Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a multifactorial process which requires an integral approach. It is also a sentinel symptom of endothelial dysfunction that opens a door to the overall health of a man.
ObjectivesTo analyze the prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors and other disorders in patients with ED. The relationship between the severity of ED and the total serum testosterone level and the therapeutic approach of doctors were also analyzed.
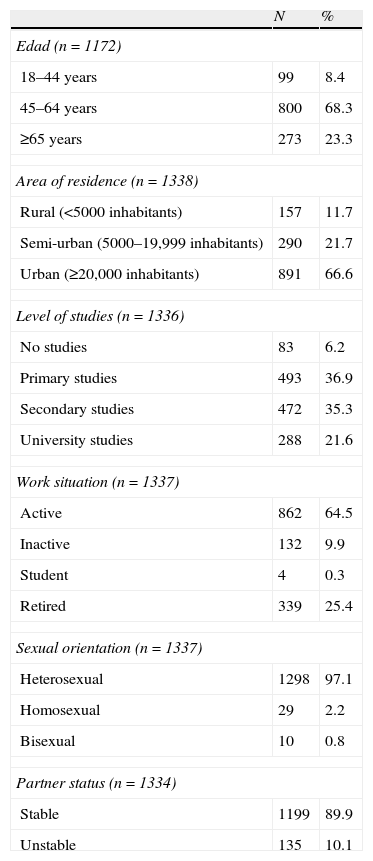
Material and methodsAn observational, multicenter, national study in patients >18 years who came to uroandrology or primary care consultations was conducted. Sociodemographic, anthropometric, lifestyle habits and medical history data of patients and the physician's therapeutic approach, were all collected. ED was diagnosed and total testosterone was assessed when necessary.
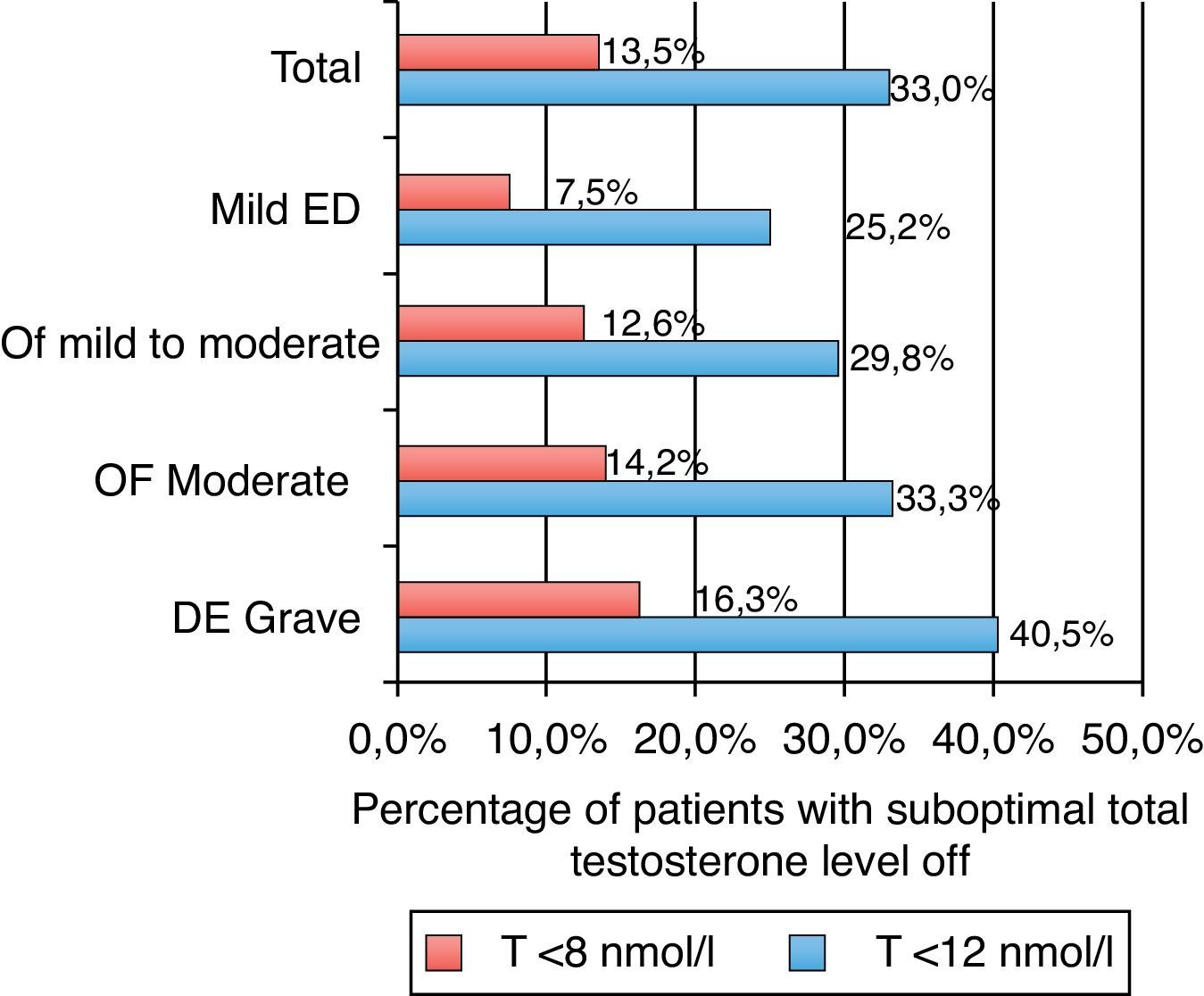
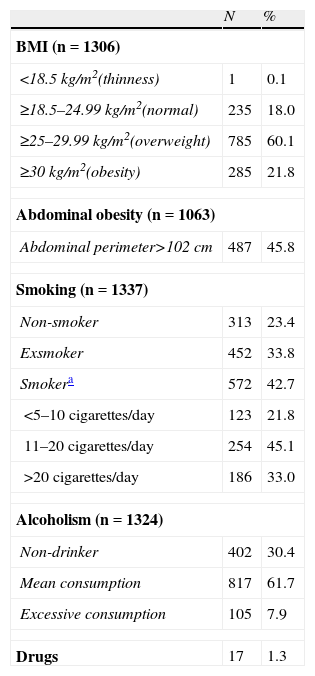
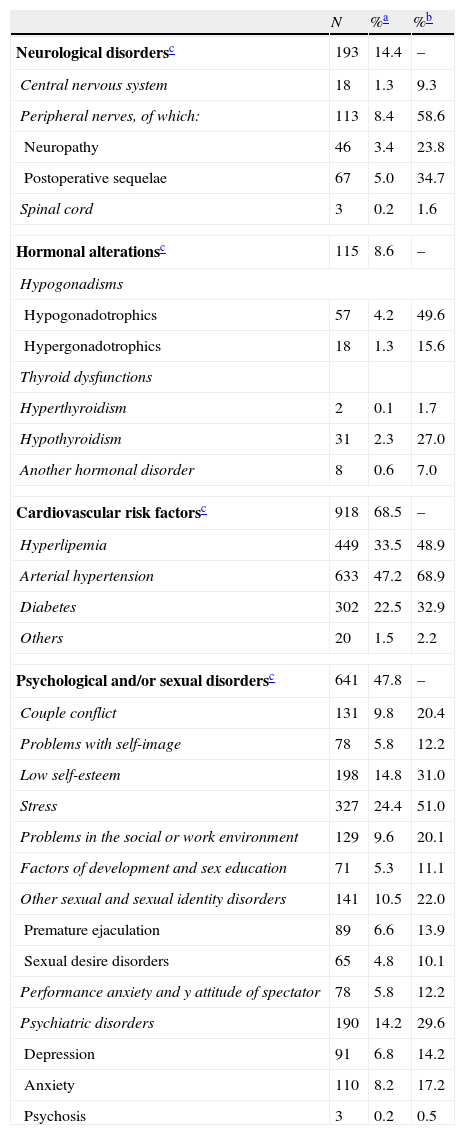
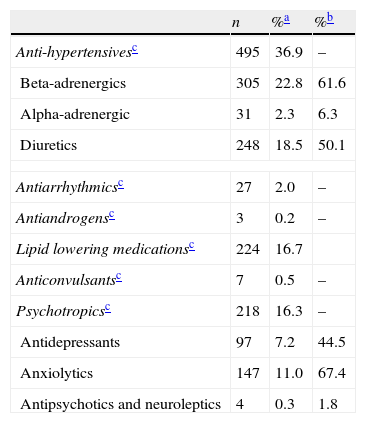
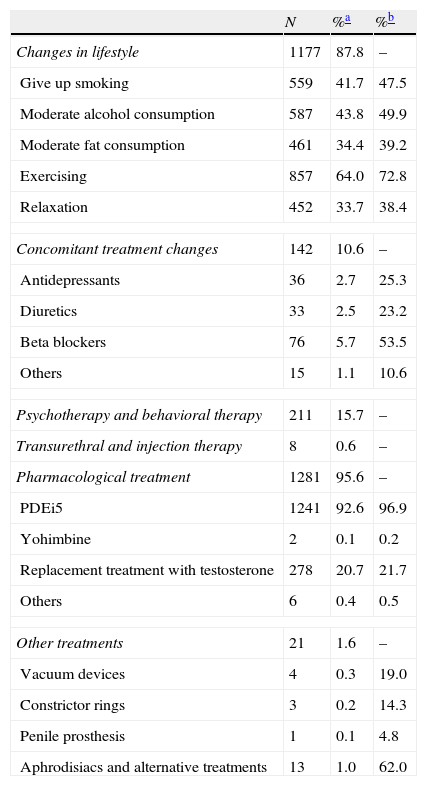
Results1340 patients aged from 22 to 81 years took part in the study. Age was the most prevalent factor to develop the condition. Abdominal obesity, diabetes, and smoking had a high prevalence. Half of the patients presented psychological and/or sexual problems. 33% and 13.5% of patients had suboptimal levels of total testosterone (cut-off point of 12nmol/l and 8nmol/l, respectively), with a direct relationship with disease severity.
ConclusionOur study supports the need to examine cardiovascular risk factors in patients with ED and to identify patients who might benefit from testosterone replacement therapy. Psychological disorders should receive specialized care.
La disfunción eréctil (DE) es un proceso multifactorial que requiere un abordaje integral. Se trata además de un síntoma centinela de disfunción endotelial que abre una puerta hacia la salud global del hombre.
ObjetivosAnalizar la prevalencia de factores de riesgo cardiovascular y de otros trastornos en pacientes con DE. Se analizaron además la relación entre la gravedad de la DE y el nivel de testosterona sérica total y la actitud terapéutica de los médicos.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, multicéntrico y nacional en pacientes con DE mayores de 18 años que acudían a consultas de uro-andrología o de Atención Primaria. Se recogieron las características sociodemográficas, antropométricas, de hábitos y estilo de vida, la historia clínica de los pacientes y la actitud terapéutica del médico. Se diagnosticó la DE y se valoró la testosterona total cuando fue necesario.
ResultadosParticiparon 1.340 pacientes de 22-81 años. La edad fue el factor para padecer DE más prevalente. La obesidad abdominal, la diabetes y el hábito tabáquico mostraron una alta prevalencia. La mitad de los pacientes presentó trastornos psicológicos y/o sexuales. Se encontraron niveles subóptimos de testosterona total en el 33 y el 13,5% de los pacientes (puntos de corte de 12 nmol/l y 8 nmol respectivamente), con una relación directa con la gravedad de la DE.
ConclusiónNuestro estudio corrobora la necesidad de analizar factores de riesgo cardiovascular en pacientes con DE y de identificar pacientes que podrían beneficiarse del tratamiento sustitutivo con testosterona. Los trastornos psicológicos han de recibir atención especializada.