Trees or tree-like plants are defined here broadly as perennial, self-supporting plants with a total height of at least 5m, without considering ascending leaves or inflorescences, and with 1 or several erect stems with a diameter of at least 10cm. In this third contribution of the taxonomic compilation of Mexico's native tree species, 271 species are presented: 27 in the family Apocynaceae (26% endemic), 63 in the Cactaceae (79%), 17 in the Ebenaceae (35%), 123 in the Fagaceae (60%), and 41 in the Sapotaceae (22%). Several cactus genera are endemic to Mexico, notably Neobuxbaumia with 10 species and heights up to 22m. The oak genus Quercus with 122 species is the most species-rich genus of Mexican trees. Several species are reported to reach heights of 60m (Aspidosperma desmanthum, Quercus benthamii, Q. corrugata, and Manilkara chicle). All species are listed in an appendix, including the original publication, references of taxonomic revisions, in some cases synonyms, existence of subspecies or varieties, maximum height in Mexico, and the indication if the species is endemic to Mexico.
Las plantas arbóreas o arborescentes se definen en este trabajo en un sentido amplio como plantas perennes que se pueden sostener por sí solas, con una altura total de al menos 5 m, sin considerar hojas o inflorescencias ascendentes y con 1 o varios tallos erectos de un diámetro de al menos 10 cm. En esta tercera contribución de la recopilación de las especies arbóreas nativas de México, se presentan 271 especies: 27 de la familia Apocynaceae (26% endémicas), 63 de Cactaceae (79%), 17 de Ebenaceae (35%), 123 de Fagaceae (60%) y 41 de Sapotaceae (22%). Algunos géneros de Cactaceae son endémicos en México, notablemente Neobuxbaumia con 10 especies y alturas de hasta 22 m. Con 122 especies, Quercus es el género arbóreo más diverso en especies de México. Algunas especies se registran con alturas de hasta 60 m (Aspidosperma desmanthum, Quercus benthamii, Q. corrugata y Manilkara chicle). Todas las especies se enlistan en un apéndice que incluye el nombre científico, los datos de su publicación original, referencias de revisiones taxonómicas, en algunos casos sinónimos, la existencia de subespecies o variedades, la altura máxima en México y la indicación de si la especie es endémica de México.
In Ricker and Hernández (2010), and slightly extended in Ricker, Hernández, Sousa, and Ochoterena (2013), trees or tree-like plants were defined broadly as perennial, self-supporting plants with a total height of at least 5m, without ascending leaves or inflorescences, and with 1 or several erect stems with a diameter of at least 10cm, measured at 1.3m above the ground level, or measured above buttresses if these are present. A tree or tree-like species contains individuals with tree characteristics at least somewhere in its geographic range, but not necessarily everywhere. After discussing the tree definition and emphasizing the need for an updated taxonomic list of Mexico's tree species, Ricker and Hernández (2010) presented 170 species of gymnosperms, monocotyledons, and tree ferns. In Ricker et al. (2013) the work was continued with 619 species in the species-rich plant families Asteraceae, Leguminosae, and Rubiaceae. The Leguminosae, with 449 tree species in its 3 subfamilies, is the most diverse tree-species family in Mexico. In the current paper, the work is continued with 5 plant families: Apocynaceae, Cactaceae, Ebenaceae, Fagaceae, and Sapotaceae.
Materials and methodsThe list of species is presented in an appendix that provides the scientific names of the tree species, as defined in Ricker et al. (2013), with original publication, references of recent taxonomic revisions, in some cases synonyms, existence of subspecies or varieties, maximum height in Mexico, and the indication if the species is endemic to Mexico. Only species native to Mexico were included in the appendix.
A taxonomic description of the families treated here can be found in Heywood, Brummitt, Culham, and Seberg (2007). The Apocynaceae, Ebenaceae, and Sapotaceae were revised in the “Flora Mesoamericana” series, which includes in Mexico the states of Tabasco, Chiapas, Campeche, Quintana Roo, and Yucatán (Davidse, Sousa, Knapp, Chiang, & Barrie, 2009). The Sapotaceae were revised by Pennington (1990) already in a “Flora Neotropica” volume, which includes all of Mexico. Furthermore, a checklist of Mexican species was published for the Apocynaceae by Juárez-Jaimes, Alvarado-Cárdenas, and Villaseñor (2007), and for the Fagaceae by Valencia (2004). For the cactus family, the taxonomic framework of Anderson (2001), and Hunt (2006a, 2006b, 2016) is adopted. In addition to compiling the tree species for each family, different taxonomic viewpoints had to be considered and synthesized for a number of species; for example, the species of Stemmadenia were synonymized with Tabernaemontana (Alvarado-Cárdenas & Juárez, 2012; Simões, Endress, & Conti, 2010), and Cascabela was recognized as a genus different from Thevetia (Alvarado-Cárdenas & Ochoterena, 2007; Alvarado-Cárdenas & Soto, 2014:163).
For any species with doubts, the specimens in the National Herbarium of Mexico (MEXU) were checked for growth form, height, and trunk diameter. In some cases, the endemism status in the herbarium was also verified, if it was not clear from the literature. The heights reported in the appendix refer to those maximum heights reached by the species somewhere in Mexico. Exceptional height values for Mexico are given in parenthesis. Endemism refers to the species distribution being restricted to Mexico, as far as currently known.
Most herbarium specimens contain growth form and height in their labels, but generally trunk diameters are not given. This made it sometimes necessary to infer trunk diameters allometrically from height. For example, if a specimen was given with 4m height and 6cm trunk diameter, and another specimen was given with 8m without information on trunk diameter, linear extrapolation indicates that it could have a diameter of around 12cm (8×6/4), though this is only a rough approximation. Furthermore, a tree of 10m or more can generally be assumed to reach a minimum trunk diameter of 10cm, unless contrary information is given. Where doubts remained about the trunk diameter reaching at least 10cm, the species was not included. Four oak species are known only from the original descriptions and without height information: Quercus edwardsiae C. H. Muller, Quercus ghiesbreghtii M. Martens et H. G. Galeotti, Quercus ignasiensis C. H. Muller, and Quercus rekonis W. Trelease. As there also exist small (non-tree) species of Mexican oaks, these 4 species were not included. Taxonomic literature for the recognized species names is cited in the appendix. The authors of species names and original publications were verified in Tropicos (www.tropicos.org). Synonyms are mentioned here only in cases when they reflect diverging opinions among different taxonomic specialists. For mentioned synonyms, species’ author names are not given here, but can be found for example in Tropicos.
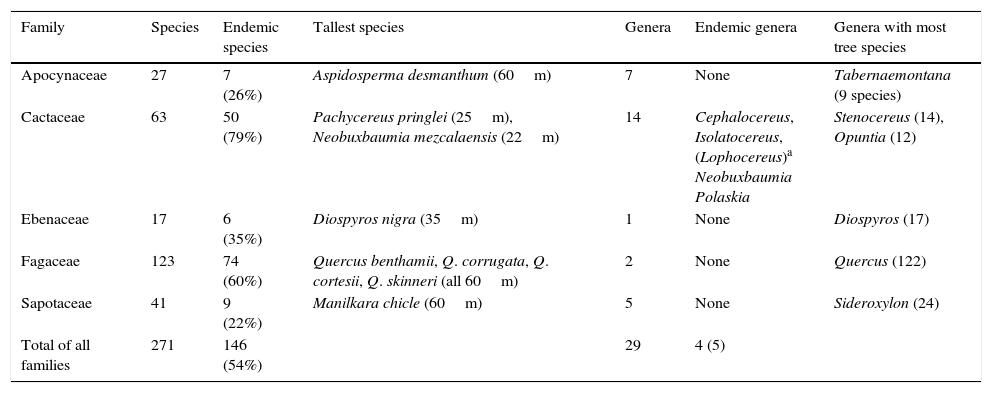
ResultsThe results for 271 species in 29 genera are detailed in the appendix, and summarized in Table 1. Of the 271 species, 45% pertain to the Fagaceae, followed by 23% in the Cactaceae, 15% in the Sapotaceae, 10% in the Apocynaceae, and 6% in the Ebenaceae. The genus with most tree species is Quercus (122 species, Fagaceae), followed by Sideroxylon (24, Sapotaceae), Diospyros (17, Ebenaceae), and Stenocereus (14, Cactaceae).
Summary of the data in Appendix.
| Family | Species | Endemic species | Tallest species | Genera | Endemic genera | Genera with most tree species |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apocynaceae | 27 | 7 (26%) | Aspidosperma desmanthum (60m) | 7 | None | Tabernaemontana (9 species) |
| Cactaceae | 63 | 50 (79%) | Pachycereus pringlei (25m), Neobuxbaumia mezcalaensis (22m) | 14 | Cephalocereus, Isolatocereus, (Lophocereus)a Neobuxbaumia Polaskia | Stenocereus (14), Opuntia (12) |
| Ebenaceae | 17 | 6 (35%) | Diospyros nigra (35m) | 1 | None | Diospyros (17) |
| Fagaceae | 123 | 74 (60%) | Quercus benthamii, Q. corrugata, Q. cortesii, Q. skinneri (all 60m) | 2 | None | Quercus (122) |
| Sapotaceae | 41 | 9 (22%) | Manilkara chicle (60m) | 5 | None | Sideroxylon (24) |
| Total of all families | 271 | 146 (54%) | 29 | 4 (5) |
There are species endemic to Mexico in all 5 families. The endemism rate is 54% for all species combined (146/271), with particularly high rates in the Cactaceae (79%) and the Fagaceae (i.e., Quercus: 60%). Notably, there are 4 endemic genera, all found in the Cactaceae (Cephalocereus, Isolatocereus, Neobuxbaumia, and Polaskia); a fifth cactus genus (Lophocereus) crosses slightly the border with the United States into Arizona. The most species-rich genus of these 5 is Neobuxbaumia with 9 species. With heights up to 22m, it is also among the cactus genera with the tallest individuals, together with Pachycereus (Table 1). The tallest trees (60m) are found in the species Aspidosperma desmanthum (Apocynaceae), Quercus benthamii, Q. corrugata, Q. cortesii, and Q. skinneri (Fagaceae), as well as in Manilkara chicle (Sapotaceae). Quercus corrugata is reported to reach a trunk diameter of up to 4m (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu, Lamant, Timacheff, Jablonski, & Spoelberch, 2006). An arborescent cactus species of impressive size is Pachycereus weberi, with individuals up to 15m high and 2m in stem diameter (Hernández, 2006).
DiscussionThere is a great need from scientists, foresters, naturalists, and conservationists for an updated checklist of tree species for Mexico. While the exact number of all Mexican tree species that reach at least 5m height and 10cm trunk diameter is unknown, the 271 species reported here represent probably close to 10% (see discussion in Ricker & Hernández, 2010). For the 5 plant families treated, the reported diversity corresponds to the total Mexican diversity, trees and non-trees, as follows.
Apocynaceae: the 27 Mexican tree species in the appendix represent only 7% of the reported 385 Mexican species in the Apocynaceae (Juárez-Jaimes et al., 2007). Despite the fact that the family does not include a high proportion of tree species, the members of this family represent some of the typical tree elements in tropical forests (Juárez-Jaimes et al., 2007; Rzedowski & Rzedowski, 1998, 2013). Furthermore, Aspidosperma desmanthum is one of the tallest tree species in Mexico.
Cactaceae: there are 560 Mexican species of Cactaceae (Hernández & Gómez-Hinostrosa, 2011), so the 63 tree-like species reported here represent 11% of the total number of Mexican Cactaceae. Remarkable is the high rate of endemism among tree-like cactus species (79%), which is similar to the endemism rate of 78% of all Mexican members of the family (Hernández & Godínez, 1994).
Ebenaceae: the persimmon family has 19 Diospyros species in Mexico, of which 2 (D. intricata and D. reinae) are not trees according to our definition, so that the number of tree species is 89% of the total number of Mexican Ebenaceae. The genus adapts to a variety of habitats; while D. juruensis is generally a rare species of tropical wet forests from Mexico to Brazil (Wallnöfer, 2012), D. texana extends from Mexico into Texas, being in some areas a highly dominant scrub species (Wallnöfer, 2011).
Fagaceae: while there is only 1 species of Fagus (beech) in Mexico, out of 10 species worldwie (Govaerts & Frodin, 1998:142), we report 122 Quercus species. The 123 tree species represent 76% of the 162 species in the Mexican Fagaceae (Govaerts & Frodin, 1998; Valencia, 2004).
Sapotaceae: the 41 reported tree species represent 95% of the 43 Mexican species; Pennington (1990) reports that in addition only Sideroxylon eriocarpum and S. verruculosum grow as shrubs smaller than 5m in height. The family is typically found in lowland wet forests.
The oak diversity in Mexico is remarkable. Govaerts and Frodin (1998:201) report 531 Quercus species worldwide, of which about 30% are found in Mexico. The distribution of the oak species in Mexico is discussed in Nixon (1993) and Valencia (2004). The genus is found throughout Mexico at elevations from sea level up to 3,650m (Q. laurina in the state of Hidalgo); the states of Oaxaca and Jalisco are particularly diverse in oak species. With 122 species representing trees, Quercus is clearly the most species-rich genus of all Mexican trees, followed by Lonchocarpus (Leguminosae Papilionoideae) with 67 species (Ricker et al., 2013). The only hybrid species is Quercus×dysophylla. In addition, the endemism rate of 60% for the Mexican oak tree species is also notably high.
| Apocynaceae |
| Aspidosperma desmanthum G. Bentham ex J. Müller Argoviensis, Flora Brasiliensis, 6(1): 51. 1860. (Potgieter, 2009: 669). Aspidosperma cruentum is considered a synonym. 30–50 (–60) m. The non-Mexican Aspidosperma spruceanum has been confused with this species. |
| Aspidosperma megalocarpon J. Müller Argoviensis, Linnaea 30(4): 400. 1860. (Diego-Pérez, 2004: 13–15; Gentry, 2001: 119; Parker, 2008: 55; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 448–449; Potgieter, 2009: 669–670). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Marcondes-Ferreira, 1991). 45m. |
| Cameraria latifolia C. Linnaeus, Species plantarum 1: 210. 1753. (Parker, 2008: 55; Zarucchi, 2009b: 671). 12m. |
| Cascabela balsaensis L. O. Alvarado et J. C. Soto, Phytotaxa 177(3): 163–170. 2014. 5m. Endemic. |
| Cascabela gaumeri (W. B. Hemsley) H. Lippold, Feddes Repertorium 91(1–2): 53. 1980. (Gentry, 2001: 120; as Thevetia gaumeri in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 98; Parker, 2008: 63; Zarucchi, 2009d: 701). 6 (–12) m. |
| Cascabela ovata (A. J. Cavanilles) H. Lippold, Feddes Repertorium 91(1–2): 53. 1980. (Gentry, 2001: 120; González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 28–31; as Thevetia ovata in Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 43–45; Diego-Pérez, 2004: 98–102; Parker, 2008: 639; Zarucchi, 2009d: 701). Thevetia plumeriifolia is considered a synonym. 10m. |
| Cascabela pinifolia (P. C. Standley & J. A. Steyermark) L.O. Alvarado et H. Ochoterena, Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 94(2): 320. 2007. (As Thevetia pinifolia in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 103–105). Thevetia peruviana var. pinifolia is considered a synonym. 7m. Endemic. |
| Cascabela thevetia (C. Linneaus) H. Lippold, Feddes Repertorium 91(1–2): 52. 1980. (Gentry, 2001: 120; as Thevetia peruviana in Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 45–47; Diego-Pérez, 2004: 102–103; Parker, 2008: 63; Rzedowski & Calderón-de Rzedowski, 1998: 50–52; Zarucchi, 2009d: 701). 8 (–12) m. |
| Cascabela thevetioides (K. S. Kunth) H. Lippold, Feddes Repertorium 91(1–2): 53. 1980. (González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 30–34; as Thevetia thevetioides in Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 47–49; Diego-Pérez, 2004: 105–107; Rzedowski & Calderón-de Rzedowski, 1998: 52–55). 10m. Endemic. |
| Plumeria obtusa C. Linnaeus, Species plantarum 1: 210. 1753. (Parker, 2008: 57, Zarucchi, 2009c: 687). 10 (–20) m. |
| Plumeria rubra C. Linnaeus, Species plantarum 1: 209. 1753. (Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 28–31; Diego-Pérez, 2004: 56–60; Felger, Johnson, & Wilson, 2001: 63–64; Gentry, 2001: 127; González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 46–50; Parker, 2008: 58; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 450–451; Rzedowski & Calderón-de Rzedowski, 1998: 30–33; Zarucchi, 2009c: 688). 20m. |
| Tabernaemontana alba P. Miller, The Gardeners Dictionary, 8th Edition no. 2. 1768. (Gentry, 2001: 131–132; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 230–236; Morales, 2009b: 698; Parker, 2008: 61; Rzedowski & Calderón-de Rzedowski, 1998: 41–43). 8 (–15) m. |
| Tabernaemontana amygdalifolia N. J. von Jacquin, Enumeratio systematica plantarum quas in insulis caribaeis 14. 1760. (Diego-Pérez, 2004: 82–85; Gentry, 2001: 132; Morales, 2009b: 698; Parker, 2008: 61). 18m. |
| Tabernaemontana arborea J. N. Rose, Botanical Gazette 18(6): 206. 1893. (Gentry, 2001: 132; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 253–258; Morales, 2009b: 698–699; Parker, 2008: 62). 25m. |
| Tabernaemontana donnell–smithii J. N. Rose, Botanical Gazette 18(6): 206–207. 1893. (As Stemmadenia donnell–smithii in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 73–74; Gentry, 2001: 130; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 405–409; Morales & Méndez, 2005: 352, 663, 665; Morales, 2009a: 696; Parker, 2008: 60; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 452–453). 30m. |
| Tabernaemontana eubracteata (R. E. Woodson) A. O. Simões et M. E. Endress, Taxon 59: 787. 2010. (As Stemmadenia eubracteata in Morales & Méndez, 2005: 352–353). 6m. Tabernaemontana glabra (G. Bentham) A.O. Simões et M.E. Endress, Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 10(1): 31. 2016. (As Tabernaemontana odontadeniiflora in Simões et al., 2010: 790; Alvarado-Cárdenas & Juárez-Jaimes, 2012: 335-336; González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 55–59; as Stemmadenia obovata in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 76–80; Gentry, 2001: 131; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 423–428; Morales & Méndez, 2005: 356–357, 367; Parker, 2008: 60; as Stemmadenia pubescens in Morales, 2009a: 697). 5 (–10) m. |
| Tabernaemontana hannae (M. Méndez et J. F. Morales) A. O. Simões et M. E. Endress Taxon 59: 787. 2010. (As Stemmadenia hannae in Morales & Méndez, 2005: 354). 6m. |
| Tabernaemontana litoralis K. S. Kunth, Nova genera et species plantarum (editio quarta) 3: 228. 1818[1819]. (As Stemmadenia litoralis in Gentry, 2001: 130; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 415–418; Morales, 2009a: 697; Morales & Méndez, 2005: 355–356, 665–366; Parker, 2008: 60; as Stemmadenia macrophylla in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 74–76). Stemmadenia galeottiana is also considered a synonym. 25m. |
| Tabernaemontana tomentosa (J. M. Greenman) A.O. Simões et M.E. Endress, Taxon 59(3): 788. 2010. (González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 59–61; as Stemmadenia palmeri in Felger et al., 2001: 64–65; Parker, 2008: 61; as Stemmadenia tomentosa in Diego-Pérez, 2004: 80–82; Leeuwenberg, 1994: 432–435; Morales & Méndez, 2005: 360). 12m. Endemic. |
| Tonduzia longifolia (A. P. de Candolle) F. Markgraf, Repertorium specierum novarum regni vegetabilis 20(561/576): 112. 1924. (González-Rocha & Cerros-Tlatilpa, 2015: 63–64; as Alstonia longifolia in Parker, 2008: 54; Zarucchi, 2009a: 667; as Alstonia pittieri in Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 5; Gentry, 2001: 118). Alstonia macrantha is also considered a synonym. 20m. |
| Vallesia antillana R. E. Woodson, Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 24(1): 13. 1937. (Zarucchi, 2009e: 702). 8m. |
| Vallesia aurantiaca (M. Martens et H. G. Galeotti) J. F. Morales, Novon 8(3): 263. 1998. (Diego-Pérez, 2004: 112–113; Parker, 2008: 64; Zarucchi, 2009e: 702). 10 (–20) m. |
| Vallesia glabra (A. J. Cavanilles) J. H. Link, Enumeratio plantarum horti regii berolinensis Altera 1: 207. 1821. (Alvarado-Cárdenas, 2004: 49–52; Diego-Pérez, 2004: 113–114; Felger et al., 2001: 66; Rzedowski & Calderón-de Rzedowski, 1998: 55–58). 8m. |
| Vallesia laciniata Brandegee, Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences, Series 2, 2: 182. 1889. (Felger et al., 2001: 66). Vallesia brandegii and V. conzattii are considered synonyms. 5m. Endemic. |
| Vallesia sinaloensis E. Meyen ex J.F. Morales, Novon 8(3): 263. 1998. 7m. Endemic. |
| Vallesia spectabilis E. Meyen ex J.F. Morales, Novon 8(3): 263. 1998. 7m. Endemic. |
| Cactaceae |
| Carnegiea gigantea (G. Engelmann) N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, Journal of the New York Botanical Garden 9(107): 188. 1908. (Anderson, 2001:138; Gibson, 2003b: 185–186; Hunt, 2006a: 36–37; Hunt, 2006b: 34–35). 16m. |
| Cephalocereus apicicephalium E. Y. Dawson, Allan Hancock Foundation Publications: Occasional Papers 1: 10–12. 1948. (As Cephalocereus totolapensis in Anderson, 2001: 140–141). 8m. Endemic. |
| Cephalocereus columna-trajani (W. F. Karwinsky ex L. K. G. Pfeiffer) K. M. Schumann, Gesamtbeschreibung der Kakteen 198. 1897. (Anderson, 2001: 139–140; Arias, Gama, Guzmán, & Vázquez, 2012: 13–17; Hunt, 2006a: 37; Hunt, 2006b: 40). 10m. Endemic. |
| Cephalocereus senilis (A. H. Haworth) L. K. G. Pfeiffer, Allgemeine Gartenzeitung 6: 142. 1838. (Anderson, 2001: 140; Hunt, 2006a: 37; Hunt, 2006b: 40). 15m. Endemic. |
| Cylindropuntia cholla (F. A. C. Weber) F. M. Knuth, Kaktus–ABC 125. 1935. (Anderson, 2001: 207; Hunt, 2006a: 71). 5m. Endemic. |
| Escontria chiotilla (F. A. C. Weber) J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 10: 126. 1906. (Anderson, 2001: 314–315; Arias et al., 2012: 40–43; Hunt, 2006a: 115; Hunt, 2006b: 41). 7m. Endemic. |
| Isolatocereus dumortieri (M. J. Scheidweiler) C. Backeberg, Cactaceae, Jahrbuch der Deutschen Kakteen–Gesellschaft 2: 47. 1941. (Anderson, 2001: 382; as Stenocereus dumortieri in Arias et al., 2012: 176–178; Hunt, 2006a: 265–266; Hunt, 2006b: 44). 15m. Endemic. |
| Lophocereus marginatus (A. P. de Candolle) S. Arias et T. Terrazas, Systematic Botany 34(1): 82. 2009. (Arias et al., 2012: 68–71; as Pachycereus marginatus in Anderson, 2001: 534; Gibson, 2003a: 184; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 28–29). 7m. Widely cultivated in Mexico. |
| Lophocereus schottii (G. Engelmann) N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 12(10): 427. 1909. (As Pachycereus schottii in Anderson, 2001: 536–537; Felger et al., 2001: 106–107; Hunt, 2006a: 217; Hunt, 2006b: 32–33). 7m. Outside of Mexico known from a few collections in Arizona (USA). |
| Myrtillocactus geometrizans (C. F. Martius) M. Console, Bollettino delle Orto Botanico e Giardino Coloniale di Palermo 1: 10. 1897. (Anderson, 2001: 473–474; Arias et al., 2012: 126–128, 130; Hunt, 2006a: 192; Hunt, 2006b: 42). 7m. Endemic. |
| Myrtillocactus schenckii (J. A. Purpus) N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 12(10): 427. 1909. (Anderson, 2001: 475; Arias et al., 2012: 128–131; Bravo, 1978: 705–706; Hunt, 2006a: 192; Hunt, 2006b: 42). 5m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia euphorbioides (A. H. Haworth) F. Buxbaum, Las Cactáceas de México 1: 658. 1978. (Anderson, 2001: 476; Hunt, 2006a: 192–193; Hunt, 2006b: 35). 5m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia macrocephala (F. A. C. Weber) E. Y. Dawson, Cactus and Succulent Journal 24: 173. 1952. (Anderson, 2001: 477; Arias et al., 2012: 132–134, 138; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 35). 15m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia mezcalaensis (H. Bravo) C. Backeberg, Beitrage zur Sukkulentenkunde und –pflege 3. 1941. (Anderson, 2001: 477; Arias et al., 2012: 134–136, 138; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 37). 16 (–22) m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia multiareolata (E. Y. Dawson) H. Bravo, L. Scheinvar et H. Sánchez, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 17: 120. 1972. (Anderson, 2001: 477–478). Neobuxbaumia mezcalaensis is considered a synonym (Hunt, 2006a). 12m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia polylopha (A. P. de Candolle) C. Backeberg, Blätter für Kakteenforschung 6. 1938. (Anderson, 2001:478; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 36). 15m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia sanchez–mejoradae A. Lau, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 39(1): 3. 1994. (Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 36; as Neobuxbaumia laui in Anderson, 2001: 476–477). 12m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia scoparia (H. Poselger) C. Backeberg, Beiträge zur Sukkulentenkunde und–pflege 3. 1941. (Anderson, 2001: 478–479; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 37). 12m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia squamulosa L. Scheinvar et H. Sánchez, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 35(1): 13. 1990. (Anderson, 2001: 479; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 38). 10m. Endemic. |
| Neobuxbaumia tetetzo (F. A. C. Weber) C. Backeberg, Blätter für Kakteenforschung 6. 1938. (Anderson, 2001: 479; Arias et al., 2012: 136–140; Hunt, 2006a: 193; Hunt, 2006b: 38). 15m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia auberi L. K. Pfeiffer, Allgemeine Gartenzeitung 8(36): 282. 1840. (Anderson, 2001: 487; Arias et al., 2012: 194–197; Hernández, Gómez-Hinostrosa, Bárcenas, Puente, & Reyes-Agüero, 2014: 195). 8m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia excelsa H. Sánchez, Cactus and Succulent Journal 17(3): 67. 1972. (Anderson, 2001: 498; Bravo, 1978: 274–276; Hernández et al., 2014: 197). 12m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia ficus–indica (C. Linnaeus) P. Miller, The Gardeners Dictionary (8th edition). 1768. (Anderson, 2001: 498–499; Hernández et al., 2014: 197; Hunt, 2006a: 202; Hunt, 2006b: 508; Parker, 2008: 130; Pinkava, 2003: 142). 7m. Cultivated or even naturalized worldwide for its “tuna” or “prickly pear” fruits, as well as the “nopales” or “cactus pads”. |
| Opuntia hyptiacantha F. A. C. Weber, Dictionnaire d’Horticulture 894. 1898. (Anderson, 2001: 502; Arias et al., 2012: 202–204; Hernández et al., 2014: 198; Hunt, 2006a: 204; Hunt, 2006b: 509). 5m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia inaperta (A. Schott ex D. Griffiths) D.R. Hunt, Cactaceae Consensus Initiatives 4: 5. 1997. (Anderson, 2001: 502; as Nopalea inaperta in Hernández et al., 2014: 198; Hunt, 2006a: 195; Hunt, 2006b: 487). 7m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia karwinskiana J. F. Salm-Dyck, Cacteae in Horto Dyckensi Cultae 1849: 239–240. 1850. (Anderson, 2001: 503; Hernández et al., 2014: 198). 7m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia leucotricha A. P. de Candolle, Mémoires du Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle 17: 119. 1828. (Anderson, 2001: 505; Bravo, 1978: 312–314; Hernández et al., 2014: 198; Hunt, 2006a: 205; Hunt, 2006b: 510). 5m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia lutea (J. N. Rose) D. R. Hunt, Cactaceae Consensus Initiatives 4: 6. 1997. (Anderson, 2001: 505; Solomon, 2001: 515; as Nopalea lutea in Bravo, 1978: 347; Hernández et al., 2014: 198). 5m. |
| Opuntia megacantha J. F. Salm-Dyck, Hortus Dyckensis ou Catalogue des Plantes 363. 1834. (Anderson, 2001: 507; Bravo, 1978: 328–330; Hernández et al., 2014: 198). 5m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia pilifera F. A. C. Weber, Dictionnaire d’Horticulture 894. 1898. (Anderson, 2001: 511; Arias et al., 2012: 209–212; Bravo, 1978: 315–317; Hernández et al., 2014: 199; Hunt, 2006a: 208; Hunt, 2006b: 511). 5m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia streptacantha C. Lemaire, Cactearum Genera Nova Speciesque Novae 62. 1839. (Anderson, 2001: 520; Bravo, 1978: 327–328; Hernández et al., 2014: 200; Hunt, 2006a: 211; Hunt, 2006b: 512). 5m. Endemic. |
| Opuntia tomentosa J. F. Salm, Observationes Botanicae in Horto Dyckensi 3: 8. 1822. (Anderson, 2001: 523; Arias et al., 2012: 219–220, 222–223; Hernández et al., 2014: 200; Hunt, 2006a: 212). 6m. |
| Pachycereus fulviceps (C. Lemaire) D. Hunt, Bradleya 9: 89. 1991. (Anderson, 2001: 532–533; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 33; as Pseudomitrocereus fulviceps in Arias et al., 2012: 163–167). 12 (–20) m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus gaumeri N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, The Cactaceae: Descriptions and Illustrations of Plants of the Cactus Family 2: 71. 1920. (Anderson, 2001: 533; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 27). 8m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus grandis J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 12(10): 421. 1909. (Anderson, 2001: 533; Arias et al., 2012: 144–145, 147; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 29). 15m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus hollianus (F. A. C. Weber) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 19. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 534; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 28; as Lemaireocereus hollianus in Arias et al., 2012: 64–67, 69). 5m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus militaris (N. Audot) D. Hunt, Bradleya 5: 93. 1987. (Anderson, 2001: 534–535; Hunt, 2006a: 216; Hunt, 2006b: 32). 6m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus pecten–aboriginum (G. Engelmann) N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 12(10): 422. 1909. (Anderson, 2001: 535–536; Felger et al., 2001: 114; Hunt, 2006a: 217; Hunt, 2006b: 29–30). 15m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus pringlei (S. Watson) N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 12(10): 422. 1909. (Anderson, 2001: 536; Felger et al., 2001: 114–120; Hunt, 2006a: 217; Hunt, 2006b: 30–31). 25m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus tepamo S. Gama et S. Arias, Novon 8(4): 359. 1998. (Hunt, 2006a: 217; Hunt, 2006b: 31). 10m. Endemic. |
| Pachycereus weberi (J. M. Coulter) C. Backeberg, Die Cactaceae 4: 2154. 1960. (Anderson, 2001: 537–538; Arias et al., 2012: 145–149; Hunt, 2006a: 217; Hunt, 2006b: 31). 15m (and up to 2m in diameter). Endemic. |
| Pereskia lychnidiflora A. P. de Candolle, Mémoires du Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle 17: 75. 1828. (Anderson, 2001: 569–570; Hunt, 2006a: 230; Hunt, 2006b: 452; Parker, 2008: 131; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 402–403; Solomon, 2001: 517). 15m. |
| Pilosocereus alensis (F. A. C. Weber) R. S. Byles et G. D. Rowley, Cactus and Succulent Journal of Great Britain 19: 66. 1957. (Anderson, 2001: 575; Felger et al., 2001: 120; Hunt, 2006a: 234; Hunt, 2006b: 144). 6m. Endemic. |
| Pilosocereus chrysacanthus (F. A. C. Weber) R. S. Byles et G. D. Rowley, Cactus and Succulent Journal of Great Britain 19(3): 66. 1957. (Anderson, 2001: 578; Arias et al., 2012: 154–156, 161; Hunt, 2006a: 235; Hunt, 2006b: 144). 6m. Endemic. |
| Pilosocereus leucocephalus (H. Poselger) R. S. Byles et G. D. Rowley, Cactus and Succulent Journal of Great Britain 19(3): 67. 1957. (Anderson, 2001: 582; Hunt, 2006a: 238; Hunt, 2006b: 146). 6m. |
| Pilosocereus quadricentralis E. Y. Dawson, Die Cactaceae 4: 2437. 1960. (Anderson, 2001: 586; Hunt, 2006a: 239; Hunt, 2006b: 148). 5m. Endemic. |
| Pilosocereus royenii (C. Linnaeus) R. S. Byles et G. D. Rowley, Cactus and Succulent Journal of Great Britain 19(3): 67. 1957. (Anderson, 2001: 586–587; Hunt, 2006a: 239–240; Hunt, 2006b: 148). 8m. |
| Polaskia chende (R. R. Gosselin) A. Gibson et K. E. Horak, Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 65(4): 1006. 1978[1979]. (Anderson, 2001: 588–589; Arias et al., 2012: 157–161; Hunt, 2006a: 241; Hunt, 2006b: 43). 7m. Endemic. |
| Polaskia chichipe (R. R. Gosselin) C. Backeberg, Blätter für Sukkulentenkunde 1: 4. 1949. (Anderson, 2001: 589; Arias et al., 2012: 160–162; Hunt, 2006a: 241; Hunt, 2006b: 43). 5m (and up to 1m in diameter). Endemic. |
| Stenocereus chacalapensis (H. Bravo et T. B. MacDougall) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 100. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 642–643; Hunt, 2006a: 265; Hunt, 2006b: 46). 15m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus chrysocarpus H. Sánchez, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 17(4): 95. 1972. (Anderson, 2001: 643; Hunt, 2006a: 265; Hunt, 2006b: 46). 9m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus eichlamii (N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose) F. Buxbaum, Las Cactáceas de México 1: 585. 1978. (Anderson, 2001: 643–644; Parker, 2008: 132; Solomon, 2001: 519). 6m. |
| Stenocereus fricii H. Sánchez, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 18(4): 89. 1973. (Anderson, 2001: 644–645; Hunt, 2006a: 266; Hunt, 2006b: 47). 7m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus griseus (A. H. Haworth) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 100. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 645; Hunt, 2006a: 266; Hunt, 2006b: 48). 9m. Unclear if native in Mexico or naturalized. |
| Stenocereus laevigatus (J. F. Salm) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 100. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 646). 7m. Endemic |
| Stenocereus martinezii (J. González) H. Bravo, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 17(4): 119. 1972. (Anderson, 2001: 646; Hunt, 2006a: 266; Hunt, 2006b: 50). 5m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus montanus (N. L. Britton et J. N. Rose) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 101. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 646–647; Felger et al., 2001: 121–123; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 50). 7 (–12) m. |
| Stenocereus pruinosus (C. F. Otto ex L. K. Pfeiffer) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 101. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 647; Arias et al., 2012: 178–181, 185; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 49). 5m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus queretaroensis (F. A. C. Weber) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 101. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 647; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 51). 6m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus quevedonis (J. González) H. Bravo, Cactáceas y Suculentas Mexicanas 17(4): 119. 1972. (Anderson, 2001: 647; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 51). 5m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus thurberi (G. Engelmann) F. Buxbaum, Botanische Studien 12: 101. 1961. (Anderson, 2001: 648; Felger et al., 2001: 123–125; Gibson, 2003c: 187–188; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 50). Two subspecies, both in Mexico (Hunt, 2006a). 10m. |
| Stenocereus treleasei (F. K. Vaupel) C. Backeberg, Cactus and Succulent Journal 23: 120. 1951. (Anderson, 2001: 649; Arias et al., 2012: 184–186; Hunt, 2006a: 267; Hunt, 2006b: 44). 7m. Endemic. |
| Stenocereus zopilotensis H. Arreola et T. Terrazas, Brittonia 56(1): 96. 2004. 5m. Endemic. |
| Ebenaceae |
| Diospyros alisu B. Wallnöfer, Annalen des Naturhistorischen Museums in Wien, Serie B 106: 237. 2005. 20m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros anisandra S. F. Blake, Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 34: 44. 1921. (Parker, 2008: 241; Wallnöfer, 2010: 102–113; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 612). 12m. |
| Diospyros bumelioides P. C. Standley, Tropical Woods 18: 31. 1929. (Parker, 2008: 241; Wallnöfer, 2010: 113–120; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 613). 12m. |
| Diospyros californica (T. S. Brandegee) I. M. Johnston, Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences (Series 4) 12: 1124. 1924. (Wallnöfer, 2016: 80–85). Two varieties, both in Mexico (distinguished already by P. C. Standley). 9m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros conzattii P. C. Standley, Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 12(17): 399. 1922. (González, 2010: 217; Wallnöfer, 2007: 233–245; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 613–614; as Diospyros riojae in Carranza-González, 2000: 5–7; Pacheco, 1981: 14–16). According to Wallnöfer (2007), Diospyros gomeziorum, D. pergamentacea, D. riojae, and D. tuxtlensis are considered synonyms. 20 (–30) m. |
| Diospyros johnstoniana P. C. Standley et J. A. Steyermark, Publications of the Field Museum of Natural History, Botanical Series 22(3): 165. 1940. (Parker, 2008: 241; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 615; Wallnöfer, 2009: 181–187; as Diospyros xolocotzii in Carranza-González, 2000: 7–9). According to Wallnöfer (2009), Diospyros xolocotzii is considered a synonym. 8m. |
| Diospyros juruensis A. C. Smith, Brittonia 2(2): 163. 1936. (Wallnöfer, 2012: 224–240; as Diospyros campechiana in Pacheco, 1981: 4–7; Parker, 2008: 241; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009). Five subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Wallnöfer, 2012). 20m. |
| Diospyros nigra (J. F. Gmelin) G. S. Perrottet, Catalogue raisoné des Plantes Introduites dans les Colonies françaises de Bourbon et de Cayenne 25: 1824. (As Diospyros digyna in Pacheco, 1981: 7–11; Parker, 2008: 241; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 446–447; Pool, 2001a: 815–816; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 614). According to Turner (2013), the widely used name Diospyros digyna is considered a synonym. The species has also been confused with Diospyros ebenaster, a synonym of D. ebenum from Sri Lanka, known for its fine jet–black ebony wood (Wallnöfer, 2014). 35m. The species has been introduced to countries outside its Mexican and Central American range for its edible “black sapote” fruits. |
| Diospyros oaxacana P. C. Standley, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 20(6): 194. 1919. (Pacheco, 1981: 11–14; Wallnöfer, 2009: 187–192). Diospyros torresii is considered a synonym (Wallnöfer, 2009). 10m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros palmeri A. Eastwood, Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences 44(21): 604. 1909. (Carranza-González, 2000: 3–4; Wallnöfer, 2010: 120–127). 10m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros rekoi P. C. Standley, Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 17(20): 527. 1927. (Wallnöfer, 2009: 193–198). 20m. This name does not replace Maba rekoi, which belongs to Diospyros salicifolia in a wide sense. |
| Diospyros salicifolia F. A. von Humboldt et A. J. Bonpland ex C. L. von Willdenow, Species Plantarum. Editio quarta 4(2): 1112. 1806. (Parker, 2008: 241; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 615–616; as Diospyros verae[-]crucis in Pacheco, 1981: 16–21; as Diospyros acapulcensis in González, 2010: 216–217). Diospyros aequoris, D. albens, D. nicaraguensis, D. spectabilis, and D. yucatanensis are also considered synonyms. The species is very variable, and is treated here in a wide sense. Provance, García-Ruiz, and Sanders (2008) divided Diospyros salicifolia sensu lato into 4 different species and many subspecies. 25m. |
| Diospyros sonorae P. C. Standley, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 18(3): 120. 1916. (Felger et al., 2001: 142–143; Wallnöfer, 2016: 96–103). Diospyros sinaloensis is a synonym. 20m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros sphaerantha P. C. Standley, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 18(3): 111. 1916. (Wallnöfer, 2016: 104–110). Diospyros rosei is a synonym. 9m. Endemic. |
| Diospyros tetrasperma O. Swartz, Nova Genera et Species Plantarum seu Prodromus 62: 1788. (Parker, 2008: 242; Wallnöfer, 2011: 182–197; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 616). 17m. |
| Diospyros texana G. H. Scheele, Linnaea 22(2):145. 1849. (Eckenwalder, 2009: 249; Wallnöfer, 2010: 128–131; Wallnöfer, 2011: 197–213). 10 (–15) m. |
| Diospyros yatesiana P. C. Standley ex C. L. Lundell, Publications of the Carnegie Institution of Washington 436(12): 281, 317. 1934. (Parker, 2008: 242; Wallnöfer, 2009: 198–208; Whitefoord & Knapp, 2009: 616). 22m. |
| Fagaceae |
| Fagus grandifolia J. F. Ehrhart, Beiträge zur Naturkunde 3: 22–23. 1788. Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Govaerts & Frodin, 1998: 144). 30m. |
| Quercus acatenangensis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 163. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 370–371; Parker, 2008: 297–298). 25m. |
| Quercus acherdophylla W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 183. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 372–373; Valencia, 2005: 88; Vázquez, 2000: 9–10). 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus acutifolia L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 267. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 27–30; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 374–377; McVaugh, 1974: 15–17; Parker, 2008: 298; Romero-Rangel, 2006: 6–11; Valencia, Gómez-Cárdenas, & Becerra-Luna, 2002: 39–42; Valencia, 2005: 89; Valencia, Flores-Franco, & Jiménez-Ramírez, 2015; Vázquez, 2000: 10–11; as Quercus conspersa in González-Villarreal, 1986: 57–60; Romero-Rangel, Rojas-Zenteno, & Rubio-Licona, 2014: 27–29; Romero-Rangel, Rojas-Zenteno, & Rubio-Licona, 2015: 158–159). Quercus vexans is also considered a synonym. 35m. |
| Quercus affinis M. J. Scheidweiler, L‘Horticulterur belge 4: 321. 1837. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 378–381; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 9–12; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 139–140; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 46–52; Valencia, 2005: 89–90). 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus agrifolia L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 271–272. 1801. (Jensen, 1997: 452; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 172–178). 30m. |
| Quercus albocincta W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20:193. 1924. (Felger et al., 2001: 214–215; Romero-Rangel, 2006: 11–14; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 142–143). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus ariifolia W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 74. 1924. (Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 53–58; as Quercus ariaefolia in Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 12–15, and Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 143–144). 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus aristata W. J. Hooker et G. A. Arnott, The Botany of Captain Beechey's Voyage 444. 1841. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 31–34; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 382–383; McVaugh, 1974: 17–19; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 144–145). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus arizonica C. S. Sargent, Garden & Forest 8: 89. 1895. (Felger et al., 2001: 215–217; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 180–183; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 499; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 146–147; Villarreal, Encina, & Carranza, 2008: 1242–1244). 18m. |
| Quercus benthamii A. P. de Candolle, Prodromus systematis naturalis regni vegetabilis 16(2): 29. 1864. (Breedlove, 2001: 1078; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 384–385; Morales, 2010: 778; Parker, 2008: 298; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 147–148; Valencia, 2005: 90–91). 30 (–60) m. |
| Quercus brandegeei E. A. Goldman, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 16: 321. 1916. (As Quercus brandegei in Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 148–150). 10m. Endemic. |
| Quercus canbyi W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 188. 1924. (Romero-Rangel, 2006: 16–20; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 151–152; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 59–65; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1243–1244). Quercus cupreata and Q. graciliramis are considered synonyms. 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus candicans L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 277. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 35–39; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 390–392; McVaugh, 1974: 19–21; Parker, 2008: 299; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 15–18; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 153–154; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 66–71; Valencia et al., 2002: 43–46; Valencia, 2005: 91). 30m. |
| Quercus carmenensis C. H. Muller, American Midland Naturalist 18: 847. 1937. (Nixon & Muller, 1997: 488–489; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1243–1245). 12m. |
| Quercus castanea L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 276. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 40–47; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 393–397; McVaugh, 1974: 21–23; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 19–27; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 154–155; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 72–77; Valencia et al., 2002: 47–50; Vázquez, 2000: 11–13; as Quercus tristis in Parker, 2008: 306). Quercus tepoxuchilensis is also considered a synonym. 18m. |
| Quercus chartacea W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 61. 1924. 8m. Endemic. |
| Quercus chihuahuensis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 85. 1924. (Felger et al., 2001: 217; González-Villarreal, 1986: 48–51; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 400–401; McVaugh, 1974: 23–25; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 501–502; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 157–158; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 78–83). 10 (–20) m. |
| Quercus chrysolepis F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 173. 1854. (Felger et al., 2001: 217; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 192–197; Manos, 1997: 469). 13m (25m in the U.S). |
| Quercus coahuilensis K. C. Nixon et C. H. Muller, Brittonia 45: 150. 1993. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 402–403; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1244–1246). 8m. Endemic. |
| Quercus coffeicolor W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 137. 1924. (As Quercus praineana in González-Villarreal, 1986: 168–171; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 408–409; McVaugh, 1974: 71–73: as Q. prainiana in Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 243–244). 12m. Endemic. |
| Quercus convallata W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 88. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 61–64; McVaugh, 1974: 62–63; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 159–160). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus conzattii W. Trelease, Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 60: 33. 1921. (Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 161–162; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 211–213). 10 (–17) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus cornelius–mulleri K. C. Nixon et K. P. Steele, Madroño 28(4): 210. 1981. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 198–199; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 492). 3 (–7) m. |
| Quercus corrugata W. J. Hooker, Icones plantarum 5: 403. 1842. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 418–420; Morales, 2010: 778–779; Valencia et al., 2002: 55–56). 35 (–60) m. |
| Quercus cortesii F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 175. 1854. (Breedlove, 2001: 1079; Morales, 2010: 779; Parker, 2008: 300). Quercus brenesii is considered a synonym. 25 (–60) m. |
| Quercus crassifolia A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 49. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 65–69; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 424–427; McVaugh, 1974: 28–30; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 29–32; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 165–166; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 84–90; Valencia et al., 2002: 57–60; Valencia, 2005: 92; Vázquez, 2000: 13–14; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 213–215; as Quercus brachystachys in Parker, 2008: 298–299). Quercus chicamolensis, Q. felipensis, and Q. miguelitensis are also considered synonyms. 15 (–25) m. |
| Quercus crassipes A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 37. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 70–74; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 430–433; McVaugh, 1974: 30–32; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 32–37; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 166–168; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 91–96; Vázquez, 2000: 14–15). Quercus cuajimalpana and Q. obovalifolia are considered synonyms. 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus crispifolia W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 147, pl. 286. 1924. (Parker, 2008: 300; Valencia et al., 2002: 61–62; Valencia, 2005: 92–93). 25m. |
| Quercus crispipilis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 184. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 434–435; Parker, 2008: 300; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 168–169; Valencia, 2005: 93). Quercus skutchii is considered a synonym. 23m. |
| Quercus cualensis L. M. González, Brittonia 55(1): 49. 2003. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 436–437). 10 (–15) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus delgadoana S. Valencia-A., K. C. Nixon et L. M. Kelly, Novon 21(2): 274. 2011. Quercus delgadoana has been separated from Quercus eugeniifolia, so that the latter does not exist in Mexico anymore. 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus deserticola W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 79. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 78–81; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 446–449; McVaugh, 1974: 33–35; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 37–40; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 170–171; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 97–102; Vázquez, 2000: 15–17). 10m. Endemic. |
| Quercus devia E. A. Goldman, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 16: 322. 1916. 18m. Endemic. |
| Quercus diversifolia L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 270. 1801. 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus duratifolia C. H. Muller, Miscellaneous Publications of the Bureau of Plant Industry (U. S. Department of Agriculture) 477: 25. 1942. 10m. Endemic. |
| Quercus durifolia K. O. von Seemen, Botanische Jahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeographie 29(1): 95. 1900. (Felger et al., 2001: 218; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 450–453). Quercus flocculenta is considered a synonym. 15 (–25) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus×dysophylla G. Bentham, Plantas hartwegianas imprimis mexicanas 55: 1840. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 454–455; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 41–44; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 103–108; Vázquez, 2000: 17–18; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 215–216). There is evidence that this species is a hybrid between Quercus crassifolia and Q. crassipes (Tovar-Sánchez & Oyama, 2004). Quercus esperanzae and Q. hahnii are considered synonyms. 10 (–20) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus eduardii W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 121. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 82–86; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 456–459; McVaugh, 1974: 35–37; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 44–48; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 176–177; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 109–116; Valencia, 2005: 94). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus elliptica L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3 (9): 278. 1801. (Breedlove, 2001: 1079–1080; González-Villarreal, 1986: 87–91; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 460–463; McVaugh, 1974: 37–38; Parker, 2008: 301; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 178–179; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 117–122; Valencia et al., 2002: 63–66; Valencia, 2005: 94–95). Quercus hondurensis, Q. nectandrifolia, and Q. pubinervis are considered synonyms. 25m. |
| Quercus emoryi J. Torrey, Notes of a Military Reconnoissance 151: 9. 1848. (Felger et al., 2001: 218–220; González-Villarreal, 1986: 217; Jensen, 1997: 453; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 210–213; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 179–180; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 123–128; Valencia, 2005: 95; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1246, 1248). 20m. |
| Quercus engelmannii E. L. Greene, Illustrations of West American Oaks 1: 33. 1889. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 214–216; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 500). 15m. |
| Quercus fulva F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 183. 1854. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 96–98; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 472–473; McVaugh, 1974: 41–43; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 185–187; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 216–218; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1246–1248). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus furfuracea F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 189. 1854. (Romero-Rangel, 2006: 27–29; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 187–188; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 129–134). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus fusiformis J. K. Small, Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 28(6): 357. 1901. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 217–219; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 505–506; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 188–190; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1247–1249). 25m. |
| Quercus gambelii T. Nuttall, Journal of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 1(2). 179. 1848. (Felger et al., 2001: 220–221; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 220–222; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 486–487; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 190–191; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1248–1250). 20m. |
| Quercus gentryi C. H. Muller, American Midland Naturalist 27(2): 474. 1942. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 99–103; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 477–479; McVaugh, 1974: 43–45; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 51–53; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 191–192; Valencia, 2005: 96). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus germana D. F. von Schlechtendal et L. K. von Chamisso, Linnaea 5: 78. 1830. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 480–482; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 53–56; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 193–194; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 140–145; as Quercus excelsa in McVaugh, 1974: 39–40). Quercus galeottii and Q. substenocarpa are also considered synonyms. 45m. Endemic. |
| Quercus glabrescens G. Bentham, Plantas hartwegianas imprimis mexicanas 56: 348. 1840. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 483–487; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 57–58; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 194–195; Vázquez, 2000: 19–20). 40m. Endemic. |
| Quercus glaucescens A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 29. 1809. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 104–107; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 488–489; McVaugh, 1974: 45–47; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 58–61; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 195–196; Valencia et al., 2002: 67–70). Quercus nigrirhachis and Q. synthetic are considered synonyms. 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus glaucoides M. Martens et H. G. Galeotti, Bulletin de l’Academie Royale des Sciences et Belles–lettres de Bruxelles 10(1): 209. 1843. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 490–493; Nixon & Muller, 1992: 65–68; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 61–64; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 196–197; Valencia et al., 2002: 71–75; Vázquez, 2000: 20–22). Quercus cancellata and Q. mixtecana are considered synonyms. 15m. Quercus laceyi was separated from this species by Nixon and Muller (1992), making Q. glaucoides endemic. |
| Quercus grahamii G. Bentham, Plantas hartwegianas imprimis mexicanas 57: 1840. (Valencia et al., 2015). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus gravesii G. B. Sudworth, Check List Forest Trees U.S. 86. 1927. (Jensen, 1997: 455; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 233–236; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1250–1251, 1253). 13m. |
| Quercus greggii (A. P. de Candolle) W. Trelease, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 23(2):185. 1922. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 494–496; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 64–67; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 198–199; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 146–151; Vázquez, 2000: 22–23; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1251–1253). 12m. Endemic. |
| Quercus grisea F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 171. 1854. (Felger et al., 2001: 221; González-Villarreal, 1986: 112–115; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 237–239; McVaugh, 1974: 48–50; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 501; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 67–70; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 199–200; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 152–159; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1252–1254). 12 (–20) m. |
| Quercus hintonii E. F. Warburg, Bulletin of Miscellaneous Information Kew 91. 1939. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 500–502; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 200–202; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 218–220). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus hirtifolia M. L. Vázquez, Brittonia 56(2): 137. 2004. (Valencia, 2005: 96). 12m. Endemic. |
| Quercus hypoleucoides A. Camus, Bulletin du Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle (série 2) 4: 124. 1932. (Felger et al., 2001: 221; Jensen, 1997: 454; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 244–248; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 202–203; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1255, 1257). 10 (–30) m. |
| Quercus hypoxantha W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 170. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 508–510; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 203–205; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 160–165; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1255–1257). 4 (–7) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus iltisii L. M. González, Brittonia 55(1): 49–60. 2003. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 511–515). 15 (–25) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus insignis M. Martens et H. G. Galeotti, Bulletin de l’Academie Royale des Sciences et Belles–lettres de Bruxelles 10(1): 219. 1843. (Breedlove, 2001: 1080; Morales, 2010: 780; Valencia et al., 2002: 75–78; as Quercus oocarpa in McVaugh, 1974: 63–64). 25 (–50) m. |
| Quercus jonesii W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 136. 1924. (As Quercus coccolobifolia in Felger et al., 2001: 217; Gónzález, 1986: 52–56; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 404–407; McVaugh, 1974: 25–26; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 71–74; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 209–210; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 166–171). Quercus aerea is also considered a synonym. 18m. Endemic. |
| Quercus knoblochii C. H. Muller, American Midland Naturalist 27: 475. 1942. (Felger et al., 2001: 221). Felger et al. (2001) mention that this species is a hybrid between Quercus jonesii (they use the name Q. coccolobifolia) and Q. viminea, but we could not find a reference with details about this issue. 8m. Endemic. |
| Quercus laceyi J. K. Small, Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 28(6): 358. 1901. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 256–259; Nixon & Muller, 1992: 61–65; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 483; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 210–211; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1259–1261). 10m. |
| Quercus laeta F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 179. 1854. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 119–124; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 524–527; McVaugh, 1974: 50–53; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 74–79; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 211–213; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 172–181; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1261). Quercus centralis, Q. clivicola, Q. prinopsis, and Q. transmontana are considered synonyms. 10 (–15) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus lancifolia D. F. von Schlechtendal et L. K. von Chamisso, Linnaea 5: 78. 1830. (Breedlove, 2001: 1080–1081; Parker, 2008: 301–302; as Quercus excelsa in González-Villarreal, 1986: 92–95; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 528–530; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 182–187; as Q. pilarius in Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 236–237). Quercus boqueronae, Q. leiophylla, and Q. toxicodendrifolia are considered synonyms. 35m. |
| Quercus laurina A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 32. 1809. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 125–129; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 532–535; McVaugh, 1974: 53–55; Parker, 2008: 302; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 79–85; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 213–214; Valencia et al., 2002: 79–82; Valencia, 2005: 97; Vázquez, 2000: 23–24). Quercus bourgaei, Q. caeruleocarpa, Q. chrysophylla, Q. floccosa, Q. orizabae, Q. treleaseana, and Q. tridens are considered synonyms. 40m. |
| Quercus laxa F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 181. 1854. (Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 85–87; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 215–216). 10m. Endemic. |
| Quercus liebmannii A. S. Oersted ex W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 66. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 536–537; Valencia et al., 2002: 83–85). Quercus poculifer is considered a synonym. 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus macdougallii M. Martínez, Anales del Instituto de Biología de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México 34: 147. 1963[1964]. (Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 216–217). 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus magnoliifolia L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 268. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 130–136; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 540–544; McVaugh, 1974: 55–57; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 87–90; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 217–218; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 188–193; Valencia et al., 2002: 86–89; Vázquez, 2000: 24–26). Quercus rubescens is considered a synonym. 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus martinezii C. H. Muller, Anales del Instituto de Biología de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México 24: 274. 1953. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 137–140; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 545–548; McVaugh, 1974: 57–59; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 90–92; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 219–220; Valencia et al., 2002: 90–93). 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus mcvaughii R. W. Spellenberg (also spelled incorrectly Q. macvaughii), American Journal of Botany, 79(10): 1200. 1992. (Felger et al., 2001: 221–222; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 220–221; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 194–199; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 220–221). 25m. Endemic. Quercus meavei S. Valencia-A., J. L. Sabás et O. J. Soto, Phytotaxa 269(2): 121. 2016. 30 m. Endemic. |
| Quercus mexicana A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 35. 82. 1809. Quercus pablillensis and Q. rugulosa are considered synonyms. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 549–551; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 92–96; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 222–223; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 200–207; Valencia, 2005: 97–98; Vázquez, 2000: 26–27; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1261–1262). 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus monterreyensis W. Trelease, Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 63: 151. 1936. 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus muehlenbergii G. Engelmann (the original spelling was Q. mühlenbergii, but both spellings are legitimate), Transactions of the Academy of Science of St. Louis 3(25): 391. 1877. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 102–107; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 477–478; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1263–1265). 30m. |
| Quercus mulleri M. Martínez, Anales del instituto de Biología de la Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México 24(1): 51. 1953. (Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 226–227; Valencia, 2005: 98). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus nixoniana S. Valencia-A. et L. Lozada, Novon 13(2): 261. 2003. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 556–558; Valencia, 2005: 98). 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus oblongifolia J. Torrey, Report of an Expedition down to the Zuni and Colorado Rivers 173: 19. 1853. (Felger et al., 2001: 222; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 559–561; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 499–500; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 227–229; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1264–1265). 10 (–22) m. |
| Quercus obtusata A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2(10): 26. 1809. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 145–150; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 562–565; McVaugh, 1974: 60–62; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 100–109; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 229–230; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 208–215; Valencia et al., 2002: 94–97; Vázquez, 2000: 28–29). 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus oleoides D. F. von Schlechtendal et L. K. von Chamisso, Linnaea 5: 79. 1830. (Breedlove, 2001: 1081–1082; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 566–568; Morales, 2010: 780–781; Parker, 2008: 302–303; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 126–127; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 109–111; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 231–232; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 216–221). 30m. |
| Quercus palmeri G. Engelmann, Geological Survey of California, Botany 2: 97. 1880. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 274–275; Manos, 1997: 469–470). 3 (–8) m. |
| Quercus paxtalensis C. H. Muller, Miscellaneous Publication of the Bureau of Plant Industry (U. S. Department of Agriculture) 477: 75. 1942. 20m. |
| Quercus peduncularis L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 270. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 151–155; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 572–575; McVaugh, 1974: 65–66; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 111–113; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 234–235; Valencia et al., 2002: 98–101). Quercus martensiana and Q. pilicaulis are considered synonyms. 15 (–20) m. |
| Quercus peninsularis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 124. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 576–577). 10m. Endemic. |
| Quercus perpallida W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 91. 1924. (Felger et al., 2001: 222–223). 16m. Endemic. |
| Quercus pinnativenulosa C. H. Muller, Journal of the Arnold Arboretum 17: 171. 1936. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 578–579; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 113–115; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 229–235; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 237–238; Valencia, 2005: 99). 20 (–40) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus planipocula W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 136. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 156–159; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 580–582; McVaugh, 1974: 66–68; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 238–239; Valencia et al., 2002: 102–105; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 221–222). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus polymorpha D. F. von Schlechtendal et L. K. von Chamisso, Linnaea 5: 78. 1830. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 583–586; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 477; Parker, 2008: 304; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 116–120; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 240–241; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 236–243; Vázquez, 2000: 29–30; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1265–1266). 20 (–30) m. |
| Quercus potosina W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 84. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 160–163; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 588–589; McVaugh, 1974: 68–70; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 120–123; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 241–242; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 244–252; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1265–1267). Quercus jaralensis is considered a synonym. 7 (–12) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus praeco W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 88. 1924. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 164–167; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 590–591; McVaugh, 1974: 70–71; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 253–257). 7m. Endemic. |
| Quercus pringlei K. O. von Seemen, Botanische Jahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflansengeographie 29(1): 96. 1900. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 592–595; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 123–126; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 244–245; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 258–263; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1267–1268, 1270). 4 (–10) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus purulhana W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 63. 1924. (Breedlove, 2001: 1082; Parker, 2008: 304). 6–20 (–25) m. |
| Quercus radiata W. Trelease, Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 60: 33. 1921. (Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 222–223). 9m. Endemic. |
| Quercus resinosa F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 182. 1854. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 172–177; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 598–601; McVaugh, 1974: 73–75; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 131–134; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 248–249; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 269–275; Valencia et al., 2002: 106–109). 12 (–17) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus rubramenta W. Trelease, Repertorium specierum novarum regni vegetabilis 33: 318. 1934. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 602–603; Valencia et al., 2002: 110–113; Valencia, 2005: 100). 40m. Endemic. |
| Quercus rugosa L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3(9): 275. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 178–182; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 604–607; McVaugh, 1974: 75–77; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 496; Parker, 2008: 304; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 135–141; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 250–251; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 276–281; Valencia et al., 2002: 114–117; Vázquez, 2000: 30–31; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1269–1271). Quercus innuncupata, Q. purpusii, and Q. uhdeana are considered synonyms. 35m. |
| Quercus rysophylla C. A. Weatherby (also spelled incorrectly Q. rhysophylla), Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences 45(17): 423. 1910. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 608–611; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 141–143; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 251–252; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 282–286). 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus salicifolia L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 265. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 183–188; McVaugh, 1974: 77–80; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 143–146; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 253–254; Valencia et al., 2002: 118–120). The species has been confused in Central America with Quercus eugeniifolia and Q. seemannii, both of which do not exist in Mexico. 20 (–35) m. Endemic. |
| Quercus saltillensis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 183. 1924. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 614–617; Valencia, 2005: 100; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1270–1272). 5m. Endemic. |
| Quercus sapotifolia F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 185. 1854. (Breedlove, 2001: 1082–1083; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 618–620; Morales, 2010: 781; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 287–292; Valencia, 2005: 100–101). Quercus bumelioides, Q. perseifolia, and Q. totutlensis are considered synonyms. 15 (–35) m. |
| Quercus sartorii F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 177. 1854. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 621–623; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 293–300; Valencia et al., 2002: 121–123; Vázquez, 2000: 31–32). Quercus huitamalcana, Q. runcinatifolia, and Q. tenuiloba are also considered synonyms. 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus scytophylla F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 180. 1854. (Felger et al., 2001: 223; González-Villarreal, 1986: 189–193; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 624–627; McVaugh, 1974: 80–81; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 146–148; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 254–255; Valencia et al., 2002: 124–127). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus segoviensis F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 186. 1854. (Breedlove, 2001: 1083; Parker, 2008: 305; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 257–258). 20 (–30) m. |
| Quercus sideroxyla A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 39. 1809. (Felger et al., 2001: 223; González-Villarreal, 1986: 194–196; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 632–635; McVaugh, 1974: 82–83; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 149–152; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 258–259; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 308–312; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1272–1273, 1275). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus sinuata T. Walter, Flora Caroliniana 235. 1788. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 148–152; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 497–498; Villarreal et al., 2008: 1273–1275). Two varieties, 1 in Mexico (Nixon & Muller, 1997). 20m. |
| Quercus skinneri G. Bentham, Plantas hartwegianas imprimis mexicanas 90. 1842. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 636–637; Parker, 2008: 306; Romero-Rangel, 2006: 29–33; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 260–261). 60m. |
| Quercus splendens L. Née, Anales de Ciencias Naturales 3: 275. 1801. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 197–200; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 638–641; McVaugh, 1974: 83–85; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 261–262; Valencia et al., 2002: 128–130; Vázquez, 2000: 33–35). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus subspathulata W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 56. 1924. (Felger et al., 2001: 223–225; González-Villarreal, 1986: 201–204; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 645–647; McVaugh, 1974: 85–86; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 152–154; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 262–263; Valencia et al., 2002: 131–134). Quercus pallidofolia is considered a synonym. 25m. Endemic. |
| Quercus tarahumara R. Spellenberg, Bacon et Breedlove, Madroño 42: 28. 1995. (Felger et al., 2001: 225–226; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 648–649; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 263–264; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 223–225). 12m. Endemic. |
| Quercus tomentella G. Engelmann, Transactions of the Academy of Science of St. Louis 3: 393. 1877. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 290–293; Manos, 1997: 470–471; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 266–267). 20m. |
| Quercus trinitatis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 144. 1924. (As Quercus ocoteifolia in Valencia, 2005: 99). Quercus zempoaltepecana is also considered a synonym. 30m. |
| Quercus tuberculata F. M. Liebmann, Oversigt over det kongelige danske videnskabernes selskabs forhandlinger og dets medlemmers arbeider 1854: 181. 1854. (Felger et al., 2001: 226; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 650–652; McVaugh, 1974: 86–88; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 154–157; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 269–270, Villarreal et al., 2008: 1274–1276). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus tuitensis L. M. González, Brittonia 55(1): 42. 2003. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 653–655). 15m. Endemic. |
| Quercus turbinella E. L. Greene, Illustrations of West American Oaks 1: 37. 1889. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 296–298; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 492–493; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 270–272). 10m. |
| Quercus urbanii W. Trelease, Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 60: 32. 1921. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 205–208; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 656–663; McVaugh, 1974: 88–90; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 272–273; Valencia et al., 2002: 135–138; Vázquez, 2000: 35–36; Vázquez & Nixon, 2013: 225–226). 20m. Endemic. |
| Quercus uxoris R. McVaugh, Contributions from the University of Michigan Herbarium 9: 513. 1972. (González-Villarreal, 1986: 209–212; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 664–666; McVaugh, 1974: 90–91; Romero-Rangel, 2006: 33–36; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 274–275; Valencia et al., 2002: 139–142). 30m. Endemic. |
| Quercus vaseyana S. B. Buckley, Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club 10(8): 91. 1883. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 302–304; Nixon & Muller, 1997: 496). 10 (–15) m. |
| Quercus vicentensis W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 59. 1924. (Parker, 2008: 306). 50m. |
| Quercus viminea W. Trelease, Memoirs of the National Academy of Sciences 20: 123. 1924. (Felger et al., 2001: 226; González-Villarreal, 1986: 213–216; Jensen, 1997: 453–454; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 667–669; McVaugh, 1974: 91–92; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 157–159; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 275–276; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 328–333; Valencia, 2005: 102). 20m. |
| Quercus wislizeni A. L. de Candolle, Prodromus systematis naturalis regni vegetabilis 16(2[1]): 67. 1864. (Jensen, 1997: 452; le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 306–308). Two varieties, both in Mexico (Govaerts & Frodin, 1998: 321). 25m. |
| Quercus xalapensis A. J. Bonpland, Plantae aequinoctiales 2: 24. 1809. (le Hardÿ de Beaulieu et al., 2006: 670–671; Romero-Rangel, 2006: 36–43; Romero-Rangel et al., 2015: 276–278; Sabás-Rosales, 2006, 2011: 334–341; Romero-Rangel et al., 2014: 159–163). Breedlove (2001: 1084) and Parker (2008: 306) report this species in Central America, apparently due to confusion with Quercus skinneri. 30m. Endemic. |
| Sapotaceae |
| Chrysophyllum cainito L. Linnaeus, Species plantarum 1: 192. 1753. (Parker, 2008: 839; Pennington, 1990: 542, 552–555; Pennington, Monro, Thornton-Wood, & Knapp, 2009: 608; Pool, 2001b: 2335). The species might be native only in the Greater Antilles (Pennington, 1990), but is naturalized and widely cultivated in Mexico (if not native). 30m. |
| Chrysophyllum mexicanum T. S. Brandegee, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 23(4): 1114. 1924. (Carranza-González, 2005: 3–6; Parker, 2008: 839; Pennington, 1990: 542, 554–557; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 434–435; Pennington et al., 2009: 608–609; Pool, 2001b: 2336). 20 (–50) m. |
| Chrysophyllum venezuelanense (J. B. Pierre) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 607. 1990. (Parker, 2008: 839; Pennington et al., 2009: 607; Pool, 2001b: 2336–2337). 25m (40m in South America). |
| Manilkara chicle (H. F. Pittier) C. L. Gilly, Tropical Woods 73: 14. 1943. (Parker, 2008: 840; Pennington, 1990: 68, 70–73; Pennington et al., 2009: 573–574; Pool, 2001b: 2338). 60m. |
| Manilkara zapota (C. Linnaeus) P. van Royen, Blumea 7(2): 410. 1953. (Newman, 2008: 2–4, 6; Parker, 2008: 841; Pennington, 1990: 56, 64–69; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 436–437; Pennington et al., 2009: 573; Pool, 2001b: 2339; Wunderlin & Whetstone, 2009a: 235). 40m. |
| Micropholis melinoniana J. B. Pierre, Notes Botaniques: Sapotacées 2: 40. 1891. (Parker, 2008: 842; Pennington, 1990: 193–195, 206, 209; Pennington et al., 2009: 585; Pool, 2001b: 2339). 40m. |
| Pouteria amygdalina (P. C. Standley) C. Baehni, Candollea 9: 360. 1942. 25m. (Parker, 2008: 843; Pennington, 1990: 511, 516–517; Pennington et al., 2009: 600). The literature does not report this species in Mexico, but collections from the state of Campeche are in MEXU. 35m. |
| Pouteria belizensis (P. C. Standley) A. J. Cronquist, Lloydia 9(5): 267. 1946. (Parker, 2008: 843; Pennington, 1990: 241, 257–259; Pennington et al., 2009: 602; Pool, 2001b: 2342). 20m. |
| Pouteria campechiana (K. S. Kunth) C. Baehni, Candollea 9: 398. 1942. (Carranza-González, 2005: 7–9; Parker, 2008: 843; Pennington, 1990: 380–383, 386; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 438–439; Pennington et al., 2009: 600–601; Pool, 2001b: 2343–2344; Wunderlin & Whetstone, 2009b: 245). 20 (–30) m. |
| Pouteria durlandii (P. C. Standley) C. Baehni, Candollea 9: 422. 1942. (Parker, 2008: 844; Pennington, 1990: 318, 323–326, 330, 332; Pennington et al., 2009: 604; Pool, 2001b: 2344). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 25m. |
| Pouteria glomerata (F. A. Miquel) L. A. Radlkofer, Sitzungsberichte der Mathematisch-Physikalischen Klasse der K. B. Akademie der Wissenschaften zu München 12(3): 333. 1882. (Carranza-González, 2005: 9–12; Parker, 2008: 844; Pennington, 1990: 417–423; Pennington et al., 2009: 589–590; Pool, 2001b: 2346). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990: 68). 30m. |
| Pouteria reticulata (H. G. Engler) P. J. Eyma, Recueil des Travaux Botaniques Néerlandais 33: 183. 1936. (Parker, 2008: 845; Pennington, 1990: 295–301; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 440–441; Pennington et al., 2009: 603; Pool, 2001b: 2347). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 40m. |
| Pouteria rhynchocarpa T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 517. 1990. 25m. Endemic. |
| Pouteria sapota (N. J. von Jacquin) H. E. Moore et W. T. Stearn, Taxon 16(5): 383. 1967. (Parker, 2008: 845; Pennington, 1990: 493–497, 499; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 442–443; Pennington et al., 2009: 596–597; Pool, 2001b: 2347–2348). 30 (–50) m. The species has been introduced to countries outside its central-american range for its edible “mamey sapote” fruits. |
| Pouteria squamosa A. J. Cronquist, Lloydia 9(4): 283. 1946. (Parker, 2008: 846; Pennington, 1990: 430, 436, 449; Pennington et al., 2009: 591). 12m. |
| Pouteria torta (C. F. von Martius) L. A. Radlkofer, Sitzungsberichte der Mathematisch-Physikalischen Klasse der K. B. Akademie der Wissenschaften zu München 12(3): 333. 1882. (Parker, 2008: 846; Pennington, 1990: 481–488; Pennington et al., 2009: 594; Pool, 2001b: 2348–2349). Four subspecies, 2 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 35m. |
| Pouteria viridis (H. F. Pittier) A. J. Cronquist, Lloydia 9(4): 290. 1946. (Parker, 2008: 847; Pennington, 1990: 497–500; Pennington et al., 2009: 597–598; Pool, 2001b: 2349). 30m. |
| Sideroxylon altamiranoi (J. N. Rose et P. C. Standley) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica, 52: 167. 1990. (Carranza-González, 2005: 14–15, 17). 10m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon americanum (P. Miller) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 118. 1990. (Parker, 2008: 847; Pennington et al., 2009: 577). 10m. |
| Sideroxylon capiri (A. P. de Candolle) H. F. Pittier, Contributions from the United States National Herbarium 13(12): 462. 1912. (Carranza-González, 2005: 15–17; Newman, 2008: 7–9; Parker, 2008: 848; Pennington, 1990: 155–160; Pennington et al., 2009: 581–582; Pool, 2001b: 2351–2352). Two subspecies, both in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 35m. |
| Sideroxylon cartilagineum (A. J. Cronquist) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 108. 1990. (Carranza-González, 2005: 18–19). 15m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon celastrinum (K. S. Kunth) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 123. 1990. (Elisens & Jones, 2009: 238–239; Parker, 2008: 848; Pennington et al., 2009: 577–578; Pool, 2001b: 2352). 12m. |
| Sideroxylon contrerasii (C. L. Lundell) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 135. 1990. (Carranza-González, 2005: 19–22; Parker, 2008: 848; Pennington et al., 2009: 578–579; Pool, 2001b: 2352). 40m. |
| Sideroxylon durifolium (P. C. Standley) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 152. 1990. (Parker, 2008: 848; Pennington, 1990: 150, 152; Pennington et al., 2009: 580). 6m. |
| Sideroxylon eucoriaceum (C. L. Lundell) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 143. 1990. (Parker, 2008: 848; Pennington et al., 2009: 579). 25m. |
| Sideroxylon excavatum T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 154. 1990. 12m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon floribundum A. H. Grisebach, Flora of the British West Indian Islands, p. 399. 1861. (Parker, 2008: 849; Pennington, 1990: 156, 160–162; Pennington et al., 2009: 582). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 25m. |
| Sideroxylon foetidissimum N. J. von Jacquin, Enumeratio systematica plantarum quas in insulis caribaeis 15. 1760. (Elisens & Jones, 2009: 239; Parker, 2008: 849; Pennington, 1990: 156, 160, 162–165; Pennington et al., 2009: 582–583). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 40m. |
| Sideroxylon lanuginosum A. Michaux, Flora boreali–Americana 1: 122. 1803. (Elisens & Jones, 2009: 239–240; Felger et al., 2001: 308–309; Pennington, 1990: 144, 166, 168–169). Three subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 15m. |
| Sideroxylon leucophyllum S. Watson, Proceedings of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, 24: 59. 1889. (Pennington, 1990: 156, 165–167). 10m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon obtusifolium (J. J. Roemer et J. A. Schultes) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 113. 1990. (Newman, 2008: 9–12; Parker, 2008: 850; Pennington et al., 2009: 576–577; Pool, 2001b: 2352–2353). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 15m. |
| Sideroxylon occidentale (W. B. Hemsley) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 125. 1990. (Felger et al., 2001: 309–310). 16m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon palmeri (J. N. Rose) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 104. 1990. (Carranza-González, 2005: 22–24; Newman, 2008: 12–14; Pennington et al., 2009: 575–576). 25m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon peninsulare (T. S. Brandegee) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 105. 1990. 5m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon persimile (W. B. Hemsley) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 100. 1990. (Felger et al., 2001: 310–311; Parker, 2008: 850; Pennington & Sarukhán, 2005: 444–445; Pennington et al., 2009: 575; Pool, 2001b: 2353). Two subspecies, both in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 20 (–30) m. |
| Sideroxylon portoricense I. Urban, Symbolae Antillanae seu Fundamenta Florae Indiae Occidentalis 5: 134. 1904. (Parker, 2008: 850; Pennington, 1990: 139–144, 70–73; Pennington et al., 2009: 579; Pool, 2001b: 2353–2354). Two subspecies, 1 in Mexico (Pennington, 1990). 40m. |
| Sideroxylon salicifolium (C. Linnaeus) J. B. Lamarck, Tableau encyclopédique et méthodique des trois règnes de la nature: Botanique 2(2): 42. 1794. (Elisens & Jones, 2009: 243; Newman, 2008: 14–16; Parker, 2008: 850; Pennington, 1990: 144, 149–152; Pennington et al., 2009: 580). 25m. |
| Sideroxylon socorrense (T. S. Brandegee) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 107. 1990. 25m. Endemic. |
| Sideroxylon stenospermum (P. C. Standley) T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 109. 1990. (Parker, 2008: 851; Pennington et al., 2009: 576; Pool, 2001b: 2354). 25m. |
| Sideroxylon stevensonii (P. C. Standley) P. C. Standley et J. A. Steyermark, Publications of the Field Museum of Natural History, Botanical Series 23(2): 68. 1944. (Parker, 2008: 851; Pennington, 1990 [homonym]: 131–134, 144; Pennington et al., 2009: 578). 45m. |
| Sideroxylon tepicense T. D. Pennington, Flora Neotropica 52: 159. 1990. (Felger et al., 2001: 311; Parker, 2008: 851; Pennington et al., 2009: 582). 25m. |
Peer Review under the responsibility of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.