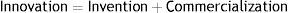This study explores previous research studies in the area of quality management and innovation performance. The study explains why different quality practices like leadership, process management, supplier relationship, customer focus and strategic planning are used for better innovation performance in firms and also explains different scenarios in which the quality practices have a positive or negative influence on innovation performance. The paper firstly categorized these studies according to the journal in which these studies are published then further divide them according to their research design into quantitative, qualitative and review types. The studies are analyzed on set criteria of industry, quality indicators, outcome indicators and results. The trends identified in this paper shows that irrespective of type of industry most studies have found a positive relationship between quality practices and firms innovation performance and in cases where the relationship is weak or negative is because of various contextual factors like uncertainty in business environment, firm size, financial resources and firms culture that has modified this relationship.
In all developed and most developing countries firms now a day's faces unprecedented levels of competition and find themselves in direct competition with both local and international competitors and the reason for this intense competition lies in fast technological changes and globalization of trade. In this scenario in order to survive firms must show higher level of efficiency at low cost to produce customer oriented novel products/services that are innovative as well as cost effective. There are many different management philosophies which can help firms achieve this goal and total quality management is among one of these philosophies.
Empirical investigations done by many researchers like Bloch and Bugge (2013), Djellal, Gallouj, and Miles (2013), Sadikoglu and Zehir (2010) in various industries have shown that TQM practices have a positive relationship with firm's performance especially its innovation performance but others like Brun (2010), Toremen and Karakus (2009) have also found a negative relationship as well so the main objective of this paper is to clearly explain TQM and innovation performance relationship from a broader perspective. Therefore this paper has reviewed various research studies undertaken in the area of quality management and firm innovation performance from different industries and it has helped to answer the following questions.
- •
What are the latest trends in total quality management literature?
- •
Which quality management practices are frequently used among different industries?
- •
How effective are these quality practices in terms of results in enhancing firm's innovation performance?
- •
Which conditions can make TQM and innovation performance relationship positive and vice versa?
Quality management is one of the most popular and durable management concepts and it has passed through a number of phases since 1920s. The roots of quality management go back to the teachings of Drucker, Juran, Deming, Ishikawa, Crosby, Feigenbaum and countless other people that have studied, practiced, and tried to refine the process of organizational management. Before exploring the different quality management practices it is better to understand what is meant by the term quality and different people interpret quality differently and few authors had defined quality in measurable terms that can be operationalized.
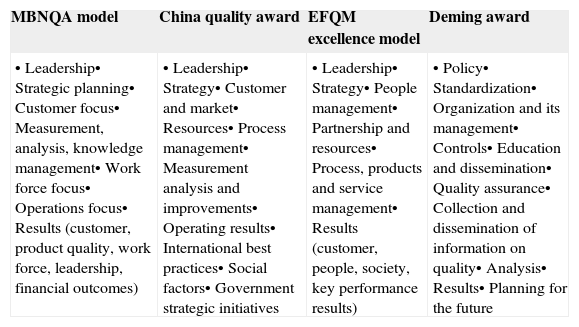
Various practitioners have defined quality in different ways as mentioned in Table 1.
Quality models and their sub-categories.
| MBNQA model | China quality award | EFQM excellence model | Deming award |
|---|---|---|---|
| •Leadership•Strategic planning•Customer focus•Measurement, analysis, knowledge management•Work force focus•Operations focus•Results (customer, product quality, work force, leadership, financial outcomes) | •Leadership•Strategy•Customer and market•Resources•Process management•Measurement analysis and improvements•Operating results•International best practices•Social factors•Government strategic initiatives | •Leadership•Strategy•People management•Partnership and resources•Process, products and service management•Results (customer, people, society, key performance results) | •Policy•Standardization•Organization and its management•Controls•Education and dissemination•Quality assurance•Collection and dissemination of information on quality•Analysis•Results•Planning for the future |
- •
“Fitness for use.” Where fitness is defined by the customer. (Joseph M. Juran)
- •
“Conformance to requirements.” But the requirements may not fully represent customer expectations and Crosby treats this as a separate problem. (Philip B. Crosby)
- •
“Uniformity around a target value.” The idea is to lower the standard deviation in outcomes, and to keep the range of outcomes to a certain number of standard deviations, with few exceptions. (Genichi Taguchi)
- •
“Quality and management are linked.” Costs go down and productivity goes up as improvement of quality is accomplished by better management of design, engineering, testing and by improvement of processes. (W. Edwards Deming)
- •
Quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for. (Peter Drucker)
- •
The characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs. (American Society for Quality)
In today's business world there is a growing recognition that isolated improvements in particular aspects of the organization are no longer adequate and that a holistic strategy is needed to bring competitive advantage and this can be done by adopting one of the few quality practices mentioned below.
- •
Quality control:
In this quality tool organizations consider laboratory and testing of products as a main activity of quality management and invest in and develop their products/services management systems, these firms usually have quality control labs and departments testing and measurements make them react to non-conformities. Quality controls include the use of affinity diagrams, pareto charts, histograms, arrow diagrams and run charts.
- •
Quality assurance standards: (ISO)
According to these quality standards a product is a result of many processes and unless these are controlled effectively quality cannot be delivered therefore they try to control all these processes that effect product/service quality and most companies assure quality by using quality programs like ISO 9000, ISO 9000-2000, ISO 14000, etc.
- •
Continuous quality improvements:
Continuous quality improvement is based on the Japanese philosophy Kaizen and firms which implement this quality tool do not just confer to the quality assurance standards but they realize that process improvements are directly proportional to competence, commitment and team work of employees, such organizations mobilize companywide campaigns for continuously developing skills of quality management at all levels and give assignments on weekly and monthly basis in cross functional teams.
- •
The quality excellence models:
These days’ practitioners working in the field of quality management are using quality models to assess and evaluate the contribution of quality practices in achieving better organizational results, and among these models the Deming application prize, MBNQA model also known as Baldrige award and the EFQM excellence model are mostly used.
According to Porter innovation means.
So according to Porter innovation can be a new product or service or an improvement in them and many innovation do not come from laboratory but from the market place so if these new inventions and properly commercialized they become innovations. Damanpour (1991) defines innovation as adaptation of internally generated or purchased device, system, policy, program, process, product or service that is new to the adopting firm so according to him innovation can be anything new that the firm adopts which could be a new process, program or a product/service. While according to Huiban and Bouhsina (1998), Sciulli (1998) innovations can be divided in two main categories i.e. product/process innovations and incremental and radical innovations so the former is in terms of area where the innovation is being done and later is on the way innovations are being adopted. Hipp, Thether, and Miles (2000) divides innovations to be of four types i.e. firstly product/service innovations which includes innovations in the form of introduction of new and improved products or services. Second type are process innovations which include new and improved work methods in the processes and third type are organizational innovations which are not limited to the individual production processes but also involve significant improvements in overall organizational structures and processes and fourth type of innovations include communication innovations both inside and outside the firm.
3.1Types of innovationsAccording to Rycroft (2006) innovations can be measured.
- •
Product/service innovation: Are measured by rates of new product/service introduction or intervals between the new product/service generations.
- •
Organization innovations: Are measured by rates of change in organizational structures, routines and capabilities.
- •
Process innovations: Are measured by the rate of capital equipment obsolesce rates.
- •
Marketing innovations: Are measured by the number of new marketing strategies adopted by firms for packaging, promotion, placement and pricing.
- •
Communication innovations: Are measured by the introduction of rate of change or adaptation of new communication channels used.
In this paper we had reviewed 62 research articles from top ranking research journals assessed different academic data bases like EBSCO, Emerald Insight, Elsevier, INFORMS and Springer, Taylor & Francis, Blackwell and Google Scholar. Other details about journal name and type of study are mentioned in Tables 2 and 3. In this paper among the sixty two articles reviewed forty five articles have used quantitative techniques and used several different types of statistical techniques to evaluate the data like regression, correlation, factor analysis, structural equation modeling, etc. so these studies are placed in the quantitative group while fifteen studies have used the case study, stories and interview approach and used respondents and experts judgment to assess the TQM and innovation performance relationship so such studies are placed in the qualitative group of articles the rest of two articles are literature reviews in a particular industry to assess the trends in literature in these sectors.
Journal paper reviewed.
Type of study.
From the review it is quite clear that in most industries i.e. manufacturing, service, IT, marketing, etc. most practitioners and managers now a day's implement quality techniques based on quality control standards (ISO series) or quality excellence models (MBNQA, EFQM) and among these models quality management techniques like top leadership training and behavior toward quality, customer focus, information sharing, participation, autonomy etc. have mostly proven to be very effective in enhancing firm performance especially its product/service quality and innovation performance (Table 4).
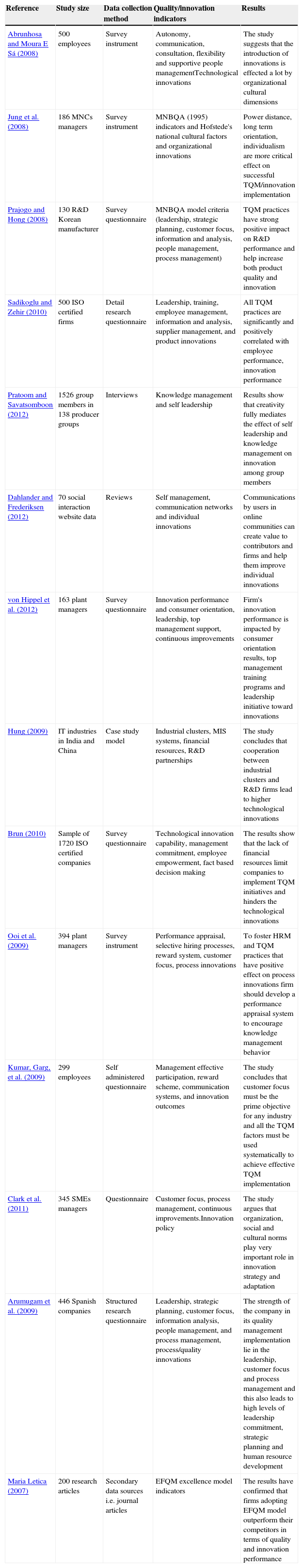
Some important research studies about quality and innovation performance.
| Reference | Study size | Data collection method | Quality/innovation indicators | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abrunhosa and Moura E Sá (2008) | 500 employees | Survey instrument | Autonomy, communication, consultation, flexibility and supportive people managementTechnological innovations | The study suggests that the introduction of innovations is effected a lot by organizational cultural dimensions |
| Jung et al. (2008) | 186 MNCs managers | Survey instrument | MNBQA (1995) indicators and Hofstede's national cultural factors and organizational innovations | Power distance, long term orientation, individualism are more critical effect on successful TQM/innovation implementation |
| Prajogo and Hong (2008) | 130 R&D Korean manufacturer | Survey questionnaire | MNBQA model criteria (leadership, strategic planning, customer focus, information and analysis, people management, process management) | TQM practices have strong positive impact on R&D performance and help increase both product quality and innovation |
| Sadikoglu and Zehir (2010) | 500 ISO certified firms | Detail research questionnaire | Leadership, training, employee management, information and analysis, supplier management, and product innovations | All TQM practices are significantly and positively correlated with employee performance, innovation performance |
| Pratoom and Savatsomboon (2012) | 1526 group members in 138 producer groups | Interviews | Knowledge management and self leadership | Results show that creativity fully mediates the effect of self leadership and knowledge management on innovation among group members |
| Dahlander and Frederiksen (2012) | 70 social interaction website data | Reviews | Self management, communication networks and individual innovations | Communications by users in online communities can create value to contributors and firms and help them improve individual innovations |
| von Hippel et al. (2012) | 163 plant managers | Survey questionnaire | Innovation performance and consumer orientation, leadership, top management support, continuous improvements | Firm's innovation performance is impacted by consumer orientation results, top management training programs and leadership initiative toward innovations |
| Hung (2009) | IT industries in India and China | Case study model | Industrial clusters, MIS systems, financial resources, R&D partnerships | The study concludes that cooperation between industrial clusters and R&D firms lead to higher technological innovations |
| Brun (2010) | Sample of 1720 ISO certified companies | Survey questionnaire | Technological innovation capability, management commitment, employee empowerment, fact based decision making | The results show that the lack of financial resources limit companies to implement TQM initiatives and hinders the technological innovations |
| Ooi et al. (2009) | 394 plant managers | Survey instrument | Performance appraisal, selective hiring processes, reward system, customer focus, process innovations | To foster HRM and TQM practices that have positive effect on process innovations firm should develop a performance appraisal system to encourage knowledge management behavior |
| Kumar, Garg, et al. (2009) | 299 employees | Self administered questionnaire | Management effective participation, reward scheme, communication systems, and innovation outcomes | The study concludes that customer focus must be the prime objective for any industry and all the TQM factors must be used systematically to achieve effective TQM implementation |
| Clark et al. (2011) | 345 SMEs managers | Questionnaire | Customer focus, process management, continuous improvements.Innovation policy | The study argues that organization, social and cultural norms play very important role in innovation strategy and adaptation |
| Arumugam et al. (2009) | 446 Spanish companies | Structured research questionnaire | Leadership, strategic planning, customer focus, information analysis, people management, and process management, process/quality innovations | The strength of the company in its quality management implementation lie in the leadership, customer focus and process management and this also leads to high levels of leadership commitment, strategic planning and human resource development |
| Maria Letica (2007) | 200 research articles | Secondary data sources i.e. journal articles | EFQM excellence model indicators | The results have confirmed that firms adopting EFQM model outperform their competitors in terms of quality and innovation performance |
Researchers like Abrunhosa and Moura E Sá (2008) argues that in an organization culture which gives its employees more autonomy and decision making power these employees show higher level of innovation performance as compared to organizations with lower level of autonomy. While Sadikoglu and Zehir (2010) argues that organizations with a free flow of information sharing makes the employees innovation skills improved and provides a very fertile ground for the generation of new ideas and Dahlander argues that an effective way of information sharing is through the use of crass functional teams where people from various diverse back ground work together to come up with more novel ideas and create new innovations but on the other hand researchers like Prajogo (2006) says that in some cases team performance hinders in the way of employees individual level of innovations due to strong level of pressure from group opinion.
According to Arumugam, Chang, Ooi, and Teh (2009) leadership emphasis toward quality outcomes and innovation performance leads firm employees to show higher number of initiatives toward innovation and quality performance.
Clark, Clark, and Jones (2011) suggests that strong customer focus leads firms to offer more customized products and services according to the changing demands of its customers which intern improves the firm innovation performance but on the other hand researchers like Kumar, Choisne, de Grosbis, and Kumar (2009) suggests that too much customer centered firms fail to see future opportunities and this effect on their long term performance and success.
Prajogo and Sohal (2006) argues that those firms which invest high amounts of money in their research and development areas show more successful innovation especially the firms which are operating in the high technology areas while Sila (2007) suggests that continuous improvements have more negative impact on firms radical innovations as this philosophy forces employees to make small and incremental changes in their work to improve quality so it supports more incremental innovations then radical innovations. Similarly Parast (2010) says that quality controls and quality assurance models and techniques limits firms innovation performance due to rigid procedures aimed to maintain a certain level of quality in the delivery of products and services.
7Findings supporting positive relationship between quality practices and innovation performanceThe following arguments are made on the basis of this review.
- 1.
Abrunhosa and Moura E Sá (2008): Those firms which give autonomy to its employees to make decisions according to their judgment in this scenario autonomy has a positive effect on innovation performance as employees feel less bounded by rules and procedures which in turn improves their creativity and innovation potential.
- 2.
Sadikoglu and Zehir (2010): Information sharing also proves to be very effective way to enhance employee innovative skills in a high information sharing plate forms more ideas are generated which intern leads to introduction of new products/services.
- 3.
Dahlander and Frederiksen (2012): Cross-functional teams are also proven to be very effective way to enhance creativity and innovation especially in project based organizations.
- 4.
In this review researchers like Arumugam et al. (2009) have found that leadership that emphasizes on innovation and reward new and effective ways to deliver product/services also lead to higher levels of innovation at both group and individual level in their firms.
- 5.
In some cases like Bou-Liusar, Escrig-Tena, Roca-Puig, and Beltrán-Martín (2009) continuous improvements leads to more incremental innovations as it concentrates on step wise improvements in all organizational processes.
- 6.
Clark et al. (2011): Customer focus can enhance firm's innovation performance and firms which try to fulfill the needs of their customers are forced to introduce new products/services that can satisfy their changing demands.
- 7.
Prajogo and Hong (2008): Firms with high level of investment in R&D had shown better innovation performance then those who invest less in R&D and this is especially applicable for firms operating in a more uncertain business environment.
- 1.
Toremen and Karakus (2009): Sometimes firms that give too much attention to customer needs fail to foresee new opportunities and markets and fail to come up with new products and services as they are reacting only toward customer's needs and demands.
- 2.
Bou-Liusar et al. (2009): In some cases continuous improvement philosophy has hindered in the way of radical innovations as its main emphasis is on increasing and improving efficiency of current products and services.
- 3.
Parast (2010): Quality controls also sometimes effect negatively on firms innovation performance as firms following this technique gives more attention to fulfill and control quality at a particular level which reduces chances for firms to make any radical innovations.
- 4.
Prajogo (2006): Employees who work in teams usually decrease their level of individual innovative performance as people who work in groups try to stick with the group opinion which decreases their individual level of creativity.
Based on the review of these research articles this paper concludes that most TQM practices inherently have a positive relationship with firms innovation performance and in those cases where we find a negative relationship is because of the contextual factors like uncertainty in business environment, firm size, financial resources and firms culture etc. so positive results can only be guaranteed through TQM practices for enhancing innovation performance if the management selects the best TQM technique which fits according to its internal and external environmental conditions.
9Contribution of the studyThis study is a sincere effort to explain the effect of various quality practices on the innovation performance of the firm in various industries from product manufacturing, health, education, banking and others, this study discusses how various quality practices can effect differently on different dimensions of firms innovation performance and gives a holistic view of quality practices and their both positive and negative effects on different forms of innovations.
I am extremely grateful to the guidance of my teacher Prof. Song Wei and other teachers of University of Science and Technology of China for their guidance and support to help me do my research work.