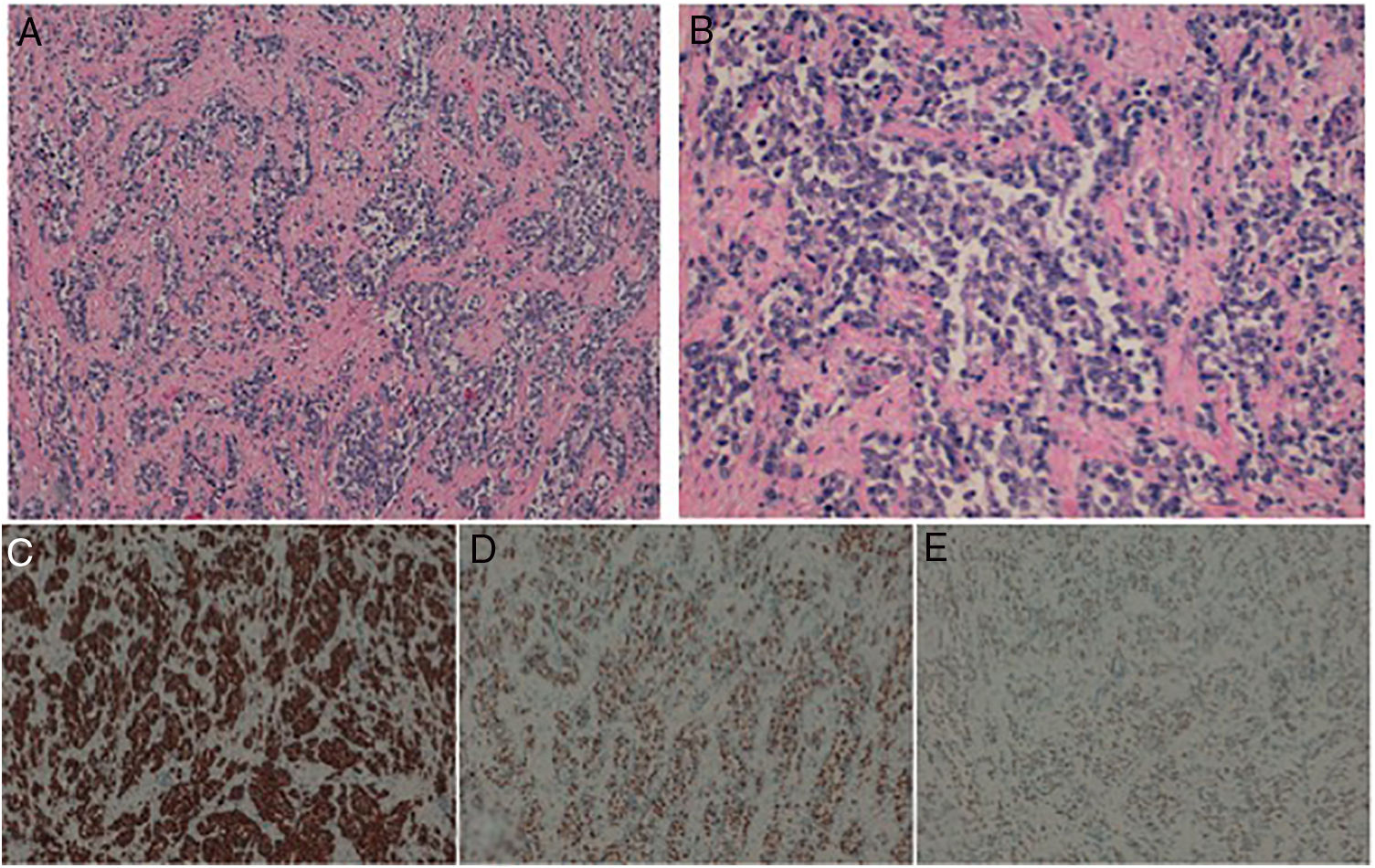
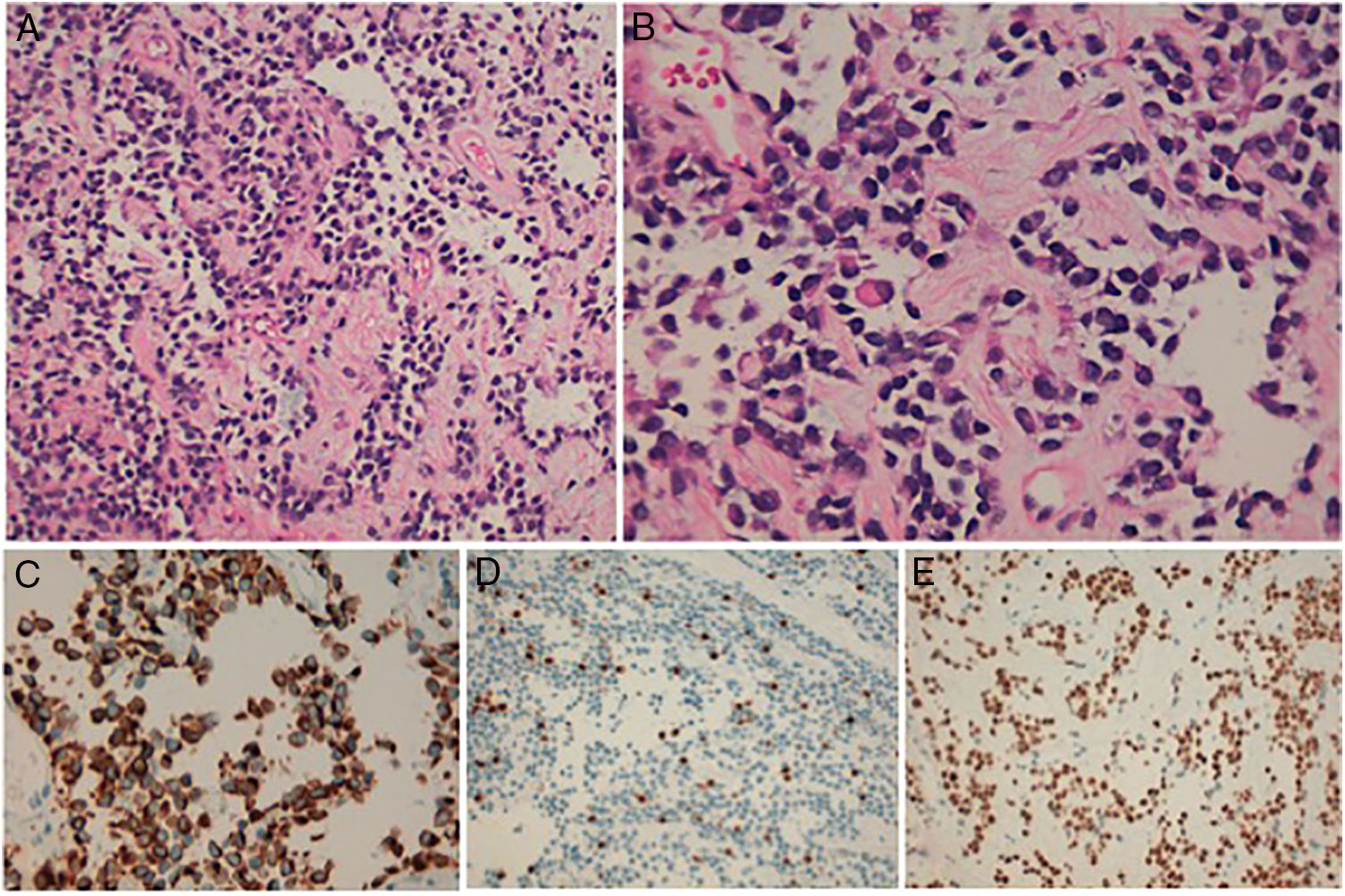
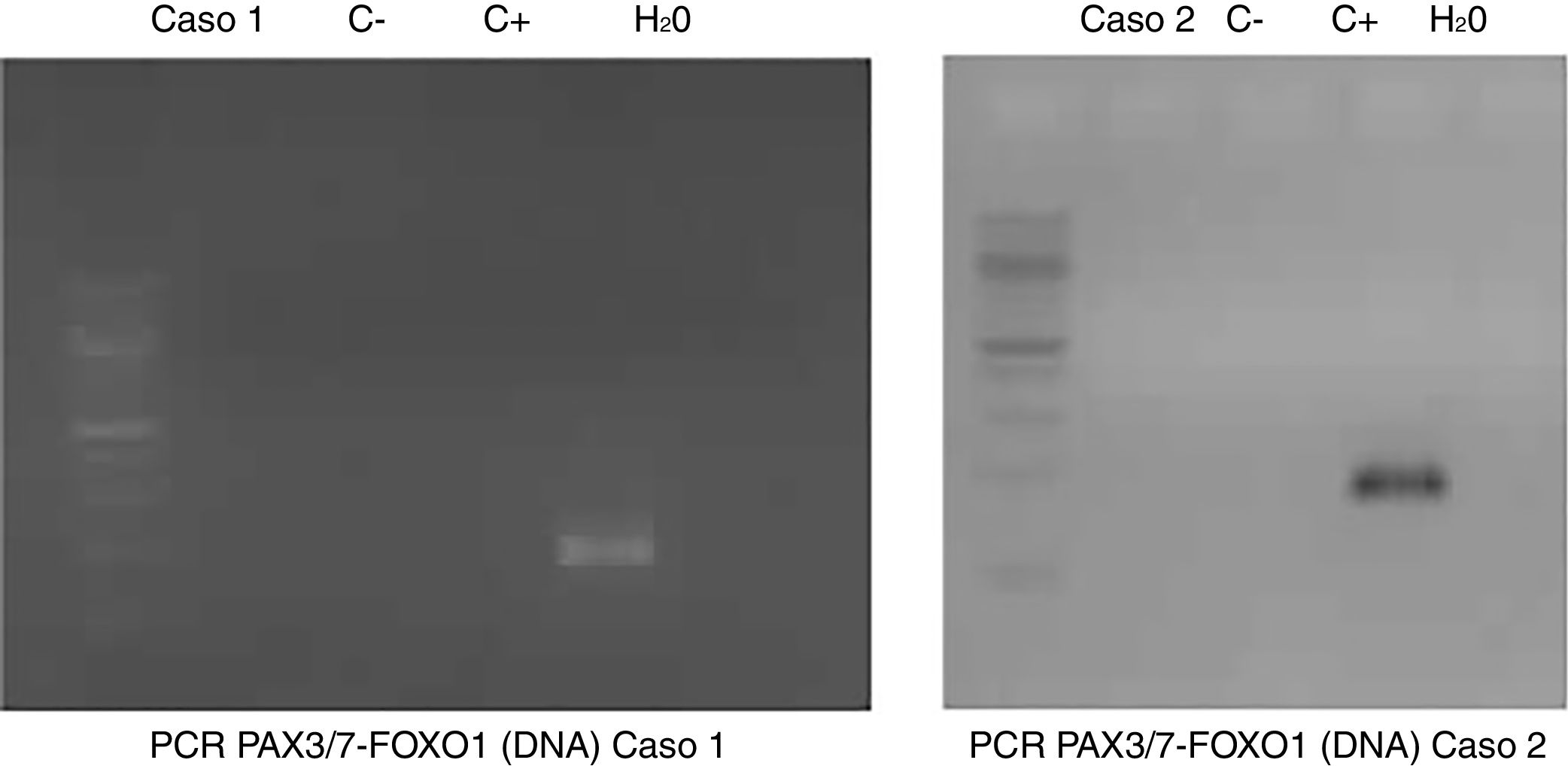
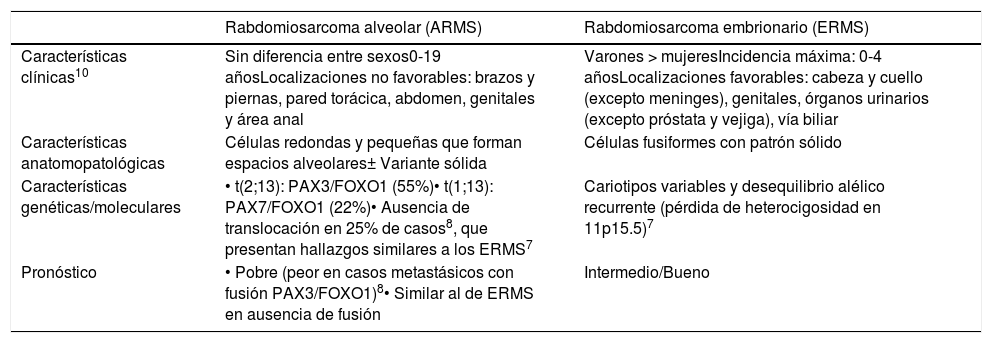
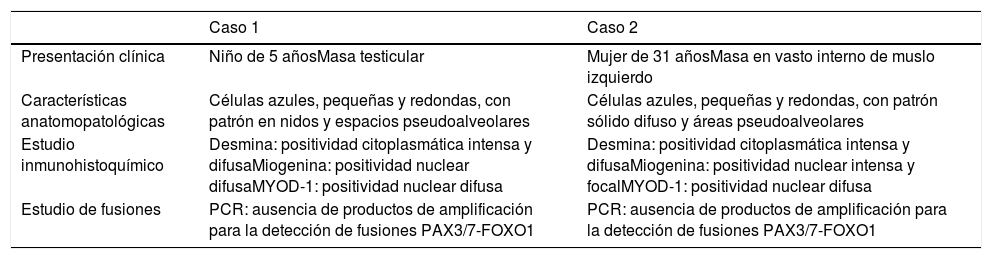
Los rabdomiosarcomas son los tumores de partes blandas más frecuentes en la edad pediátrica y en adultos jóvenes. Morfológicamente se distinguen dos subtipos principales: el rabdomiosarcoma alveolar y el rabdomiosarcoma embrionario. El subtipo alveolar se asocia generalmente con un peor pronóstico y presenta una fusión génica característica que clásicamente se ha utilizado para confirmar el diagnóstico: PAX3/7-FOXO1.
Presentamos dos casos que fueron remitidos a nuestro centro. Ambos mostraron morfología alveolar clásica y diferenciación muscular basada en la inmunohistoquímica; no obstante, carecían de la fusión característica PAX3/7-FOXO1. El objetivo de este artículo es resaltar la importancia del estudio molecular de estos casos no solo como herramienta diagnóstica sino también como factor pronóstico importante.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in childhood and adolescence. Morphologically, two major forms are described: alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. The former is generally associated with a poorer prognosis and it usually harbors a characteristic fusion gene, PAX3/7-FOXO1, that is used to confirm the diagnosis.
We present two cases, both of which exhibited the classic alveolar histology with immunohistochemical myogenic differentiation (Desmin, MYOD-1 and Myogenin expression) and lacked the characteristic fusion gene PAX3/7-FOXO1. The aim of this report is to highlight the importance of the molecular status in the study and diagnosis of these cases, as it seems to be not only a useful diagnostic tool, but also an important prognostic factor.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora