The Investigator Argus X-12 kit is a valuable complementary tool for human identification purposes, especially for solving complex kinship cases. The analysis of these cases generates valuable information in routine forensic work, such as a posteriori informativeness (LR: likelihood ratio) and mutation rates.
AimTo analyze the LR offered by the Argus X-12 QS kit in 74 Mexican families, including the father, mother, and daughter(s), respectively.
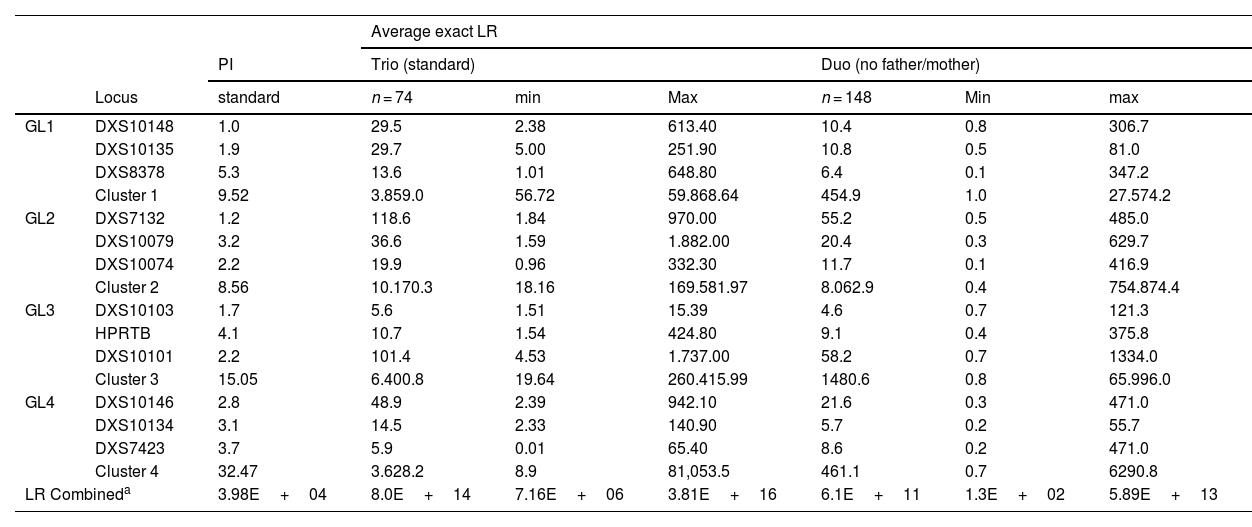
MethodsExact LRs were estimated with the FamlinkX software in the families as paternity trio cases (n = 74; average 8.E+14) and duo cases (n = 148; average 6.1E+11), omitting the mother and father, respectively.
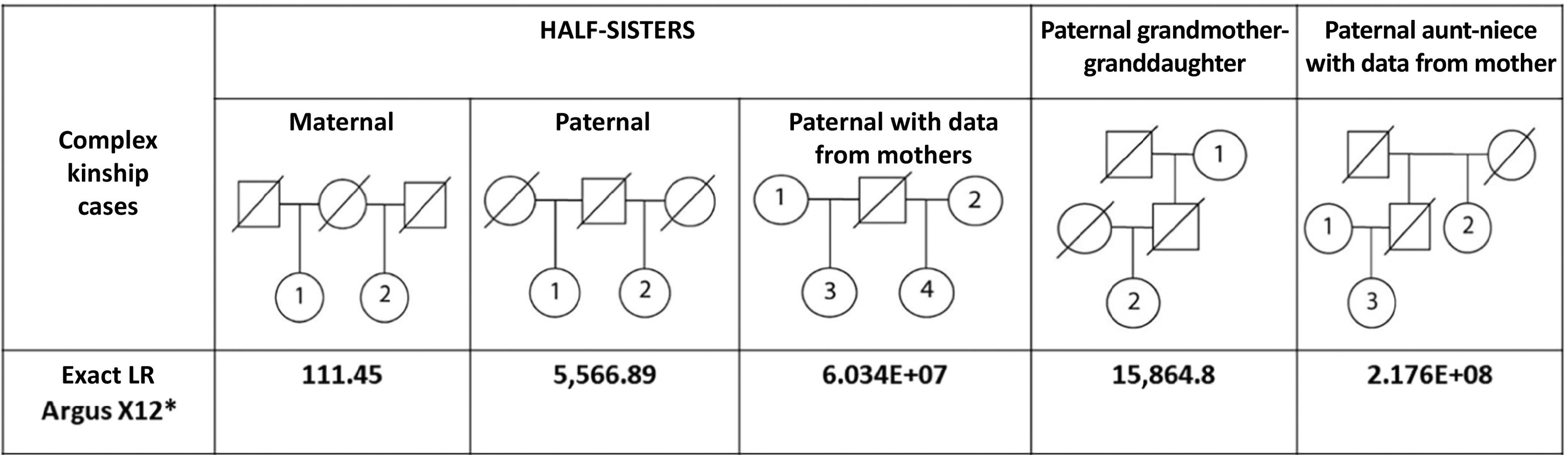
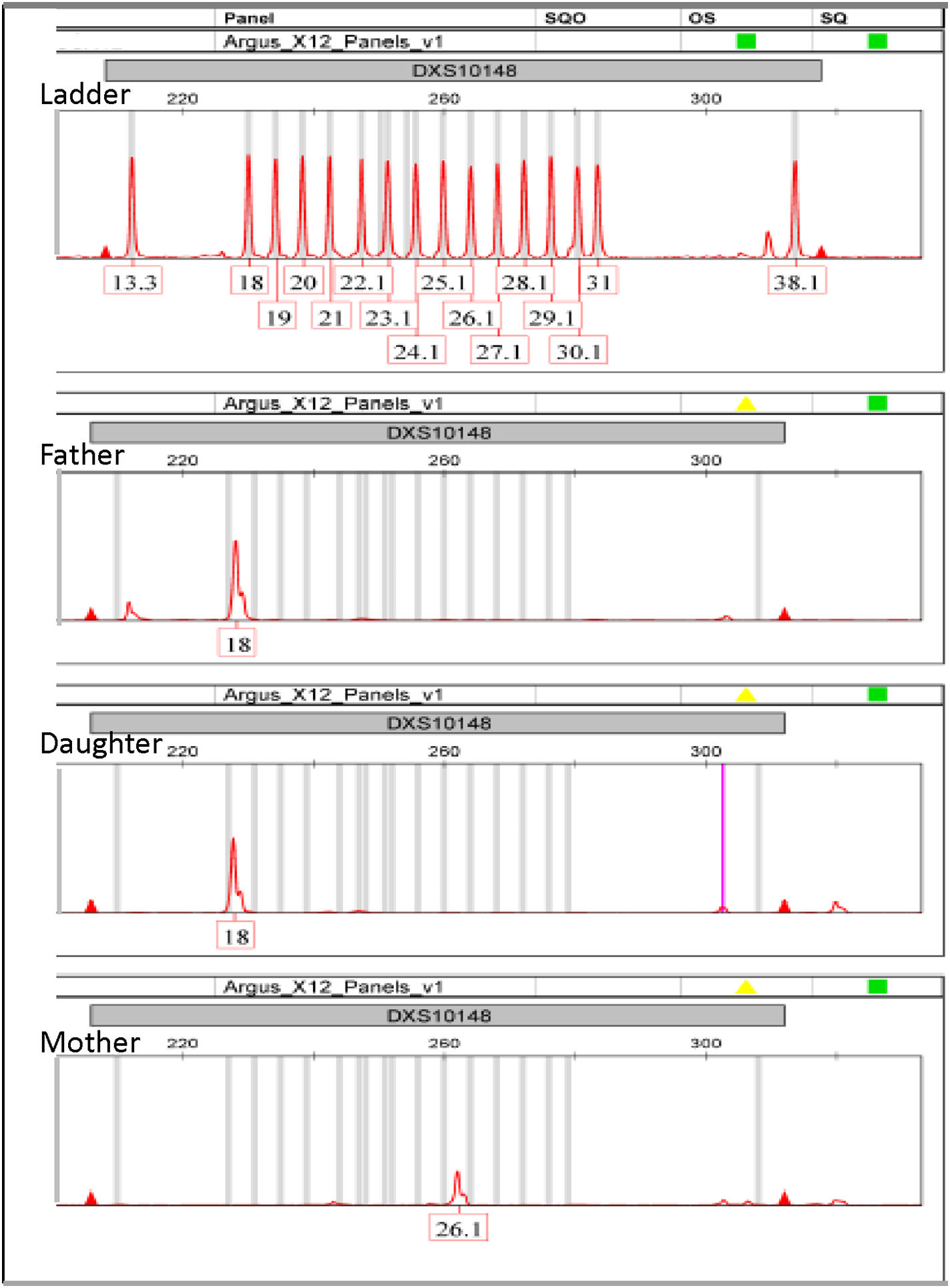
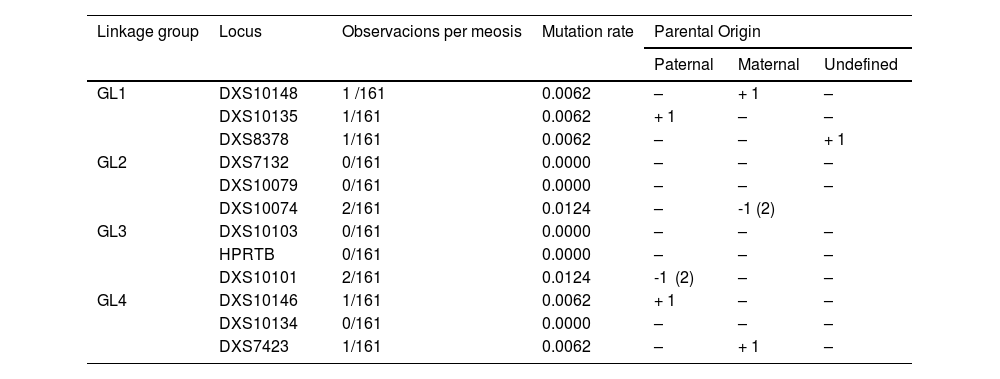
ResultsThe LR of the trios (a posteriori) was significantly higher than the -a priori- parameter IP typical (3.98E+04). As a reference, we report the LR of complex kinship cases solved with X-STRs: maternal half-sisters (LR = 111), paternal half-sisters (LR = 5567), paternal half-sisters with their mothers (LR = 6.0E+07, and paternal grandmother-granddaughter (LR = 15,864). Nine mutations were detected in 161 meiosis. The mutation rate was estimated in seven X-STRs, which was 0.0062 (1/161) for DXS10148, DXS10135, DXS8378, DXS10146, and DXS7423, and 0,0124 (2/161) for DXS10074 and DXS10101. These findings will be useful in future meta-analyses to achieve more conclusive estimates. A null allele in DXS10148 was inferred between a mother and daughter, supported by the low probability that the finding is explained by an 8-step mutation (26.1 → 18), and the low frequency of the 26.1 homozygote.
ConclusionThe a posteriori informativeness of Argus X-12 in paternity and kinship cases described herein justifies the inclusion of the X-STRs in forensic genetics labs.
El kit Investigator Argus X-12 es una herramienta complementaria valiosa con fines de identificación humana, especialmente para resolver casos de parentesco complejos. El análisis de éstos casos de parentesco genera información valiosa en el trabajo de rutina forense, como informatividad a posteriori (LR: likelihood ratio) y las tasas de mutación.
ObjetivoAnalizar el LR que ofrece el kit Argus X-12 QS en 74 familias mexicanas, incluyendo al padre, madre e hija(s).
MétodosSe estimaron LR exactos con el software FamlinkX en las familias como casos de paternidad tipo trío (n = 74; promedio 8.E+14) y tipo dúo (n = 148; promedio 6.1E+11), al no incluir a la madre y al padre, respectivamente.
ResultadosEl LR de los tríos (a posteriori) resultó ser significavamente mayor que el parámetro -a priori- IP típico (3.98E+04). Como referencia, se reporta el LR de casos de parentesco complejo resueltos con X-STRs: media hermandad via materna (LR = 111), media hermandad paterna (LR = 5567), medias hermanas paternas y sus madres (LR = 6.0E+07) y abuela-paterna-nieta (LR = 15,864). Se detectaron 9 mutaciones en 161 meiosis, con las que se estimó la tasa de mutación en siete X-STRs, en el rango de 0,0062 (1/161) para DXS10148, DXS10135, DXS8378, DXS10146 y DXS7423, hasta 0,0124 (2/161) para DXS10074 y DXS10101. Estos hallazgos serán de utilidad en futuros metaanálisis para lograr estimaciones más concluyentes. Se infirió un alelo nulo en DXS10148 entre una madre e hija, sustentado por la baja probabilidad de una mutación materna de 8 pasos (26.1 → 18; p = 9.15E−05), y la baja frecuencia poblacional del homocigoto 26.1.
ConclusiónLa informatividad a posteriori del kit Argus X-12 en casos de paternidad reales y los casos de parenteso descritos, justifican la inclusión de los X-STRs en los laboratorios de genética forense.