Kidney failure is the main cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with myelodysplasia. We analyzed the presence of renal lesions in these patients using dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy and related their presence with the type of vesical function and the delay in receiving appropriate management.
Material and methodsWe performed a retrospective study of patients with myelodysplasia treated in our hospital since 2004. We analyzed the epidemiological and clinical data and the pattern of bladder function according to urodynamic studies. We classified the patients into 4 urodynamic patterns according to detrusor and sphincter behavior. We linked this behavior to renal function in the scintigraphy and the care received since birth.
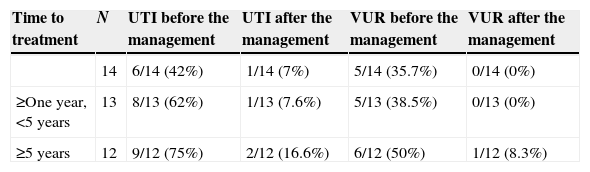
ResultsThe study included 39 patients with myelodysplasia. The most common bladder pattern was type A (61.5%), with sphincter and detrusor hyperactivity, followed by type D (20.5%), C (7.8%) and B (5.1%). Some 38% of our patients (n=15) had some type of nephropathy. Some 92.9% of the children who were properly treated during the first year of their life had no renal lesions in the scintigraphy. We found some type of nephropathy in 56% of the patients for whom appropriate treatment was delayed for more than a year. The nephropathy was more severe the later the management was started.
ConclusionsThere is a statistically significant relationship between a delay in treatment and impairment in renal scintigraphy in patients with neurogenic bladders. The early study and treatment of patients is essential for decreasing renal impairment, reducing the need for surgery and improving the continence options.
El fallo renal es la principal causa de morbimortalidad en pacientes con mielodisplasia. Analizamos la presencia de lesiones renales en la gammagrafía (DMSA) de estos pacientes y la relacionamos con el tipo de funcionamiento vesical, así como con el retraso en recibir un manejo adecuado.
Material y métodosRealizamos un estudio retrospectivo de pacientes con mielodisplasia en nuestro hospital desde 2004. Analizamos datos epidemiológicos, clínicos y el patrón de funcionamiento vesical según estudios urodinámicos. Clasificamos a los pacientes en 4 patrones urodinámicos según el comportamiento del detrusor y del esfínter; y lo relacionamos con la función renal en la gammagrafía y el manejo recibido desde el nacimiento.
ResultadosEstudiamos 39 pacientes con mielodisplasia. El patrón vesical más frecuente fue el tipo A (61,5%) con hiperactividad del esfínter y del detrusor, seguido del D (20,5%), C (7,8%) y B (5,1%). El 38% de nuestros pacientes (n=15) presenta algún tipo de nefropatía. El 92,9% de los niños que reciben tratamiento adecuado en el primer año de vida, no presentan lesiones renales en la gammagrafía. Encontramos algún tipo de nefropatía en el 56% de los pacientes en los que el tratamiento adecuado se demora más de un año; siendo la nefropatía más severa cuanto más tarde se inicia el manejo.
ConclusionesExiste una relación estadísticamente significativa entre el retraso en el tratamiento y la alteración en la gammagrafía renal en pacientes con vejiga neurógena. Es fundamental el estudio y tratamiento precoz de los pacientes para disminuir el deterioro renal, disminuir la necesidad de cirugía y mejorar las opciones de continencia.