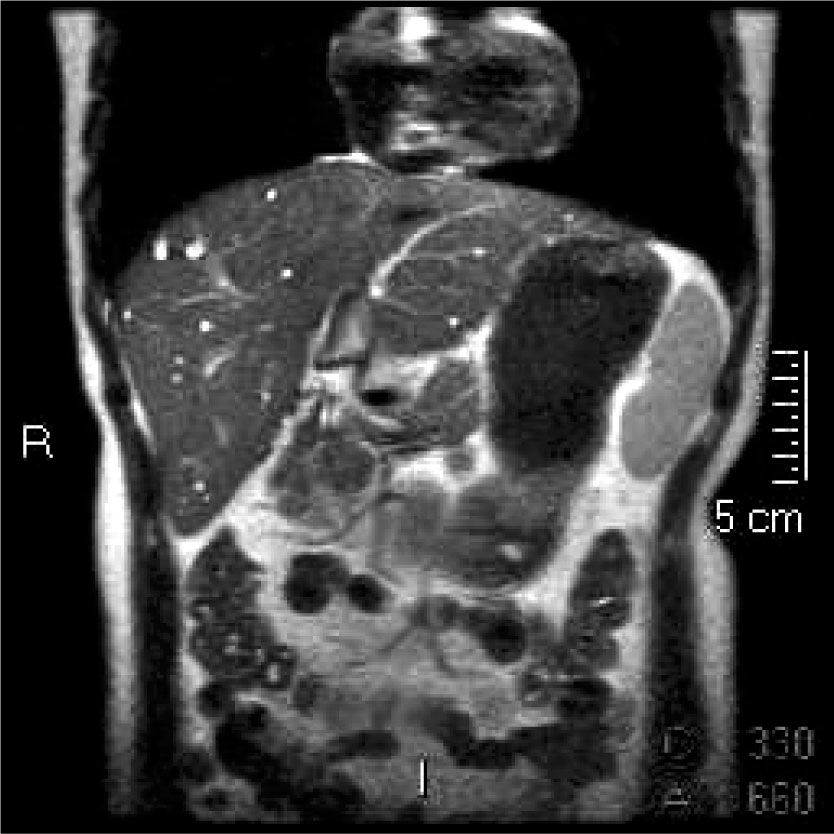
Caroli’s disease is a rare congenital condition characterized by sacular or fusiform dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts and should be considered in the differential diagnosis of chronic cholestasis of unknown cause. Most patients present before 30 years of age and its estimated incidence is I in 1.000,000 population.1,2 Imaging studies are important for the diagnosis of Caroli’s disease and its complications (cholangitis, liver cirrhosis and cho-langiocarcinoma).3,4 Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is used to treat and prevent episodes of hepatolithia-sis and cholangitis.5 Orthotopic liver transplantation is the best therapeutic option for diffuse forms of Caroli’s disease.6
Case PresentationA 30-year-old woman presented to our institute with jaundice, pruritus, and weight loss. Liver tests showed alkaline phosphatase of 1078 IU/mL, total bilirubin of 2.4 mg/dL, conjugated bilirubin of 1.7 mg/dL, gamma glutamyl transpeptidase of 573 U/L, alanine aminotransferase of 195 U/L, aspartate aminotransferase of 167 U/L, and albumin of 3.5 g/dL. Common causes of cholestasis were excluded. Magnetic resonance image confirmed Caroli’s disease (Figures 1-3). UDCA and cholestyramine was initiated achieving partial resolution of cholestasis and symptoms. Patient is in the waiting list for liver transplantation.