To evaluate the impact of metabolic syndrome and its individual components on prostate biopsy findings, the radical prostatectomy specimen and on biochemical recurrence.
Materials and methodsAn observational study was conducted of 1319 men who underwent prostate biopsy between January 2007 and December 2011. The impact on the biopsy findings, the radical prostatectomy specimen and biochemical recurrence was evaluated using logistic regression and Cox regression.
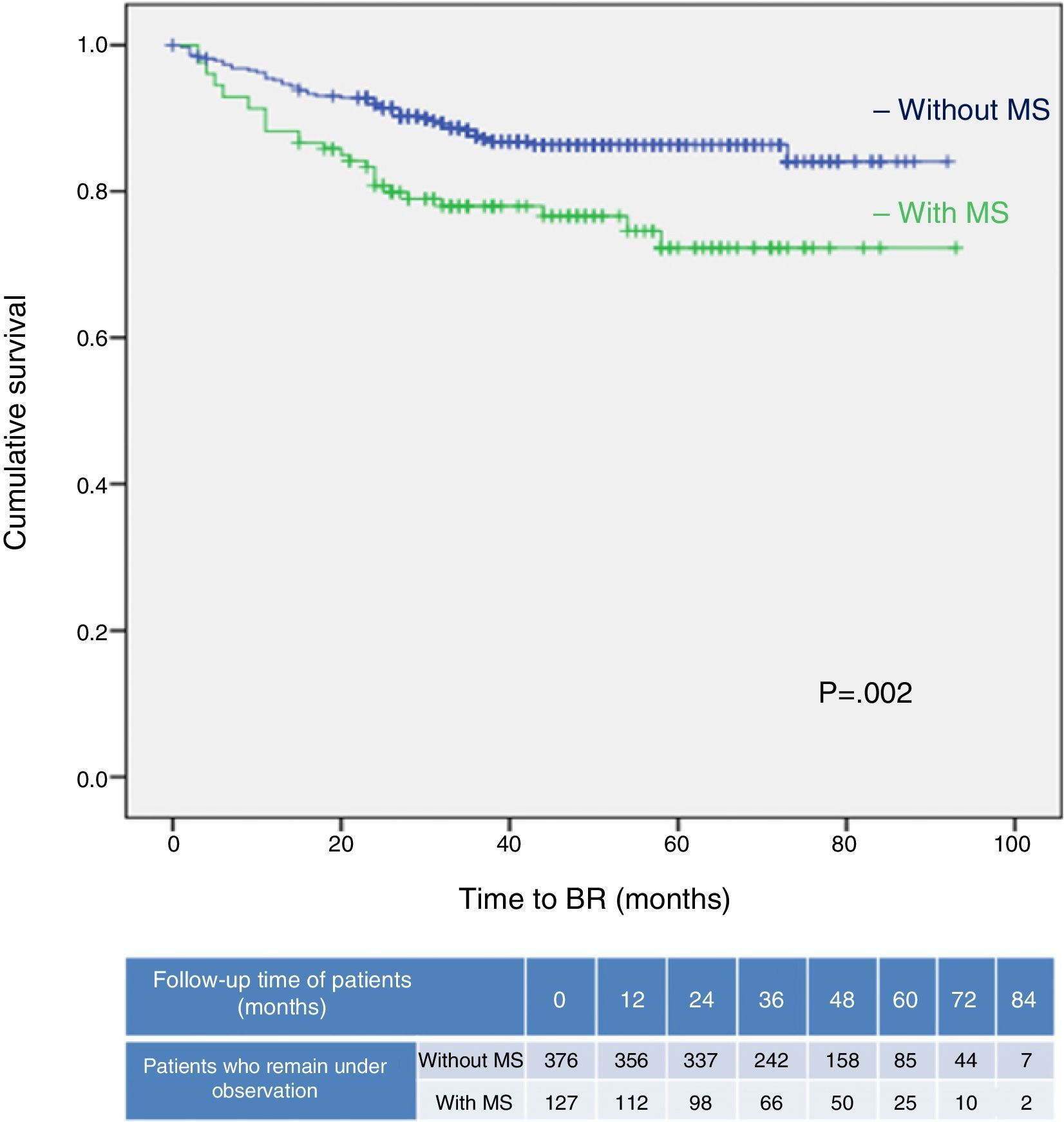
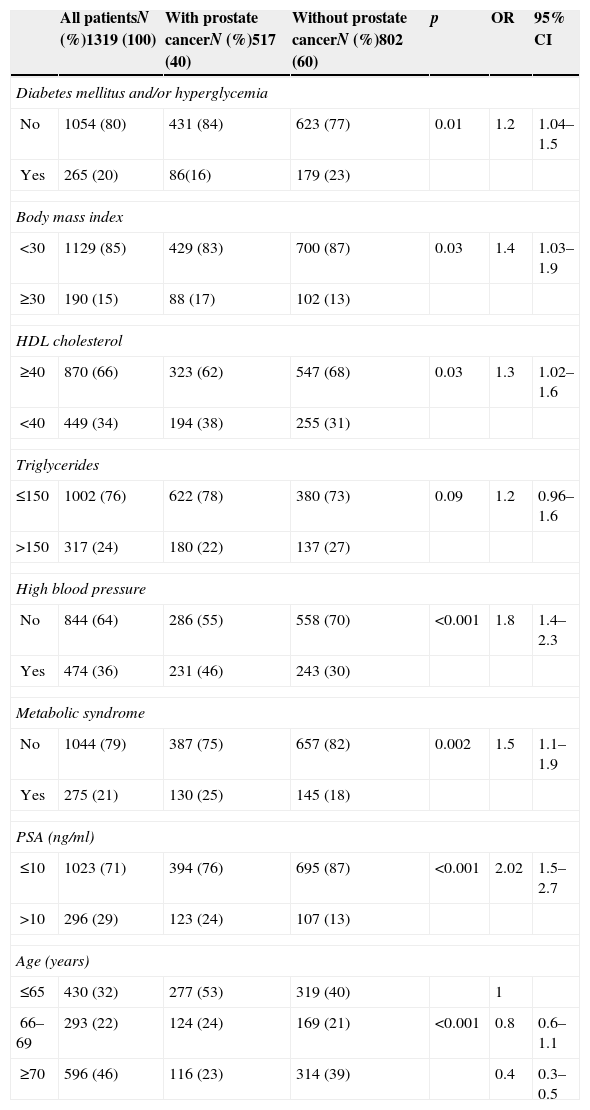
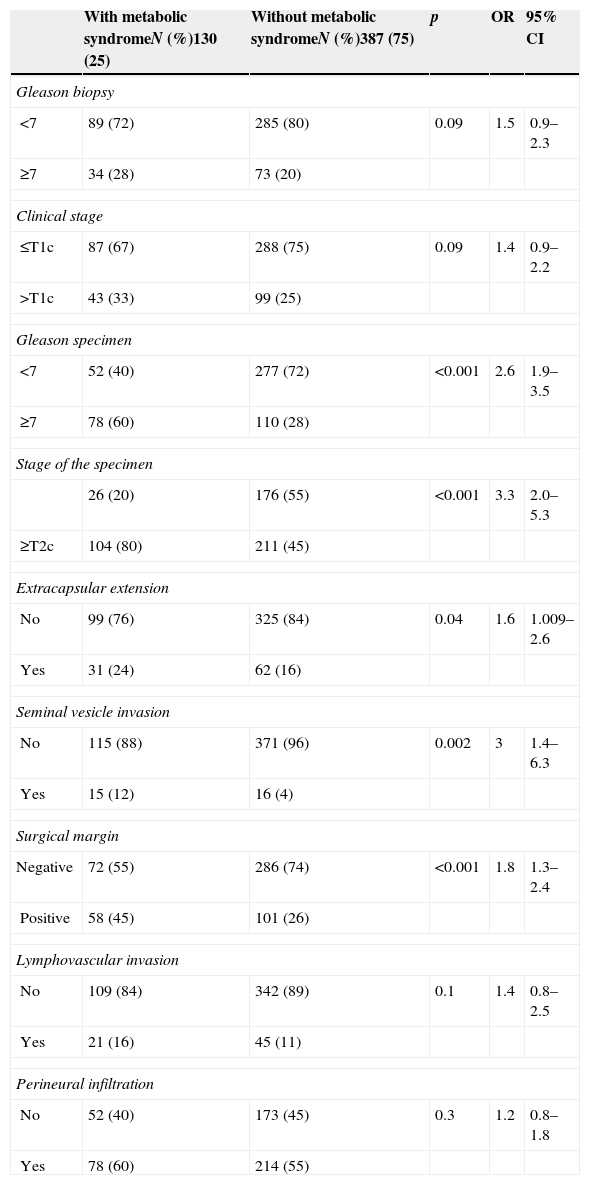
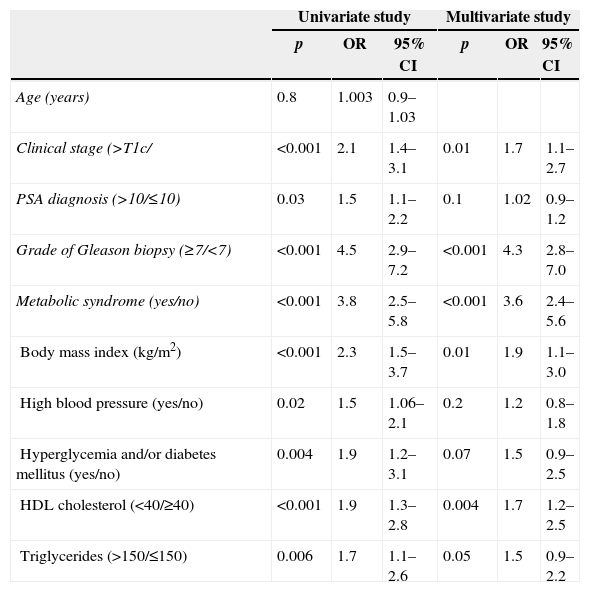
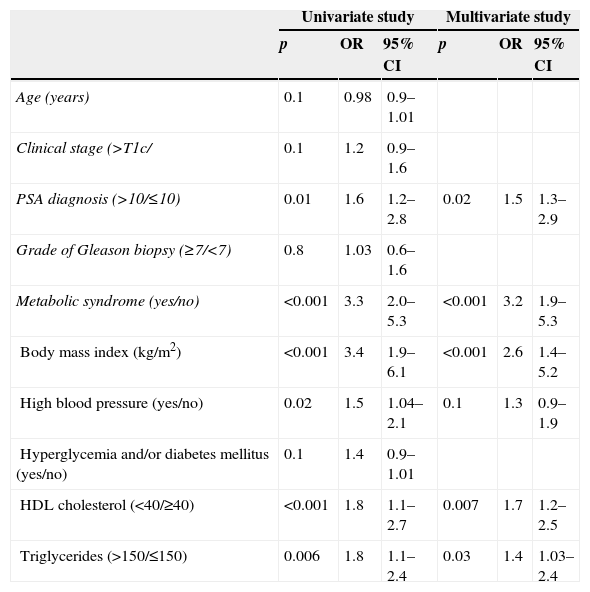
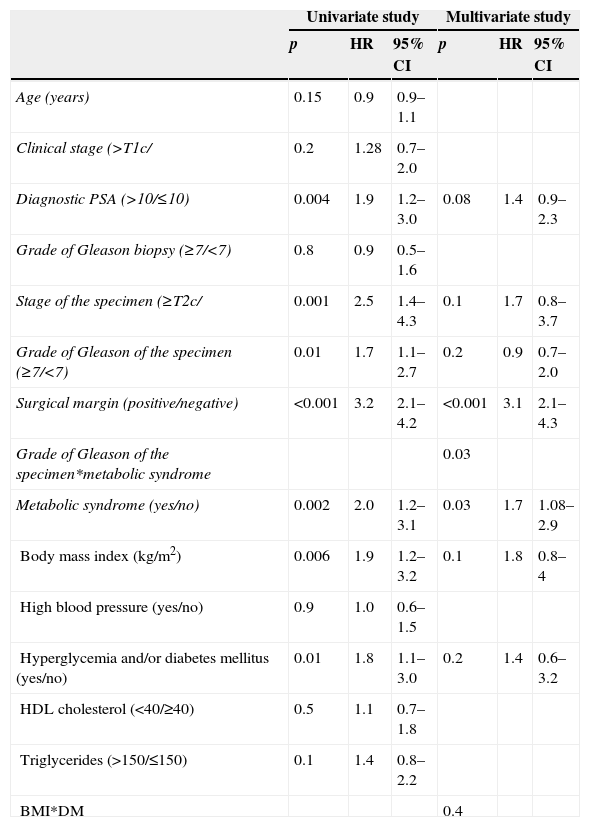
ResultsOf the 1319 patients, 275 (21%) had metabolic syndrome, and 517 prostate cancers were diagnosed. A greater percentage of metabolic syndrome was found among patients with prostate cancer than among patients without prostate cancer (25% versus 18%; p=.002). Poorer results were found in the radical prostatectomy specimens (Gleason score≥7, p<.001; stage≥T2c, p<.001; positive surgical margins, p<.001), and there was a greater percentage of biochemical recurrence in patients with metabolic syndrome than in those without metabolic syndrome (24% versus 13%; p=.003). Metabolic syndrome behaved as an independent predictive factor of finding a Gleason score≥7 for the specimen, as well as for finding a specimen stage≥T2c. Metabolic syndrome was also able to independently predict a greater rate of biochemical recurrence (OR: 3.6, p<.001; OR: 3.2, p=.03; HR: 1.7; respectively).
ConclusionsMetabolic syndrome is associated with poorer findings in the radical prostatectomy specimens and is an independent prognostic factor of biochemical recurrence.
Evaluar el impacto del síndrome metabólico y de sus componentes individuales en los hallazgos en la biopsia de próstata, la pieza de prostatectomía radical y en la recidiva bioquímica.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional de 1.319 varones sometidos a biopsia de próstata entre enero de 2007 y diciembre de 2011. El impacto en los hallazgos en la biopsia, en la pieza de prostatectomía radical y en la recidiva bioquímica se ha evaluado mediante regresión logística y regresión de Cox.
ResultadosDe los 1.319 pacientes 275 (21%) presentaban Síndrome metabólico y se diagnosticaron 517 cánceres de próstata. Se encontró un mayor porcentaje de síndrome metabólico entre pacientes con cáncer de próstata que entre pacientes sin cáncer de próstata (25% frente a 18%; p=0,002). Se encontraron peores hallazgos en la pieza de prostatectomía radical (grado de Gleason≥7, p<0,001; estadio≥T2c, p<0,001; márgenes quirúrgicos positivos, p<0,001) y un mayor porcentaje de recidivas bioquímicas en pacientes con síndrome metabólico que sin síndrome metabólico (24% frente a 13%; p=0,003). El síndrome metabólico se comportó como factor predictivo independiente de encontrar un grado de Gleason de la pieza≥7, así como de encontrar un estadio de la pieza≥T2c, y fue capaz de predecir de forma independiente una mayor tasa de recidivas bioquímicas (p<0,001, OR: 3,6; p<0,001 OR: 3,2; p=0,03 HR: 1,7, respectivamente).
ConclusionesEl síndrome metabólico se asocia a peores hallazgos en la pieza de prostatectomía radical y es un factor pronóstico independiente de recidiva bioquímica.