl2 y EMA. La expresión de WT1, calretinina, miogenina, CK(AE1/AE3), desmina, H-caldesmona, CD34, ALK, CKIT, DOG1, MUC4 y STAT6 fue negativa. MDM2 mostró positividad nuclear intensa y difusa por IHQ y alto nivel de amplificación génica mediante hibridación fluorescente in situ (FISH). La FISH no reveló reordenamiento del gen SYT. En el estudio histológico del corte remitido no encontramos evidencias de componente liposarcomatoso bien diferenciado, aunque el aspecto macroscópico de la pieza lo sugería. El liposarcoma desdiferenciado puede presentar hallazgos histológicos que recuerdan a un tumor miofibroblástico inflamatorio y que expanden el espectro histológico de esta variante de liposarcoma. El conocimiento de la existencia de esta variante de liposarcoma es de crucial importancia para no confundirla con otras neoplasias que, aunque histológicamente similares, difieren en la evolución clínica y/o tratamiento.
We report the histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular findings of a dedifferentiated liposarcoma with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor-like features occurring in the paratesticular region. Histologically, the dedifferentiated component closely resembled an inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. The neoplastic cells were positive for smooth muscle actin with focal CD56, CD99, Bcl2 and EMA expression. WT1, calretinin, myogenin, CK(AE1/AE3), desmin, H-caldesmon, CD34, ALK, CKIT, DOG1, MUC4 and STAT6 were negative. MDM2 showed diffuse and strong nuclear positivity in neoplastic cells and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) revealed amplified MDM2 (high level) but no SYT rearrangement. Although a lipomatous component was evident macroscopically, well-differentiated liposarcomatous components were not evident in the section examined. Dedifferentiated liposarcoma can have prominent inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor-like features. Pathologists should be aware of this histological variant in order to avoid misdiagnosing dedifferentiated liposarcoma as inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor or other spindle cell tumors which have different behavioral patterns and treatment requirements.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora