Scedosporium species are considered emerging pathogens causing illness in immunocompetent and immunocompromised hosts.
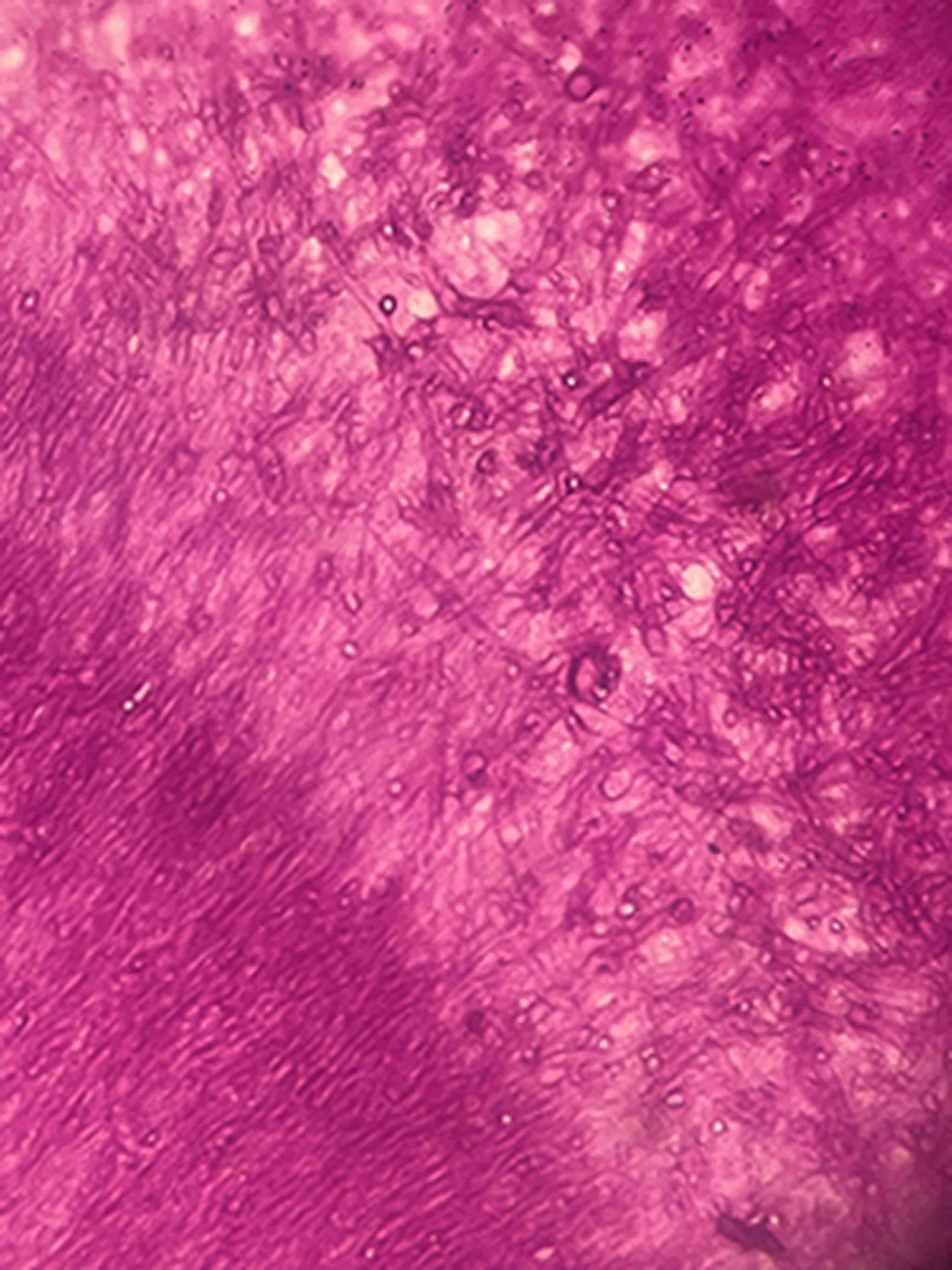
Case reportA case of non-invasive pulmonary (fungal ball) infection by Scedosporium apiospermum complex in a 49-year-old female with bronchiectasis and cavities secondary to tuberculosis is described. The patient had a history of three years of cough and hemoptysis. A computed tomography scan of the thorax revealed the presence of a cavity in the lower lobe of the right lung, associated with bronchiectasis. A combination of surgical debridement and antifungal therapy (voriconazole) was the treatment of choice. Pulmonary resection (right lower lobectomy) was performed, and samples were sent for microbiological culture and histopathological examination; by means of the latter technique, hyphae were shown. The identification of Scedosporium angustum, a phylogenetic species of the S. apiospermum complex, was obtained by amplifying and sequencing the β-tubulin locus. Voriconazole therapy was started at a loading dose of 800mg/12h for the first 24h, followed by 200mg/12h for 6 months. The patient responded favorably to the treatment and remained asymptomatic.
ConclusionsThis case emphasizes the importance of considering Scedosporium species in the differential diagnosis of fungal balls by Aspergillus.
.
Las especies de Scedosporium se consideran patógenos emergentes que pueden causar enfermedades en hospedadores inmunocompetentes e inmunodeprimidos.
Caso clínicoSe describe un caso de infección pulmonar no invasiva (bola fúngica) por una especie del complejo Scedosporium apiospermum en una mujer de 49 años con bronquiectasias y cavitaciones secundarias a tuberculosis. La paciente tenía antecedentes de tos y hemoptisis de tres años de evolución. La tomografía computarizada de tórax reveló, como secuela, la presencia de una cavidad en el lóbulo inferior del pulmón derecho, asociada a bronquiectasias. El tratamiento de elección fue la combinación de desbridamiento quirúrgico y tratamiento antimicótico (voriconazol). Se realizó resección pulmonar (lobectomía inferior derecha), y se enviaron muestras para cultivo microbiológico y examen histopatológico. En el examen del tejido se observaron hifas. La identificación de Scedosporium angustum, una especie filogenética del complejo Scedosporium apiospermum, se obtuvo mediante amplificación y secuenciación del locus de la β-tubulina. Se inició tratamiento con voriconazol con una dosis de carga de 800mg/12h durante las primeras 24h, seguida de 200mg/12h durante 6 meses. La paciente respondió bien al tratamiento y permaneció asintomática.
ConclusionesEste caso enfatiza la importancia de considerar las especies de Scedosporium en el diagnóstico diferencial de bolas fúngicas en pulmón por Aspergillus.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora