Inguinal hernia repair is one of the most common surgeries performed worldwide by general surgeons. More than 750,000 inguinal hernia repairs are performed each year in the United States. Complications of inguinal or femoral hernia are relatively rare, depending on the clinical circumstances in which the patient is admitted to the operating room and the type of hernia. The complications are classified as: intraoperative, short term and long term. Arterial lesions are the rarest but most dangerous.
ObjectiveTo describe surgical techniques used to repair injuries to the external iliac artery during an inguinal hernia repair that is reproducible by general surgeons.
Materials and methodsA case report of an intraoperative external iliac artery injury is presented in which is a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft was used over the length of the lesion. Different techniques may be used for revascularisation: autogenous vein graft, synthetic grafts, revascularisation with ipsilateral or contralateral internal iliac artery and femoro-femoral crossover graft.
ConclusionThe surgical technique using PTFE grafts is effective for repairing arterial injuries and it results in timely revascularisation that promotes satisfactory progress.
La plastia inguinal es una de las cirugías más frecuente realizadas a nivel mundial por cirujanos generales. En Estados Unidos más de 750,000 hernioplastias inguinales se realizan por año. Las complicaciones de una hernia inguinal o femoral son relativamente infrecuentes, depende de las circunstancias clínicas en las que se ingresa a quirófano y el tipo de la hernia. Las complicaciones se clasifican en: intraoperatoría, a corto plazo y a largo plazo. Las lesiones arteriales son las más raras pero más graves.
ObjetivoDescribir técnicas quirúrgicas para reparación de lesiones de la arteria iliaca durante una plastia inguinal y reproducible por cirujanos generales.
Material y métodoSe presenta un caso clínico con lesión de arteria iliaca externa intraoperatoría la cual se realiza injerto de politetrafluoroetileno (PTFE) por la longitud de la lesión. Se puede utilizar diferentes técnicas para la revascularización: injerto de vena autóloga, injertos sintéticos, revascularización con arteria hipogástrica ipsi o contralateral e injerto cruzado femoro-femoral.
ConclusiónLa técnica quirúrgica utilizando injerto de PTFE es eficaz para la reparación de lesión arterial y tener una revascularización oportuna que favorece una satisfactoria evolución.
Inguinal hernia repair is one of the most common surgeries performed worldwide by general surgeons. More than 750,000 inguinal hernia repairs are performed each year in the United States.1 Hernias are more common in men than in women, and in Caucasians than in blacks. There are many techniques for repairing the hernia which can be categorised as tension-free repair (using a mesh) and tension repair where the primary tissues are pulled tight and no mesh is used.2 Lichtenstein tension-free repair using polypropylene mesh is the gold standard for inguinal hernia repair.3 The procedure is easy for surgeons to learn, and can even be performed under local anaesthesia which is attributed to reducing hernia recurrence to <5%.4
Hernias are classified based on anatomical location: inguinal (direct or indirect), femoral or crural. Approximately 96% of hernias are inguinal and 4% are femoral.5 They can be classified according to their aetiology (congenital or acquired).5 The most commonly used classifications for inguinal hernias are those by Gilbert, Hyhus, and Schumpelick. Other classifications systems have been proposed by Bendavid, Alexander, and Zollinger; however, they are difficult to remember and too complex. For this reason, a process to reach a consensus was used to develop an easier classification to categorise hernias into the updated traditional classification as shown in Table 1.6
Updated traditional classification of inguinal hernias.
| Updated traditional | Nyhus–Stoppa | Gilbert | Schumpelick |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Small indirect | I | 1 | L1 |
| 2. Medium indirect | II | 2 | L2 |
| 3. Large indirect | IIIB | 3 | L3 |
| 4. Small direct | IIIA | 5 | M1 |
| 5. Medium direct | IIIA | – | M2 |
| 6. Large direct | – | 4 | M3 |
| 7. Combined | IIIB | 6 | MC |
| 8. Femoral | IIIC | 7 | F |
| 0. Other | – | – | – |
Risk factors for developing a hernia include the following3,7–14:
History of hernia or prior hernia repair (including in childhood)
Being older
Being male
Being Caucasian
Chronic cough
Increased intra-abdominal pressure
Chronic constipation
Abdominal wall injury
Smoking
Ascites
Prostatism
Family history of hernia
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Complications of inguinal or femoral hernia are relatively rare, depending on the clinical circumstances in which the patient is admitted to the operating room and the type of hernia. In a randomised study to determine the frequency of complications in a total of 1,983 patients who underwent laparoscopic and open inguinal hernia repair surgery, it was found that 35% had a significant complication and there was a higher range in those who underwent laparoscopic repair than in those who underwent open repair (39% vs 33%; P=.02).1
The complications can be grouped into three types depending on when they presented:
- -
Intraoperative complications (bleeding, nerve injury, vascular injury, vessel injury in the vas deferens, anaesthesia complications), 2% of which occurred in open repair using the Lichtenstein mesh technique and 5% in laparoscopic repair. Vascular injury complications were reported in 5 patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery. No major vascular lesions were found in open repair surgeries.
- -
Short-term post-operative complications (surgical site injection, trocar site infection, wound haematoma, scrotal haematoma, orchitis, seroma or hydrocele, chronic leg pain, chronic inguinal pain, urinary tract infection, and urinary retention) are reported with similar percentages for laparoscopic vs open surgery, with 26% and 20%, respectively. Complications such as wound haematoma, scrotal haematoma, and hydrocele were the most common in both groups.
- -
Long-term complications (chronic leg pain, chronic inguinal pain, seroma or hydrocele) were the most common.8,15
External iliac artery injury has a low incidence in open inguinal hernia repair and there are no case reports in the literature.
Case reportA 28-year-old male patient. Originally from and residing in Cuyamecalco Cuicatlán with no prior relevant history, the complaint started with pain in the left inguinal region, which was exacerbated with effort and decreased when taking analgesics. There was an increase in volume that grew when performing the Valsalva manoeuvre. He was assessed by the Department of General Surgery and diagnosed with an inguinal hernia. Surgery was scheduled for inguinal hernia repair surgery, plus placement of a Lichtenstein polypropylene mesh. During the surgery he presented incidental arterial injury with 400ml of blood loss. The site of bleeding was unable to be identified, and so two ring forceps were placed which stopped the bleeding and ended the procedure. He was transferred to this unit.
He was assessed in the Emergency Department at the Hospital Regional de Alta Especialidad de Oaxaca. The patient was conscious, oriented, well-hydrated, normal-coloured skin, uncompromised chest, abdomen flat, bowel sounds present, soft, depressible, non-tender upon palpation, no organomegaly. Transverse wound in the left inguinal region with two forceps inside, left pelvic extremities with no femoral, popliteal, or pedal pulse with diminished capillary refill 6s after digital pressure and decreased temperature in comparison to the right side.
Blood work at admission: Blood gases: venous pH: 7.24, pCO2: 39 pO2: 50 HCO3−: 16.7, BEb−: 10.7, SO2: 77. Blood chemistry: glucose 98mg/dl, urea 15mg/dl, creatinine 0.6mg/dl, albumin 3.8g/dl, AST 29U/l, ALT 36U/l, ALP 90U/l, LDH 758mg/dl, sodium 139mmol/l, K 3.8mmol/l, Cl 105mmol/l, calcium 9.3mg/dl, total bilirubin: 2.06mg/dl, indirect 1.96mg/dl, complete blood count: white blood cells 17,000, haemoglobin 14.5g/dl, platelets 218,000, neutrophils 14.68fl, PT 14s, aPTT 28s, INR 1.07%.
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) was performed with the following significant findings: The left external iliac artery showed no contrast enhancement throughout its entire trajectory. The presence of the ring forceps with which it was clamped were seen at the juncture with the common femoral artery, later bypassing this clamping. A Doppler ultrasound was performed, observing very slow flow rates in this artery, at 22cm/s (Fig. 1). The common femoral artery was also partially clamped as is seen from the blood flow with the Doppler ultrasound. Diagnosis: occlusion of the left external iliac artery. The common femoral artery and common femoral vein were clamped, showing a bypass in their distal segment with diminished flow rates.
Per surgical protocol he was admitted to the operating room where surgery was performed using a Gibson incision. Findings included external iliac artery integrity and a complete blockage just below the inguinal ligament. Full dissection was performed (Fig. 2). An 8 French Fogarty catheter was introduced into the proximal and distal end of the severed artery and the thrombus was extracted. Adequate blood flow was confirmed and end-to-end anastomosis using polypropylene 6-0 was performed to connect the external iliac artery to the PTFE vascular graft (Fig. 3). Distal flow was confirmed, haemostasis was confirmed, and a layered polypropylene 1 closure was used. The procedure was ended.
Injury to the external iliac artery during open inguinal hernia repair is extremely rare. However, it is a devastating scenario that can result in the loss of the limb if it is not properly treated in time to re-establish normal blood flow to the limb.16 This type of lesion requires immediate surgical treatment. The CT angiography used for the diagnosis is a versatile technique with a wide range of applications beyond arteriography. Delineating the vascular anatomy is achieved well within a very short acquisition time and vessel injuries can be identified and characterised by the millimetre to be able to determine the type of lesion and its extent.17,18 Managing the lesions depends on the anatomical location, the mechanism of the injury, and its nature. Endovascular diagnosis and treatment may be performed, including placing a stent. A good tolerance has been described, with a short hospital stay, and a combination of endovascular therapy may be performed as a complement to definitive surgical treatment.23 It is possible to treat most lesions with just polypropylene vascular sutures (4-0 to 6-0). However, in more extensive lesions, an autologous vein graft is the material of choice in traumatic wounds, although in new studies the data do not favour vein grafts and even lean towards prosthetic materials to repair traumatic arterial lesions.19,20 In this case, a synthetic polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft was placed and its permeability assessed using Doppler ultrasound, observing good blood flow through the femoral artery while also performing a vein check to rule out thrombosis.
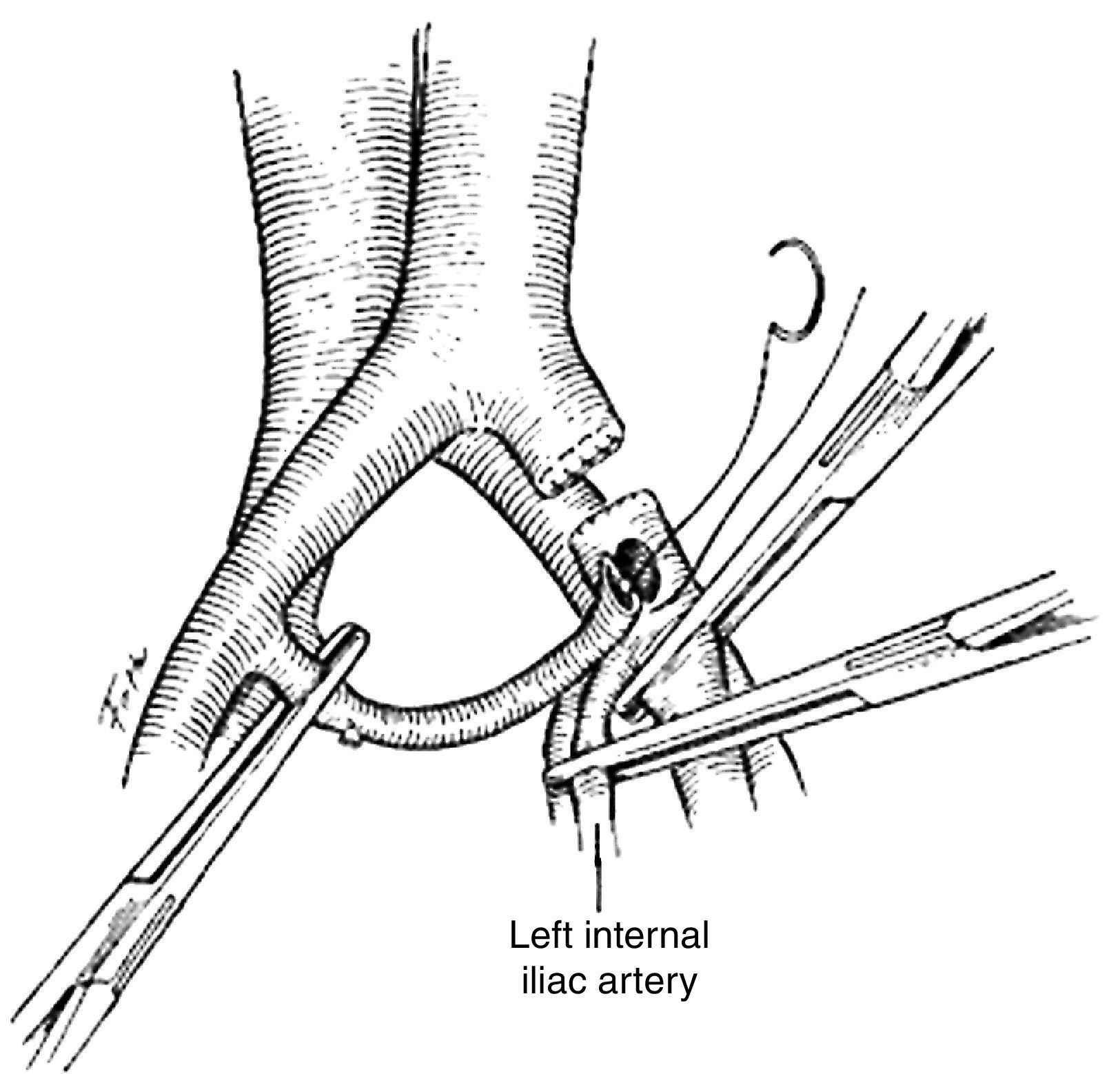
Sometimes the necessary graft materials are not at hand, and so different techniques may be used. The ipsilateral internal iliac artery may serve to re-establish blood flow. The artery is moved to the level of the middle rectal artery. Once the internal iliac artery has been moved, the middle rectal artery is severed and the distal end is sutured with a continuous 4-0 polypropylene suture (Fig. 4).21 Should the lesion be continuous to the internal iliac artery and unable to be moved, the contralateral artery can be used following the same steps (Fig. 5).21 The extra-anatomical bypass is a femoro-femoral crossover graft. The two femoral arteries should preferably be exposed by two surgical teams, one for each side, and the conserved distal artery identified. A subcutaneous tunnel is created, going over the pubic symphysis between the two groins, and then anastomosis is performed below the inguinal ligament with 4-0 to 6-0 polypropylene vascular sutures.22
The most important thing with artery lesions is early identification, as well as damage control. It is important for the surgeon performing the reconstruction to have all the necessary materials to successfully complete the procedure. Should they not be available, it is best for the patient to be sent to a specialised centre where treatment can be offered.23 For our patient, the quick decision to transfer him and the partial perfusion were a factor in his favour for saving the limb. Full knowledge of the anatomy is among the most important technical aspects for performing hernia repair.
Ethical disclosureProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work centre on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.